The Booted Eagle is an elegant raptor, known for its narrow wings and ability to move quickly through the air. Found mainly in Europe, Asia, and the Middle East, this eagle is often seen hunting small mammals and birds in open landscapes such as meadows or fields. While it is smaller than other eagles, its agile flight and hunting technique make it an impressive bird.During courtship displays, the Booted Eagle performs aerial acrobatics, where males dive in spirals before quickly climbing to attract the attention of females.
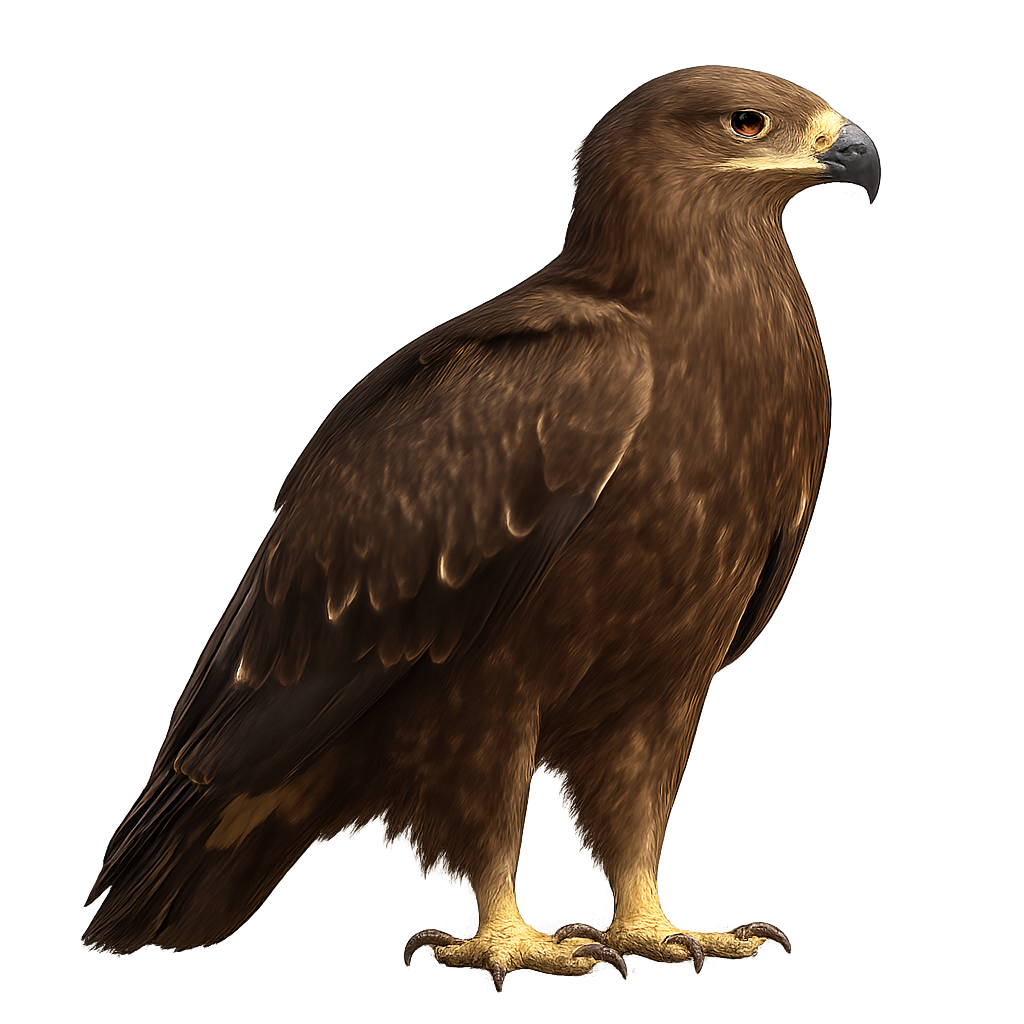
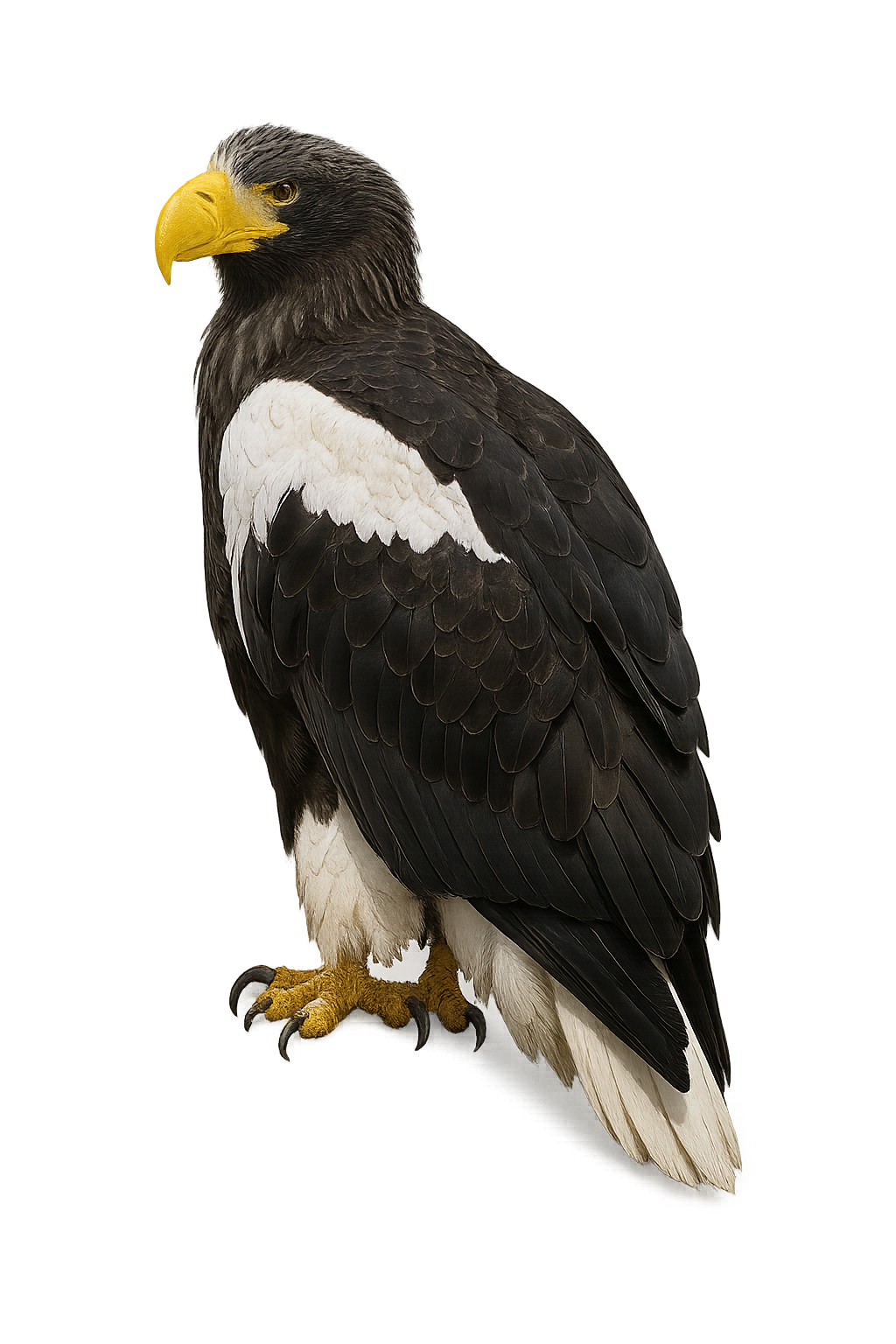
The Greater Spotted Eagle is an imposing raptor, recognizable by its dark plumage and robust silhouette. This large eagle is mainly found in Eastern Europe and Asia, where it hunts large mammals, birds, and sometimes even reptiles. It mainly inhabits open landscapes such as meadows, steppe areas, and marshes. Its powerful call, which is the source of its name, is often seen as a symbol of strength and sovereignty in local cultures.
During the breeding season, the Greater Spotted Eagle performs majestic flights and powerful calls to mark its territory and attract a mate.
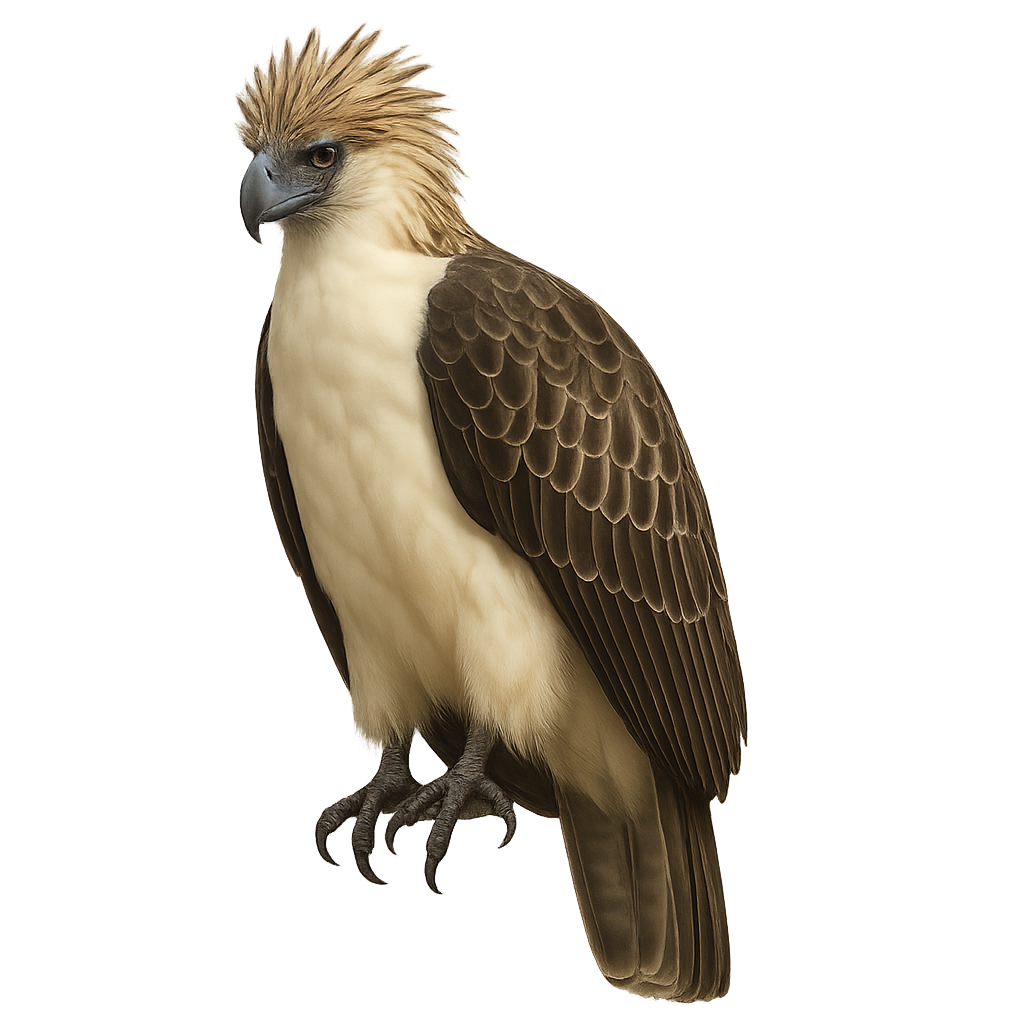
The Philippine eagle is one of the largest eagles in the world and the national emblem of the Philippines. This majestic raptor is recognizable by the plume crest on its head and its piercing gaze. It primarily lives in the tropical forests of the Philippine mountains, where it hunts primates, reptiles, and other small mammals. Due to massive deforestation and hunting, the Philippine eagle is now considered critically endangered. Its population has drastically declined in recent decades, and conservation efforts are underway to protect this unique species.
The Black-and-white Hawk-Eagle is an elegant forest raptor of tropical America, measuring between 51 and 61 cm in length with a wingspan of 110 to 135 cm. It is distinguished by its contrasting plumage: white head, neck, and underparts; black wings and back; and a tail barred with black and white. A small black crest adorns its head, and a black band crosses its yellow eyes. This predator inhabits humid tropical forests, forest edges, and open woodlands from southern Mexico to northern Argentina. It primarily hunts arboreal birds like toucans and parrots, but also preys on mammals, reptiles, and amphibians. Although listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, it is sensitive to deforestation and habitat fragmentation.
The Ornate Hawk-Eagle is a forest raptor from tropical America, measuring between 58 and 67 cm in length. It features a raised black crest, rufous head and flanks, a white throat bordered with black, and a black-and-white barred underside. Juveniles have paler plumage with a white head. An agile predator, it primarily hunts medium to large birds (toucans, parrots, tinamous), arboreal mammals (squirrels, agoutis), and occasionally reptiles. It inhabits primary and secondary humid tropical forests from southern Mexico to Argentina. Deforestation and hunting have led to population declines, classifying it as Near Threatened by the IUCN.
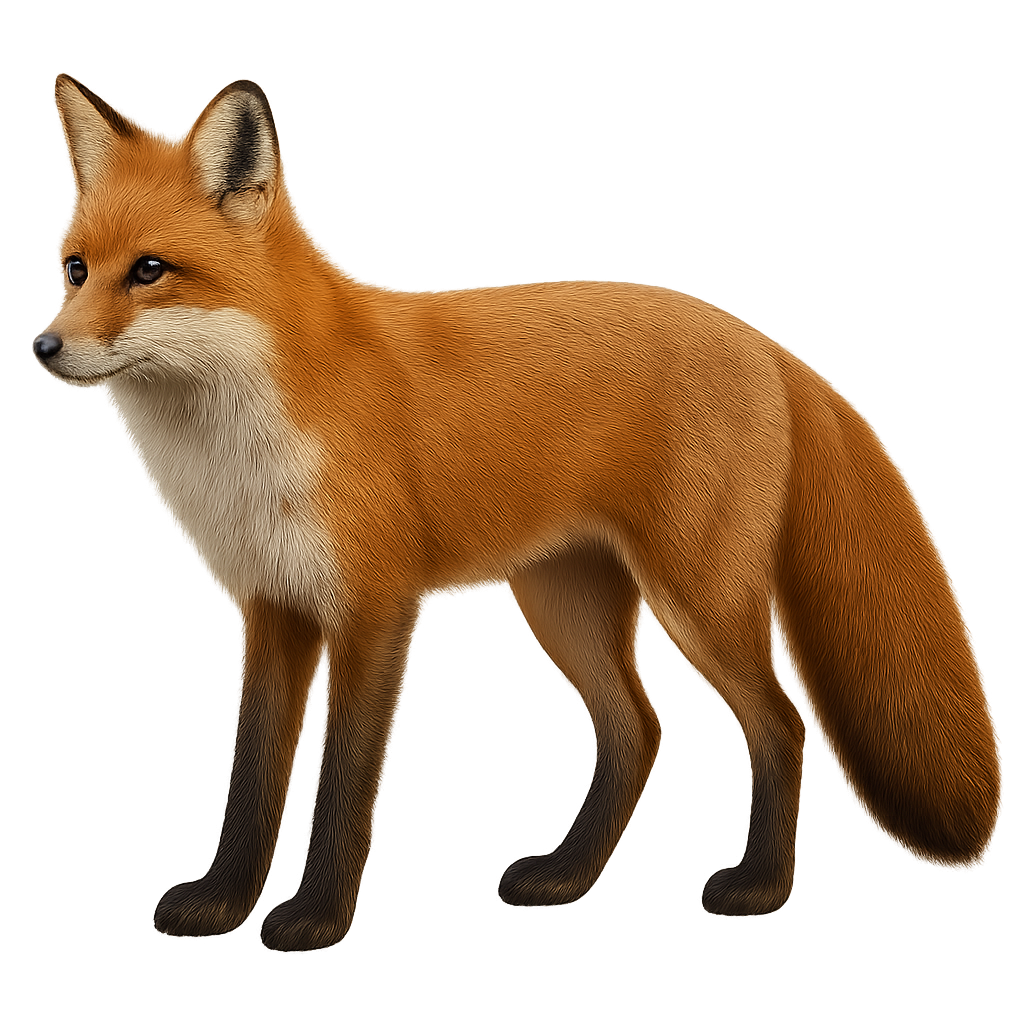
The Golden Eagle is one of the most majestic raptors, easily recognized by its golden-brown plumage and imposing silhouette. This large eagle is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, from the mountains of Europe and Asia to the more arid regions of North America. It primarily hunts medium-sized mammals but can also target larger birds. The Golden Eagle is a solitary bird, known for its flying prowess and its ability to cover great distances in search of food.
During the breeding season, the Golden Eagle performs spectacular courtship displays, where males execute aerial acrobatics to impress females.
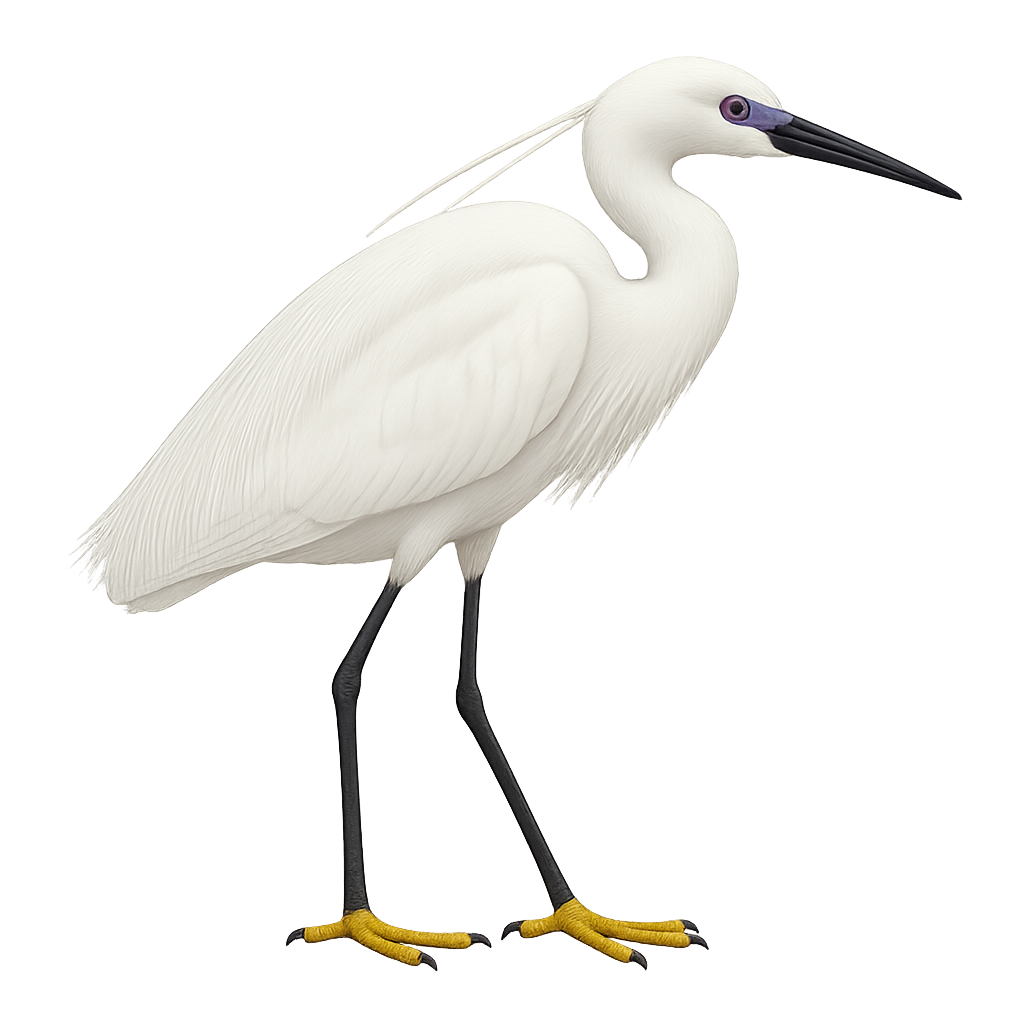
The Little Egret is an elegant bird, easily recognized by its pure white plumage and long black legs. It is mainly found in wetland areas of Europe, Asia, and Africa, where it hunts small fish, insects, and crustaceans. This small heron is known for its graceful behavior, moving slowly through shallow waters to spot its prey. During the breeding season, it sports spectacular nuptial plumes that add to its beauty.
The Little Egret is a social bird, often feeding in groups in marshes and lagoons, creating scenes of great beauty.
The Royal Albatross is one of the largest and most majestic species of albatross, easily recognizable by its long, tapered wings that can span up to 3 meters. This seabird, which frequents the Australian and Antarctic oceans, is a master of gliding flight, capable of covering vast distances without flapping its wings. The Royal Albatross hunts fish and squid, which it captures with great precision by diving from the air.
During the breeding season, the Royal Albatross performs complex courtship dances to attract a mate, an impressive display that reflects the majesty of this bird.
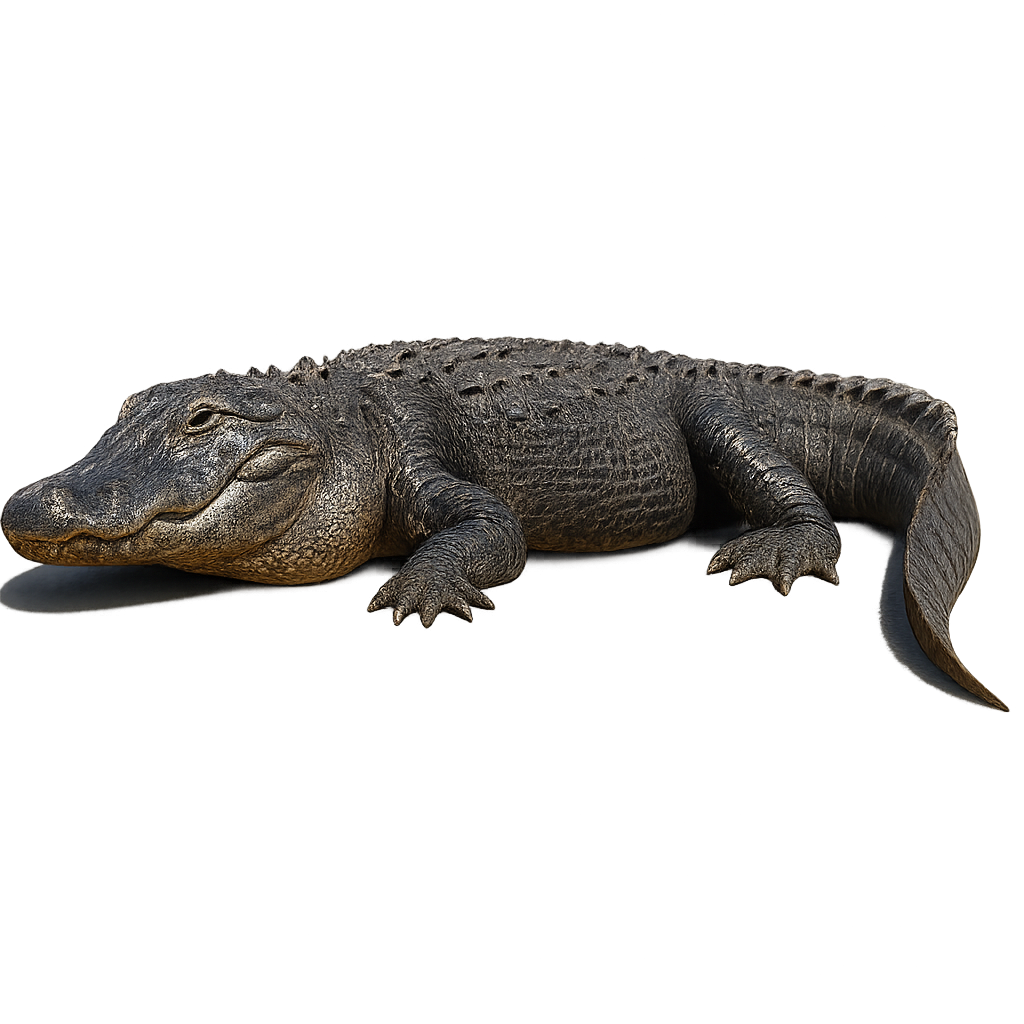
The American Alligator, often simply referred to as the Mississippi Alligator, is an imposing and formidable reptile, easily recognizable by its dark skin and sharp eyes. It primarily inhabits the swamps, rivers, and lakes of the southeastern United States, where it is a top predator in the food chain. The alligator is an opportunistic hunter, feeding on fish, birds, small mammals, and even carrion. It has a remarkable ability to adapt and can survive in various environments, from freshwater swamps to salty coastal areas.
During the breeding season, males emit powerful calls that echo through the swamps to attract females, and nests are built in strategic locations to maximize egg protection.
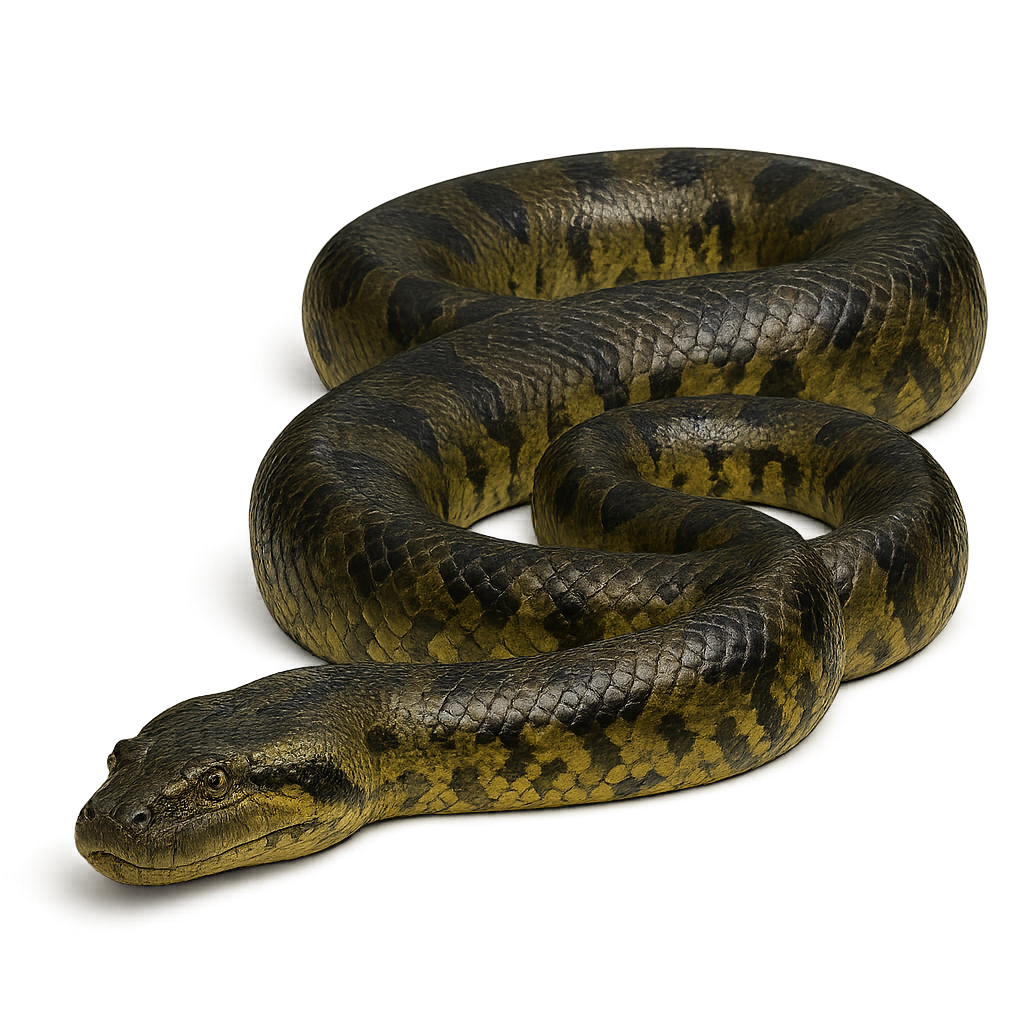
The Green Anaconda is one of the largest and most powerful snakes in the world, known for its impressive size, which can exceed 8 meters in length. This semi-aquatic snake lives in the rivers and swamps of the tropical forests of South America, where it preys on animals as large as caimans, deer, and fish. With its muscular body and constriction technique, the Anaconda can immobilize and swallow prey much larger than itself. It spends most of its time in the water, where it moves with remarkable agility.
Although often feared, the Green Anaconda is a discreet predator, preferring to camouflage itself in dense vegetation while waiting for prey.
The Blue Anole is a small arboreal lizard, measuring approximately 13 to 15 cm in total length. It is notable for its uniform bright blue coloration, unique among reptiles. Males have a pure white dewlap. This species is endemic to Gorgona Island, off the coast of Colombia, where it inhabits the canopy of humid tropical forests. It is diurnal and primarily insectivorous. Reproduction is oviparous, with eggs laid on vegetation surfaces. Classified as Near Threatened by the IUCN, the species is vulnerable due to its limited distribution and deforestation.
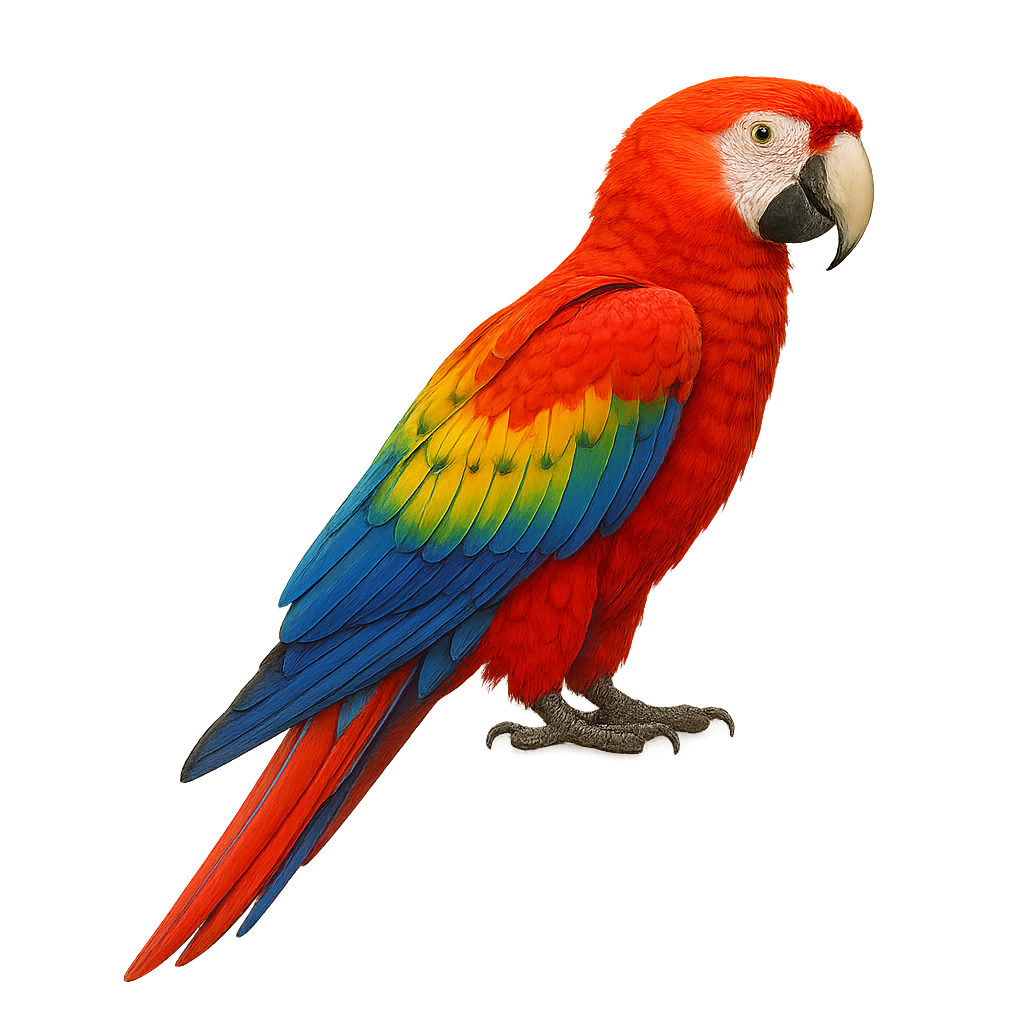
The Scarlet Macaw is one of the most iconic and colorful parrots, easily recognized by its vibrant red, blue, and yellow plumage. This large parrot primarily inhabits the humid tropical forests of Central and South America, where it feeds on fruits, nuts, and seeds. The Scarlet Macaw is a social bird, living in groups and possessing a highly developed vocal behavior. Its powerful call is often heard throughout the forest canopy. It is also known for its ability to fly long distances, gliding with grace and agility.
Unfortunately, the Scarlet Macaw is threatened in certain regions due to habitat loss and illegal wildlife trade. Conservation efforts are underway to protect this majestic species.
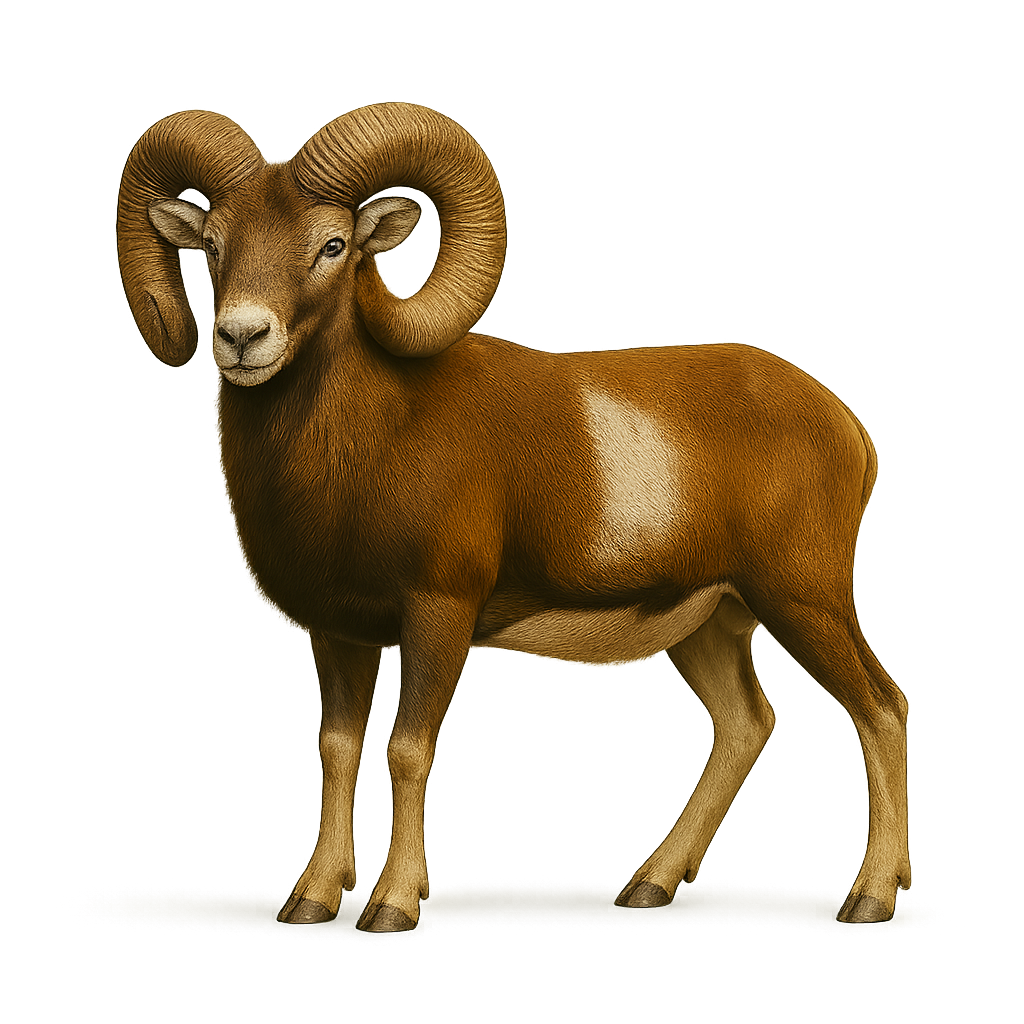
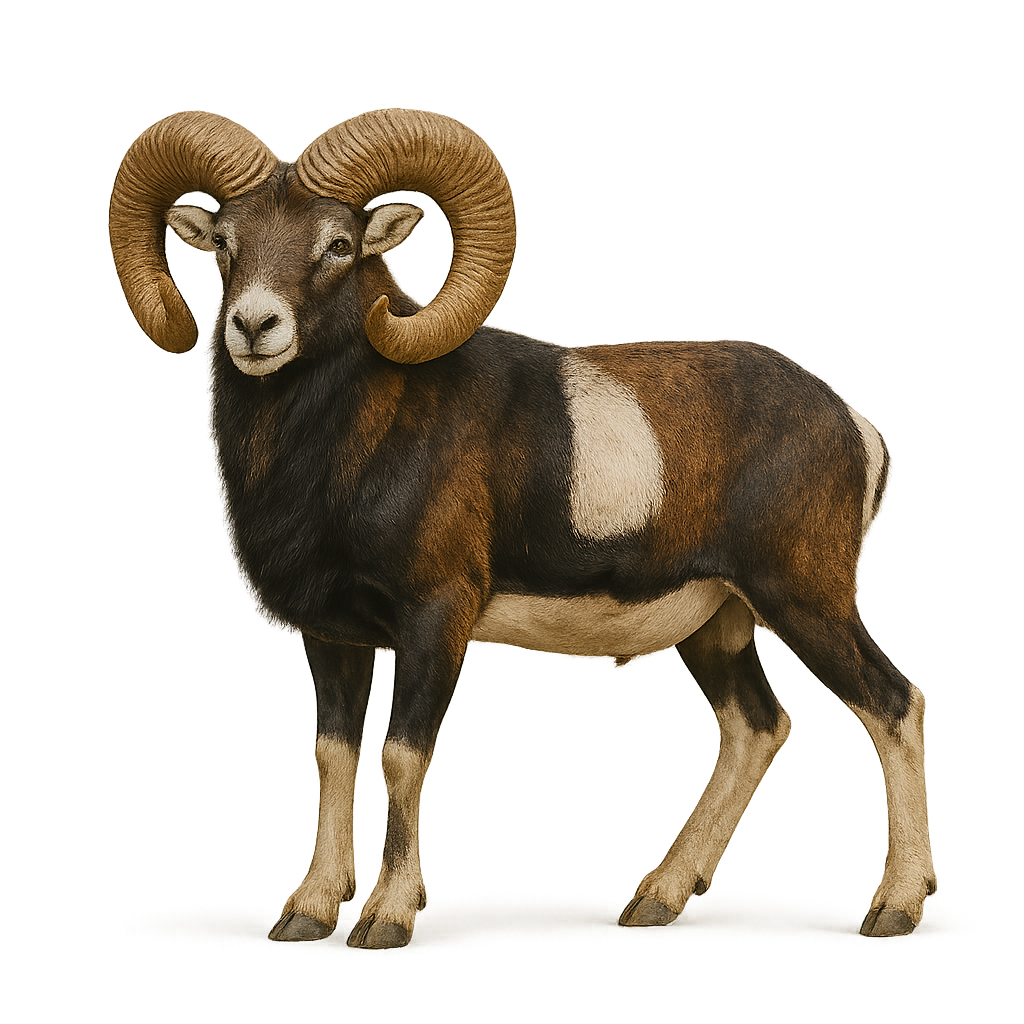
The Argali is the largest wild sheep in the world, known for its imposing size and majestic spiral horns. It primarily inhabits the mountains of Central Asia, where it frequents the arid and semi-arid regions of steppes and high plateaus. This large ungulate is perfectly adapted to mountainous environments, moving nimbly on steep terrain at high altitudes. The Argali is a herbivore, feeding on grasses and woody plants.
The Argali is also a symbol of strength and resilience, but it is threatened by habitat loss and overhunting. Conservation efforts are underway to protect this iconic species and preserve its natural habitat.
The Northern Goshawk is an elegant and powerful raptor, known for its slender silhouette and rapid, erratic flight through dense forests. This medium-sized hawk primarily inhabits temperate forests in Europe, Asia, and North America, where it hunts birds, primarily wood pigeons, doves, and sometimes smaller prey. The Northern Goshawk is an exceptional hunter, using its speed and precise aerial maneuvers to catch its prey.
Despite its remarkable flying skills, the Northern Goshawk is discreet and often difficult to spot, preferring to blend into its forest environment. While not currently threatened, habitat loss and human disturbance pose risks to its population.
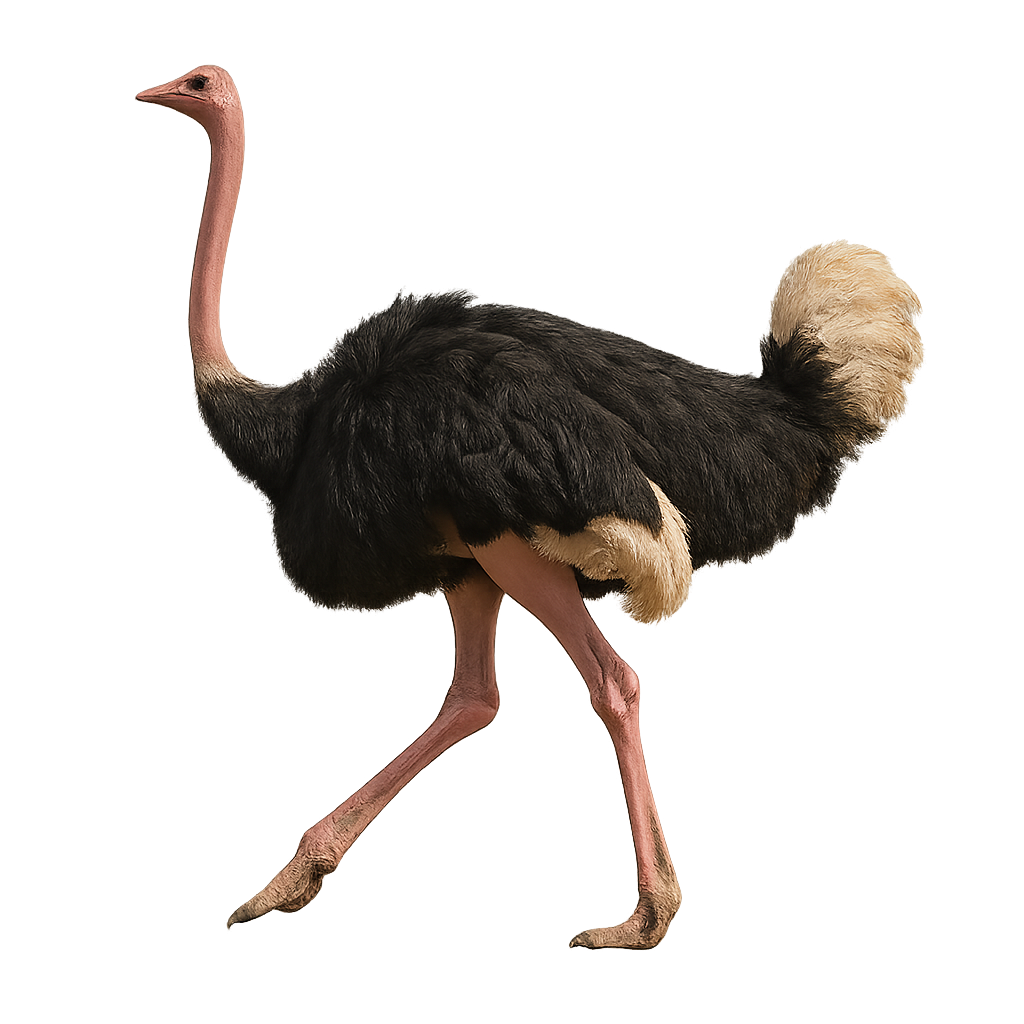
The Ostrich is the largest living bird on Earth, known for its impressive size and powerful long legs that allow it to run at remarkable speeds, reaching up to 70 km/h. Native to Africa, the Ostrich inhabits savannas and desert regions, where it primarily feeds on plants, seeds, and small insects. Although it cannot fly, its wings and plumage help it maintain balance and protect itself from the sun.
The Ostrich is a social bird, living in groups and known for its interesting defense behaviors. When threatened, it can run at high speeds to flee or crouch to blend into the ground, a method that helps it escape predators.
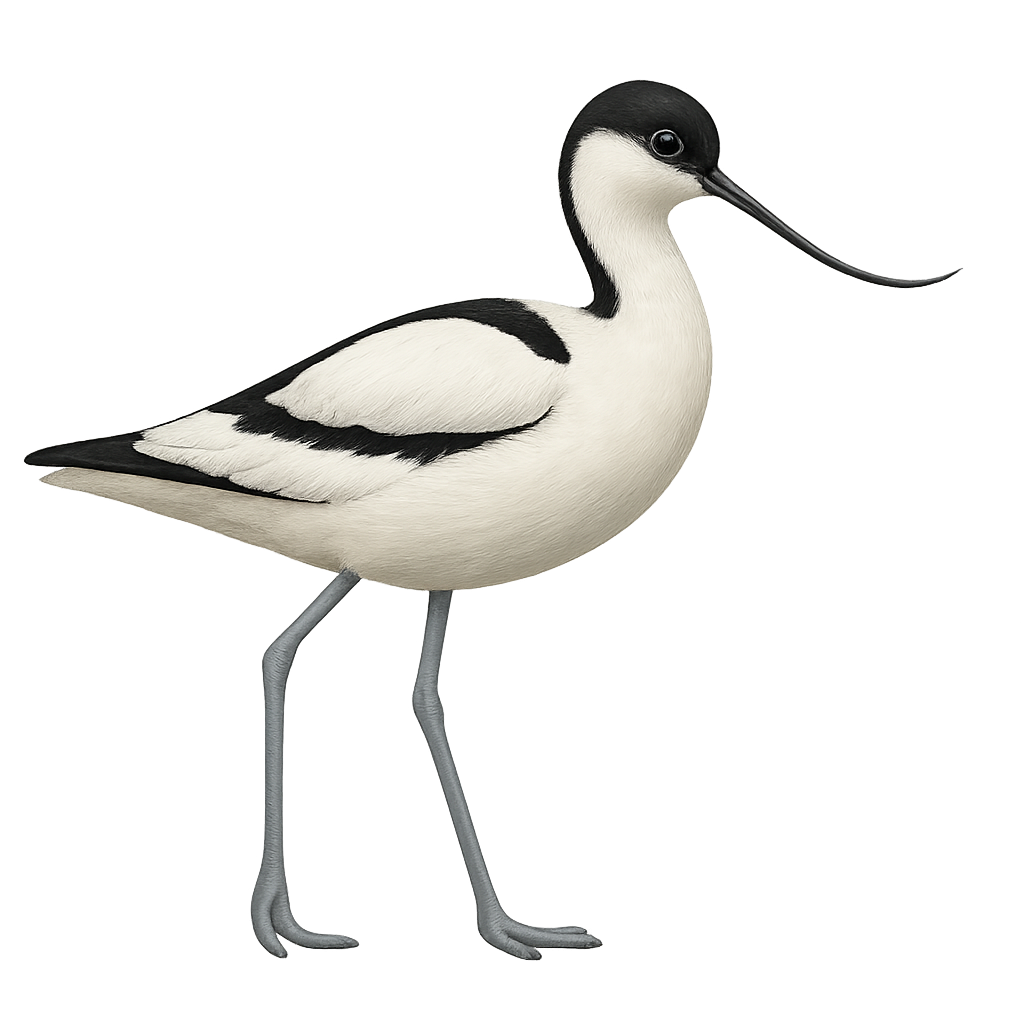
The Pied Avocet is a graceful bird, easily recognizable by its long, upturned bill and striking black-and-white plumage. This bird inhabits wetlands, lagoons, and estuaries in Europe, Asia, and North Africa. The Avocet primarily feeds on small aquatic invertebrates, which it catches by sweeping its bill characteristicly through the water. Its flight is light and elegant, and it often moves in small groups, creating scenes of great beauty.
During the breeding season, the Pied Avocet exhibits courtship behaviors where males display their plumage and perform graceful movements to attract females.
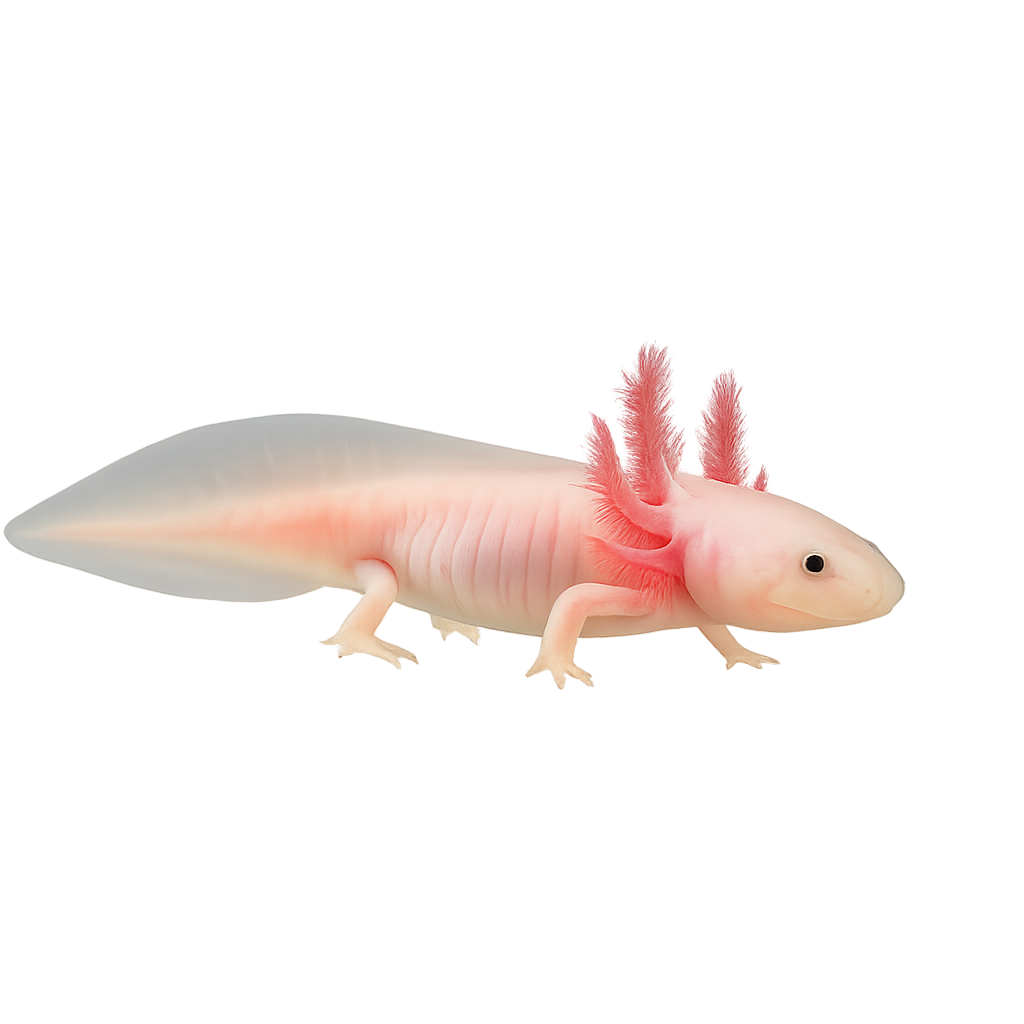
The Axolotl is a fascinating species of amphibian native to lakes around Mexico City, Mexico. Unlike most other amphibians, the Axolotl retains its juvenile form throughout its life, a phenomenon known as neoteny. It is famous for its exceptional ability to regenerate parts of its body, including limbs, internal organs, and even its heart. It has a distinctive appearance with its pale pink skin and external gills, giving it the appearance of a small aquatic dragon. The Axolotl primarily lives in cold, deep waters of lakes, where it feeds on small invertebrates.
The Osprey is a remarkable raptor, easily identifiable by its white and brown plumage and keen eyes. This large bird of prey is specialized in fishing, catching fish by diving at high speed from the air. It is mainly found near lakes, rivers, and coastal areas in Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas, where it builds large nests on trees or pylons. The Osprey is a solitary bird and an extremely precise hunter, often seen hovering over the water before diving to catch its prey.
Despite its great agility and ability to catch fish, the Osprey is vulnerable to water pollution and habitat destruction. Conservation efforts are underway to protect this iconic species.
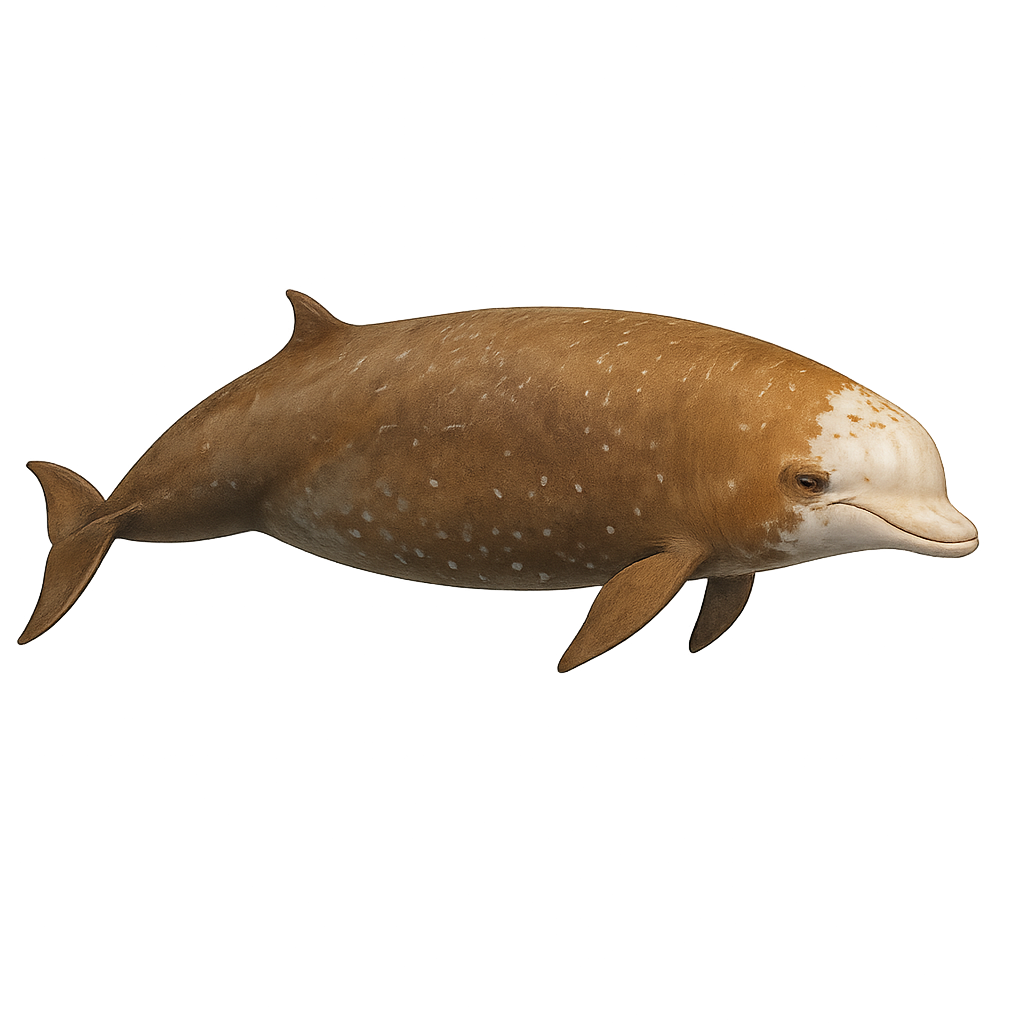
Cuvier's beaked whale, also known as the Cuvier's whale, is a deep-diving cetacean found primarily in tropical and temperate oceans worldwide. It is easily recognized by its elongated head and prominent beak. This cetacean is one of the deepest diving whales, capable of descending more than 2000 meters in search of food. Its diet primarily consists of squid and deep-sea fish. Although it is a difficult animal to observe due to its deep habitat, it is sometimes seen at the surface to breathe. Cuvier's beaked whale is known for its long dives and mysterious behaviors.
The Humpback Whale is one of the most iconic whale species, known for its spectacular jumps and fascinating songs. This massive whale can grow up to 16 meters long and weigh up to 36 tons. It is found in oceans worldwide, migrating between the cold waters of the Arctic and the warmer tropical waters to breed. Humpback whales primarily feed on krill and small fish, which they capture using a group hunting technique known as "bubble netting," where they create bubbles underwater to trap their prey.
In addition to their impressive hunting behaviors, Humpback Whales are also famous for their complex songs, which males use to attract females during the breeding season.
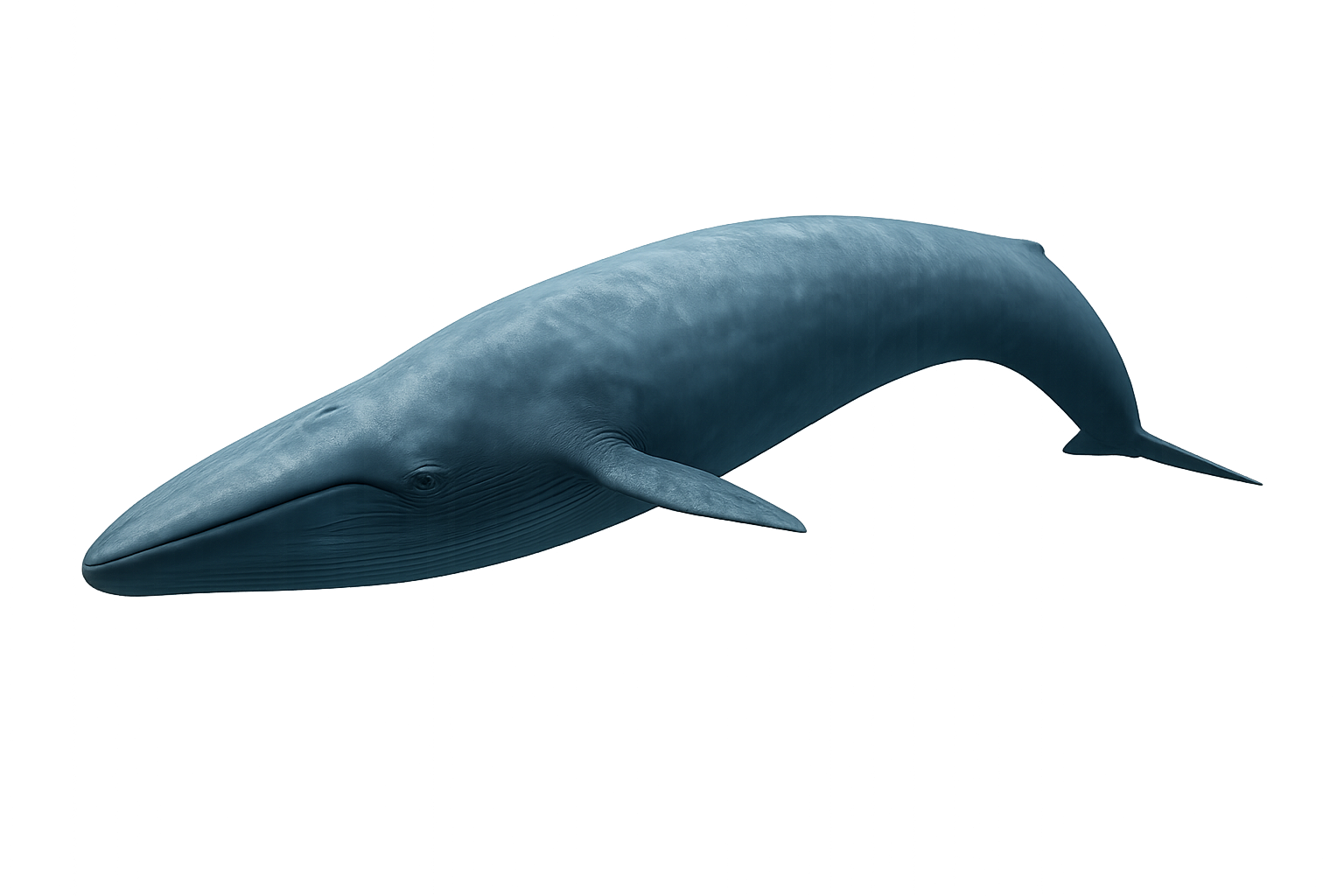
The Blue Whale is the largest animal ever known to have existed on Earth. This impressive cetacean can grow up to 30 meters long and weigh as much as 180 tons. Its gray-blue skin and streamlined body are perfectly adapted to ocean life, and despite its enormous size, the Blue Whale primarily feeds on small marine organisms such as krill, which it consumes in large quantities. Using its massive tongue and enormous mouth, it can swallow up to 4 tons of krill in a single gulp.
Unfortunately, although once abundant, the Blue Whale is now classified as an endangered species due to commercial whaling, which has significantly reduced its population. Conservation efforts are now in place to protect this majestic creature.
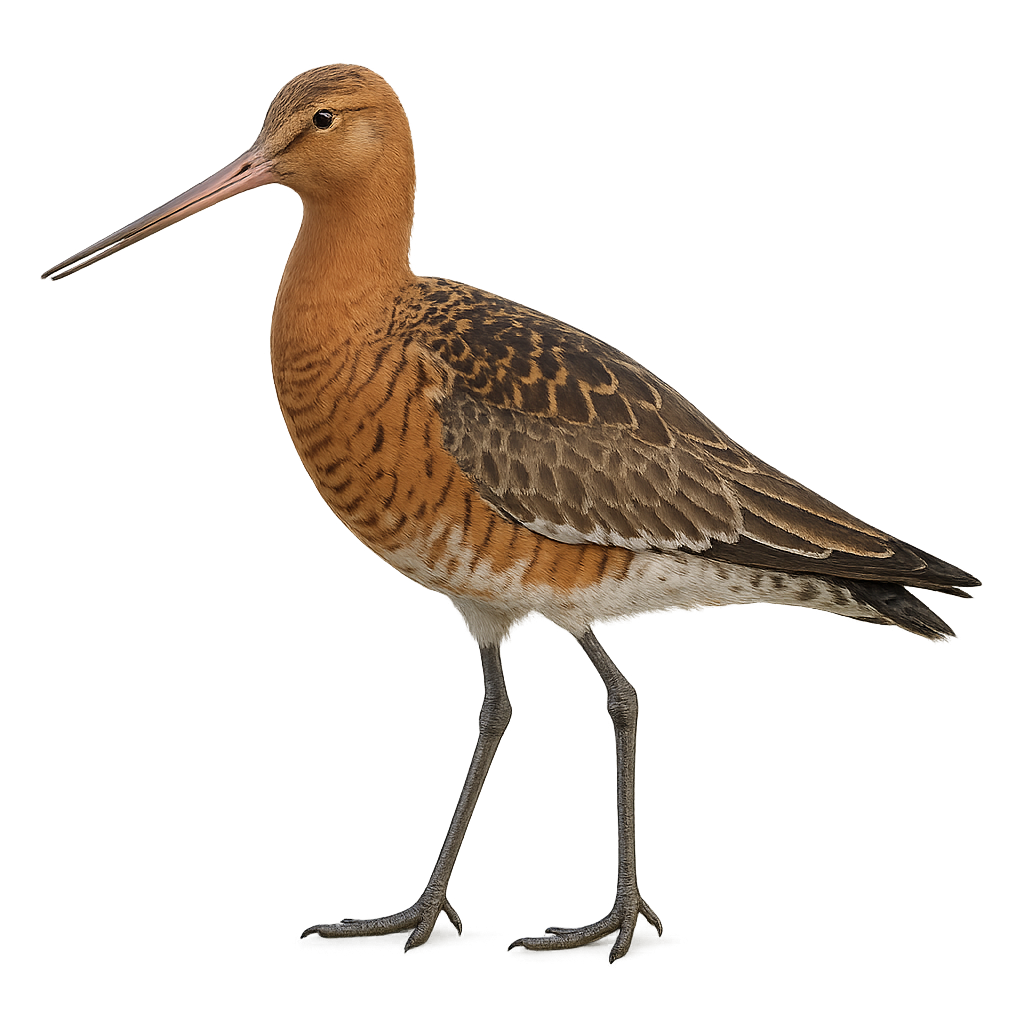
The Black-tailed Godwit is an elegant wader, easily recognizable by its long, slightly curved bill and long legs. It primarily inhabits wetlands and estuaries in Europe, Asia, and North Africa, where it feeds on aquatic invertebrates, worms, and insects, which it detects in the soft sediments along the shores. The Black-tailed Godwit is also known for its long migration, covering great distances between its breeding grounds in temperate regions and its wintering sites in warmer areas.
During the breeding season, males perform spectacular courtship displays, flying gracefully and emitting distinctive calls to attract females.
The Bar-tailed Godwit is a remarkable wader, easily recognized by its distinctive plumage, which varies from reddish-brown to gray and white, and its long, slightly downward-curved bill. It primarily inhabits coastal areas and wetlands in Europe and Asia, where it feeds on small marine invertebrates, mollusks, and insects, which it detects in the sediment. The Bar-tailed Godwit is a migratory bird, covering great distances between its breeding grounds in the Arctic regions and its wintering areas in more temperate zones.
During the breeding season, the Bar-tailed Godwit engages in particularly interesting nesting behavior, establishing nests on the ground in grasses or boggy areas.
The Green Crested Basilisk is an impressive species native to the tropical forests of Central America. This lizard is famous for the distinctive crest on its head and back, as well as for its ability to run on water, earning it the nickname 'Jesus Christ lizard.' It uses this ability to escape predators by running at high speed across shallow water surfaces. Primarily arboreal, it spends much of its life in trees and bushes, where it feeds on small insects, fruits, and flowers. This lizard is also known for its bright green color and distinctive patterns.
The Jesus Christ Lizard is a fascinating reptile, named for its unique ability to run across water for short distances. This striking lizard, recognizable by the distinctive crest on its back and its vibrant coloration, primarily inhabits the tropical forests of Central and South America, particularly in Costa Rica and Panama. The Jesus Christ Lizard feeds on insects, fruits, and small animals, hunting them in the understory. When threatened, it uses its ability to run across water to escape predators, creating a spectacular fleeing scene.
Although it is a master of escape, the Jesus Christ Lizard is vulnerable to deforestation and the loss of its natural habitat.
The Savanna Hawk is an impressive bird of prey, easily recognized by its light brown plumage and large wings, which allow it to fly with agility over the grasslands and savannas of sub-Saharan Africa. This bird is particularly known for its unique hunting techniques, where it chases and captures insects, small mammals, and birds, often flying at low altitudes at high speeds. The Savanna Hawk gets its name from its erratic behavior, often seen during its swift and precise attacks.
The Savanna Hawk is a solitary bird, building its nest in trees, often at great heights, to avoid predators. While not currently threatened, the loss of its habitat due to human expansion could pose a risk to its population.
The Shoebill stork is a majestic and imposing bird, easily recognized by its large, shoe-shaped bill that allows it to capture fish and small aquatic animals. It is found primarily in swamps, lakes, and wetlands of East Africa, especially in Sudan, Uganda, and Rwanda. This large wader is a slow yet precise predator, sometimes waiting for long hours before striking its prey. The Shoebill is a vulnerable species due to habitat loss and hunting.
The Woodcock is a discreet and nocturnal bird, difficult to spot due to its speckled plumage that allows it to blend perfectly into the undergrowth of forests in Europe and Asia. This bird, with its silent flight, is primarily insectivorous, feeding on earthworms, insects, and small arthropods it finds by probing the ground with its long, straight bill. The Woodcock is known for its erratic flights and mysterious calls during the breeding season, often heard as a "wingbeat" in the woods.
It leads a quiet and solitary life, creating a nest on the ground, well-hidden among dense vegetation. Although its population is relatively stable, the Woodcock is sometimes threatened by deforestation and disturbance of its natural habitats.
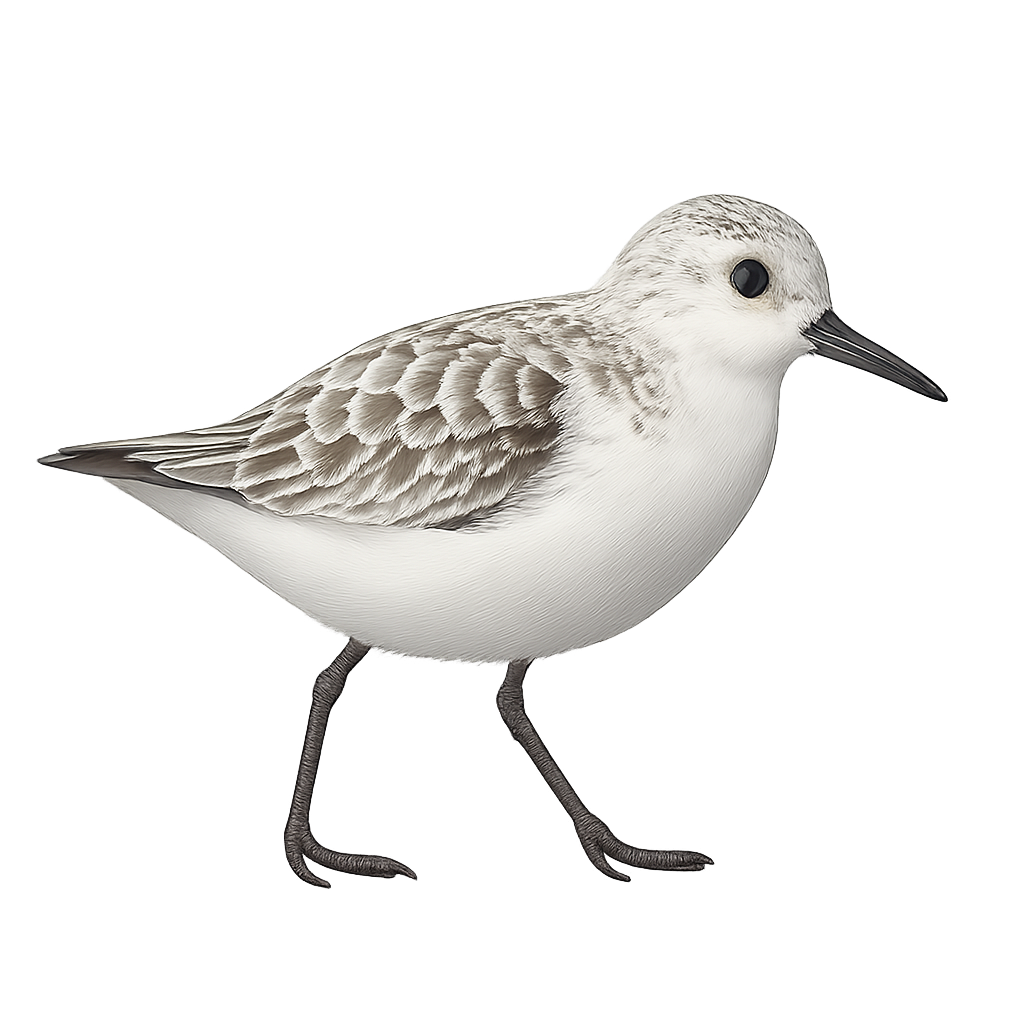
The Sanderling is a small wader with a subtle plumage, mostly white and light gray, known for its quick movements along the shore to capture marine insects, crustaceans, and mollusks. This small migratory bird inhabits beaches and coastal areas of Europe, Asia, North America, and South America, primarily feeding at low tide. The Sanderling is often seen in groups, moving in perfect synchronization, a fascinating sight to observe.
During migration, it covers long distances, leaving the cold regions of winter to reach temperate or tropical beaches where it finds food. While not currently threatened, it is sensitive to human disturbance and the loss of its coastal habitats.
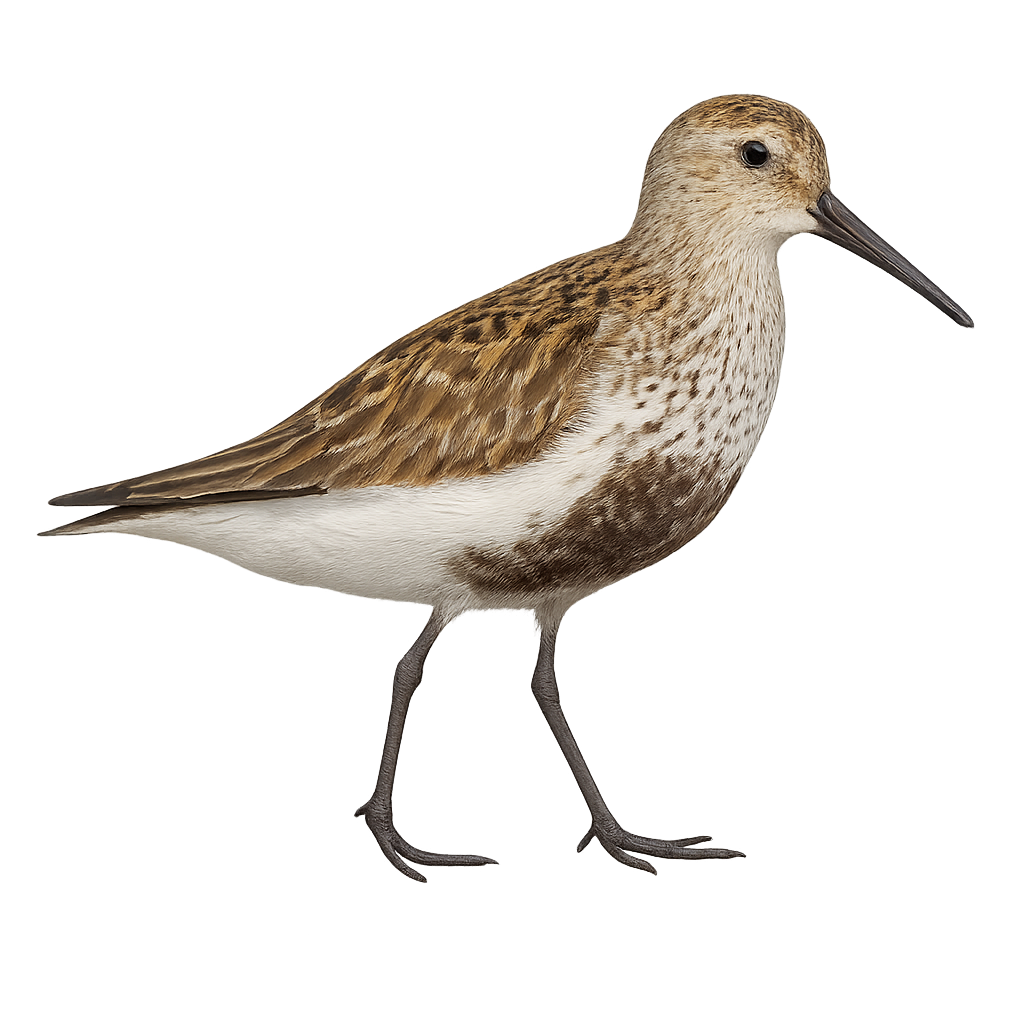
The Dunlin is a small, graceful wader, easily recognizable by its plumage that changes with the seasons, transitioning from gray-brown in winter to more contrasting black and white tones during breeding. This small bird primarily inhabits coastal areas of Europe, Asia, and North America, where it feeds on marine invertebrates, primarily worms and mollusks, which it finds by probing the sand and mud. The Dunlin exhibits social behavior and is often seen in groups, especially during migration.
This migratory wader covers long distances, leaving the cold regions of winter to reach more temperate or tropical areas for feeding and breeding. While relatively common, it can be affected by the disturbance of its coastal habitats.
The Purple Sandpiper is a small wader distinguished by its plumage, which features shades of gray, brown, and purple, especially visible during the breeding season. This small bird primarily inhabits the Arctic coasts of Europe and North America, feeding on small marine invertebrates, mainly crustaceans and mollusks, which it finds in the mud and sand of beaches. The Purple Sandpiper is a long-distance migrant, covering vast distances between its breeding grounds in the Arctic regions and its wintering areas in more temperate zones.
The social behavior of the Purple Sandpiper is also noteworthy, often seen in large groups during migration. While this species is still relatively abundant, it can be affected by disturbance to its coastal habitats and climate change.
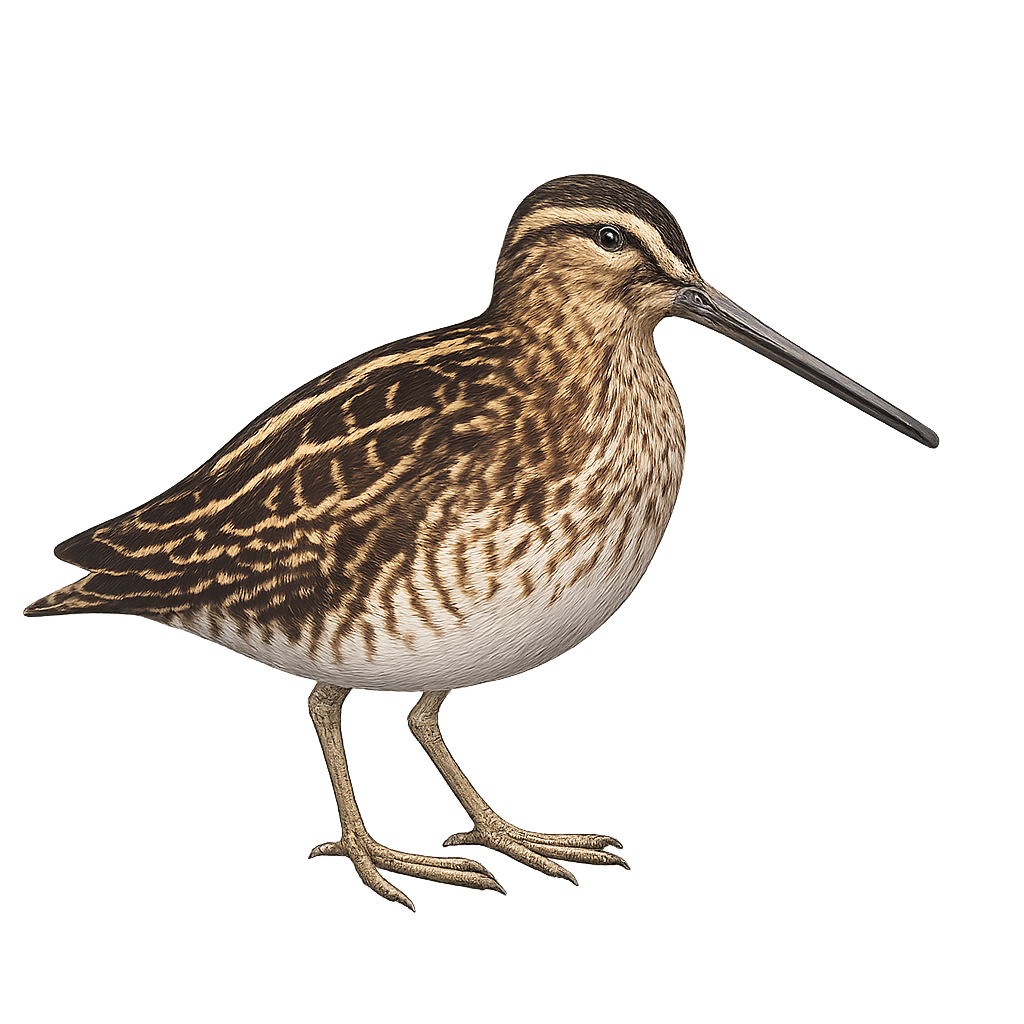
The Common Snipe is an elegant small wader, easily recognized by its long, slender bill and mottled brown and beige plumage. This bird primarily inhabits marshes, wet meadows, and riverbanks in Europe, Asia, and North Africa, where it feeds on aquatic invertebrates, mainly worms, insects, and mollusks. The Common Snipe uses its long, flexible bill to probe the mud in search of food.
It is a migratory bird, leaving the cold regions of winter to move to more temperate zones for breeding. While its population is relatively stable, the Common Snipe is sensitive to habitat changes and water pollution.
The Great Snipe is an elegant wader, easily recognized by its mottled brown and beige plumage and two long white bands visible on its wings, from which it gets its name. This species, slightly larger than the Common Snipe, inhabits marshes, wetlands, and riverbanks in Europe and Asia, where it primarily feeds on worms, insects, and small crustaceans found in the mud. The Great Snipe is a particularly discreet bird, often blending into its environment.
Migratory, it covers long distances between its breeding grounds in Europe and its wintering sites in North Africa and Asia. Although less abundant than other waders, the Great Snipe is affected by habitat loss and changes in the hydrological regime in its breeding areas.
The Jack Snipe is a small, discreet wader, often difficult to spot due to its cryptic plumage that blends perfectly with its environment. This small bird, with its brown and mottled plumage, primarily inhabits marshes and bogs in Northern Europe and Asia. It feeds on invertebrates, mainly worms, insects, and mollusks, which it finds by probing the mud with its short, straight bill.
The Jack Snipe adopts a stealthy behavior and is often observed hiding in dense vegetation or freezing when threatened. While more difficult to observe due to its discretion, it is threatened by habitat loss and changes in the hydrological regime in its breeding areas.
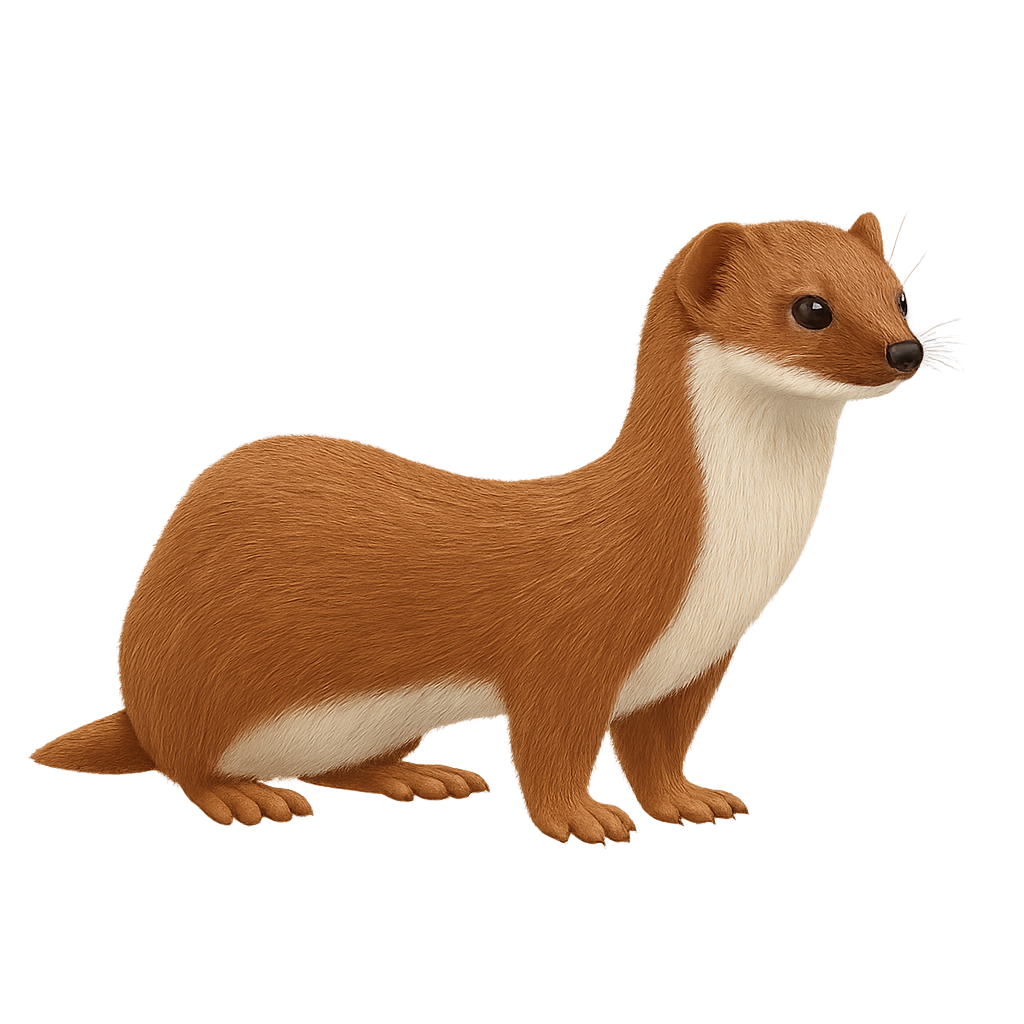
The European Weasel is the smallest carnivore in Europe, easily recognizable by its tiny size and brown coat with a white throat and belly. It primarily inhabits a variety of environments such as forests, meadows, and agricultural areas, where it hunts small mammals, birds, insects, and eggs. Agile and fast, the European Weasel is a stealthy hunter, capable of slipping into tight spaces to capture its prey.
Solitary and territorial, the European Weasel is active both day and night, and it uses its own burrows or those of other animals to hide and rest. Though small, it is a formidable predator, often seen as beneficial for regulating small rodent populations. However, it can be threatened by habitat destruction and changes in agricultural practices.
The Beluga is a remarkable cetacean, easily recognizable by its immaculate white color and streamlined shape. Unlike many other dolphins, the Beluga has a rounded forehead, called a "melon," which allows it great head flexibility. What also makes the Beluga unique is its ability to produce a wide variety of sounds, which it uses to communicate and navigate in the cold waters of the Arctic seas, the North Atlantic, and rivers. It primarily feeds on fish, crustaceans, and mollusks, hunting them with its excellent echolocation ability.
Belugas live in social groups called "pods" and are known for their social behavior and interaction with humans. Despite its popularity, the Beluga is vulnerable to water pollution and climate change, which affect its natural habitats.
The Black-crowned Night Heron is a medium-sized bird, easily recognized by its silver-gray plumage and piercing yellow eyes. It primarily inhabits marshes, estuaries, and lake shores in Europe, Asia, and North Africa. This nocturnal bird is an excellent fisherman, feeding on fish, crustaceans, and invertebrates, which it captures with its strong, pointed bill. Unlike many other aquatic birds, the Black-crowned Night Heron is primarily active at dusk, searching for food in the darkness.
The Black-crowned Night Heron is a social bird, forming colonies for breeding, but it prefers a quiet and hidden environment. While not directly threatened, it faces risks from water pollution and the destruction of its natural habitats.
The binturong is an arboreal mammal with a stocky body and long prehensile tail. Its shaggy black fur and unique scent reminiscent of popcorn make it easily identifiable. Active at night, it moves slowly through the canopy of Southeast Asian rainforests in search of fruits, small animals, and eggs. Solitary and elusive, it is increasingly rare due to habitat loss.
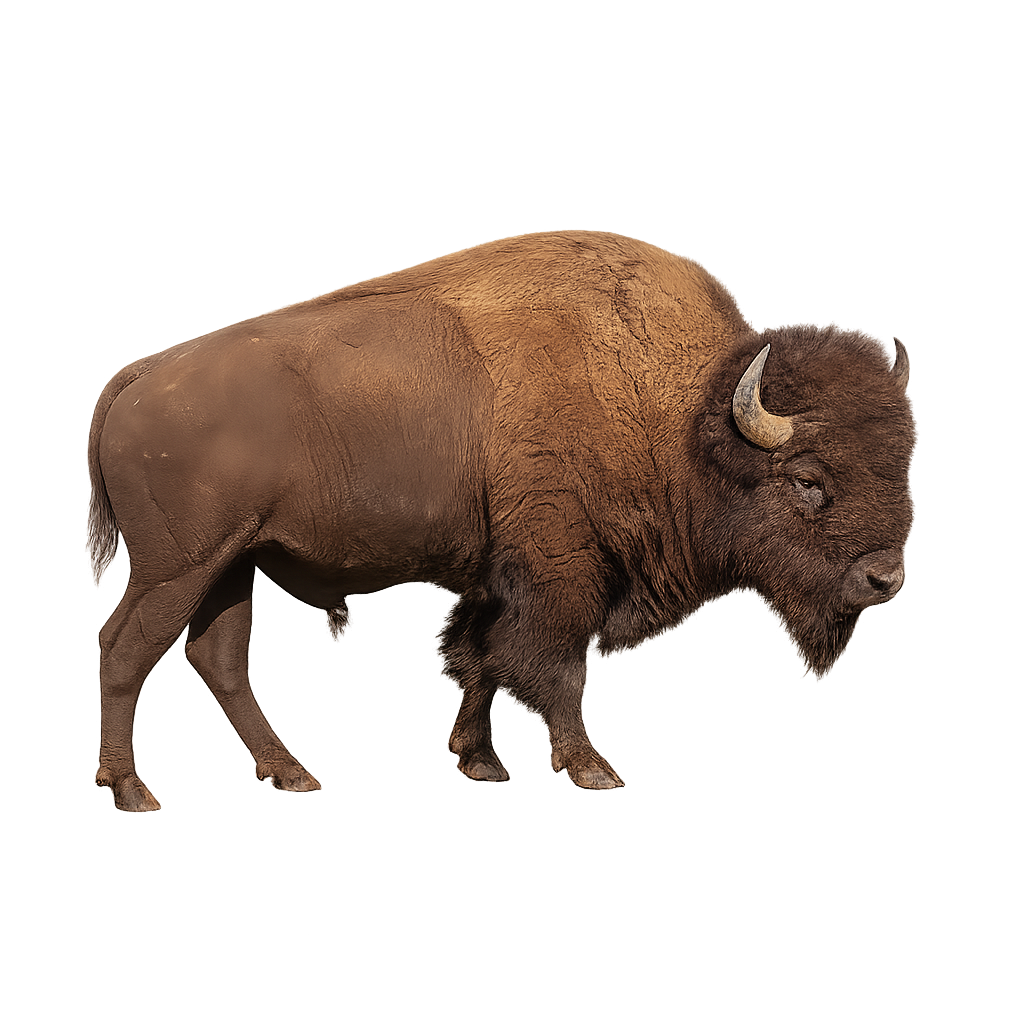
The American Bison is one of the largest land mammals in North America, recognizable by its massive head, thick fur, particularly on its back. Once widespread, it nearly went extinct in the 19th century due to overhunting and habitat loss. Today, thanks to conservation efforts, the population of American Bison is growing, though the species remains protected in many areas.
The American Bison lives in herds, primarily in grasslands and plains. Herbivorous, it feeds on grasses, woody plants, and some vegetation. As it moves, it creates powerful tracks in the plains. This social mammal is also known for its territorial behavior, with males fighting for dominance within the group.
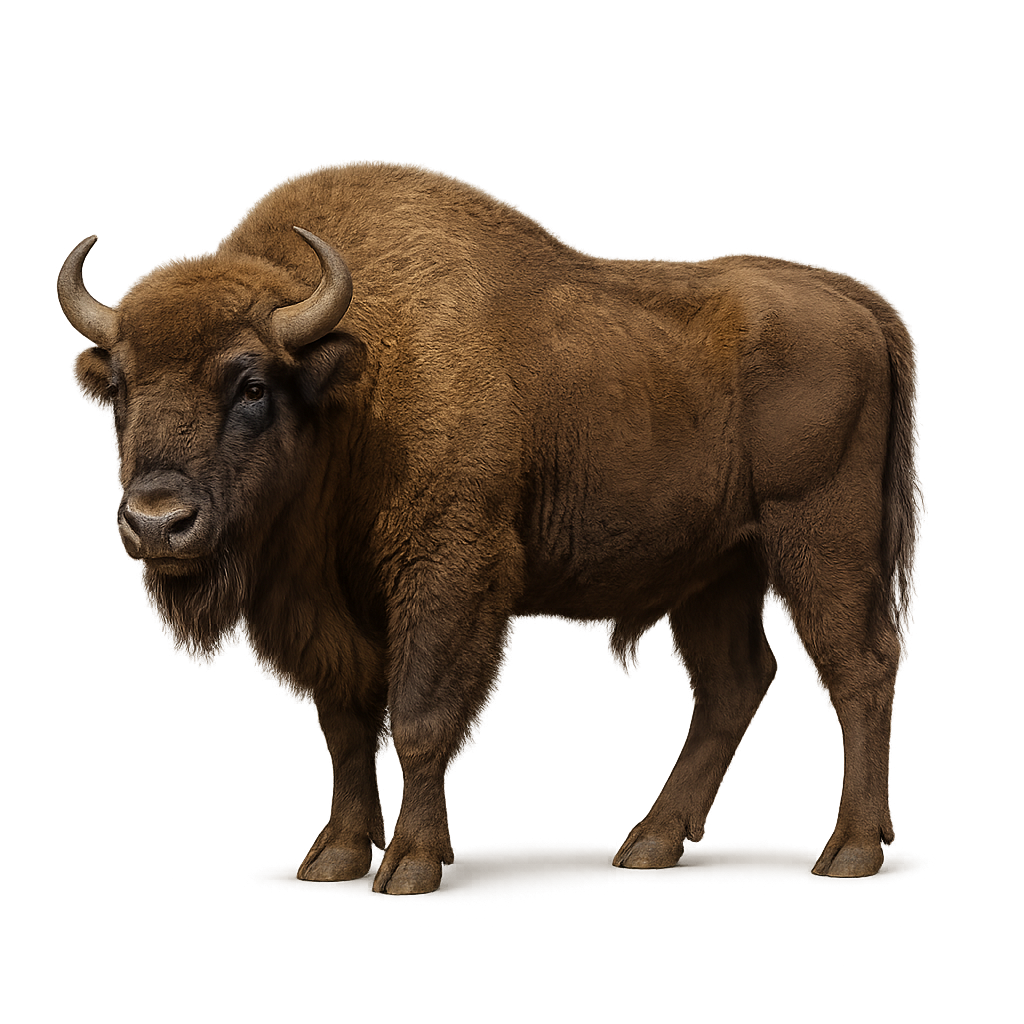
The European Bison is the largest land mammal in Europe, characterized by its imposing size, thick fur, and arched back. Once widespread across the forests of Europe, it nearly went extinct in the early 20th century, but thanks to conservation programs, wild populations have been reintroduced in several European regions. The European Bison primarily inhabits forests and wooded meadows, where it feeds on grasses, leaves, twigs, and young tree shoots.
This bison is a social animal, living in small groups or large herds, with males fighting for dominance. While its population is growing, the European Bison remains a vulnerable species due to habitat loss and fragmentation of its territory. The protection and management of its habitats remain essential for its survival.
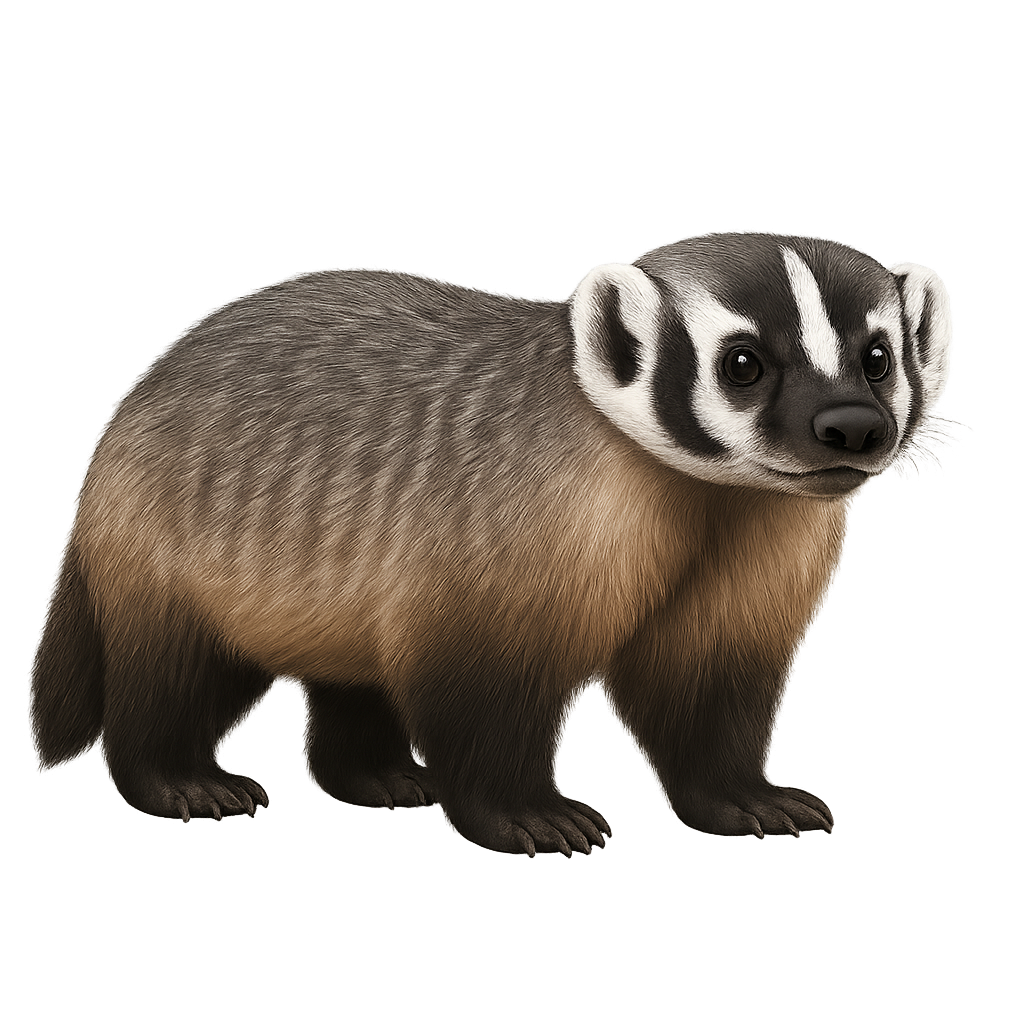
The American Badger is a medium-sized carnivore, easily recognizable by the distinctive white stripes on its head and its sturdy, stocky body. It primarily inhabits prairies and semi-arid areas in North America, where it digs complex burrows for shelter and raising its young. The American Badger is mainly insectivorous, feeding on worms, insects, and occasionally small mammals and reptiles. Its powerful claws allow it to dig quickly and efficiently into the ground.
The American Badger is a solitary animal, often active at dusk and during the night. While not immediately endangered, it can be affected by habitat loss and illegal hunting in some regions.
The European Badger is a medium-sized carnivorous mammal, easily recognizable by its gray fur, white stripes on its head, and stocky build. It primarily inhabits forests and hedgerows in Europe, where it digs complex burrows called "setts" for shelter and raising its young. The European Badger is omnivorous, feeding mainly on worms, insects, fruits, roots, and small mammals. Its nocturnal habits and solitary nature make it a difficult animal to observe.
It is an excellent digger and uses its powerful claws to modify its environment in search of food or to expand its burrow. While its population is generally stable, the European Badger faces threats such as habitat loss and road accidents. Protecting its habitats and managing its territories are crucial for the species' conservation.
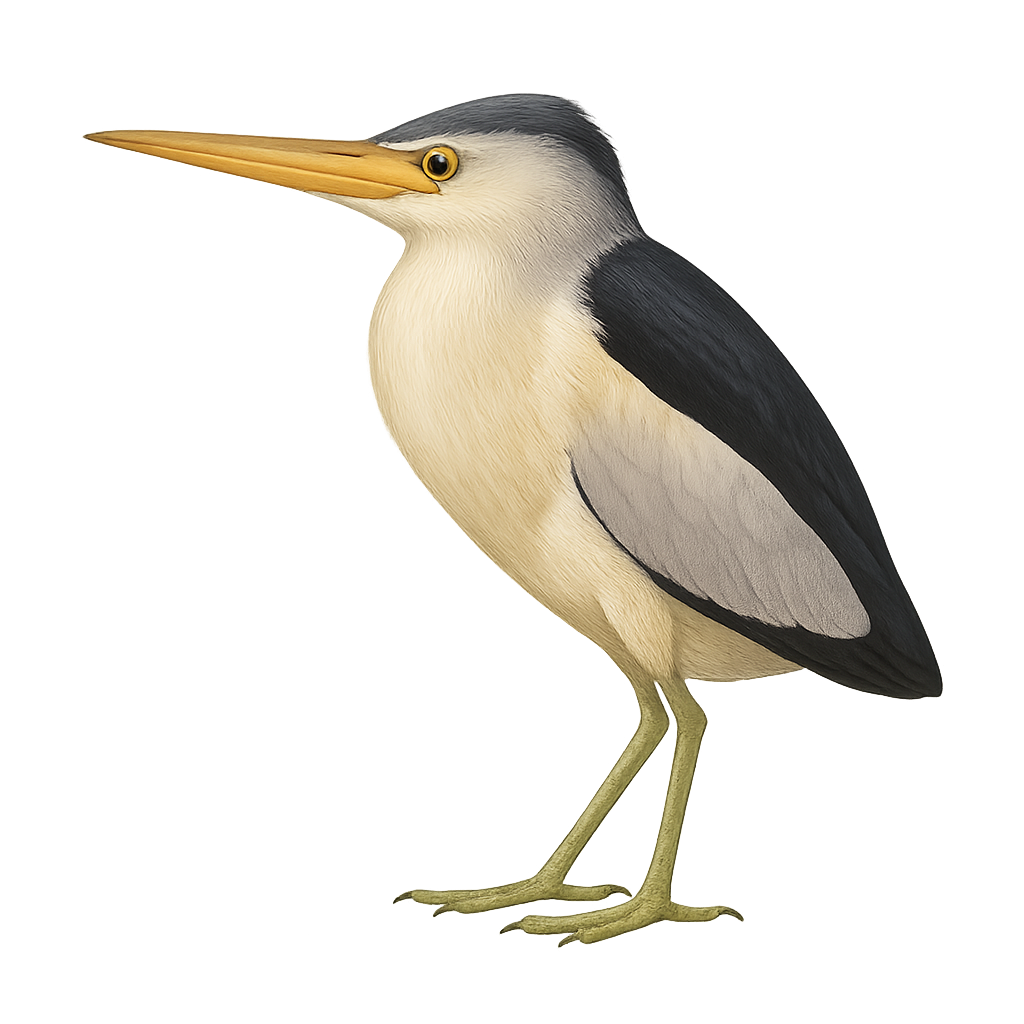
The Little Bittern is a small and discreet heron, particularly hard to observe due to its brown and beige plumage, which allows it to blend perfectly into the vegetation of marshes, ponds, and rice fields. This heron is about 30 cm long and is known for its furtive behavior and quick, low flight. It primarily feeds on small fish, aquatic insects, and amphibians, hunting silently as it sneaks through the grasses or hides in reed beds.
This small heron is mainly active at dusk and during the night, making it even more discreet. While not directly threatened, the Little Bittern faces habitat loss due to the destruction of wetlands and the draining of marshes. The conservation of these habitats is crucial for the preservation of the species.
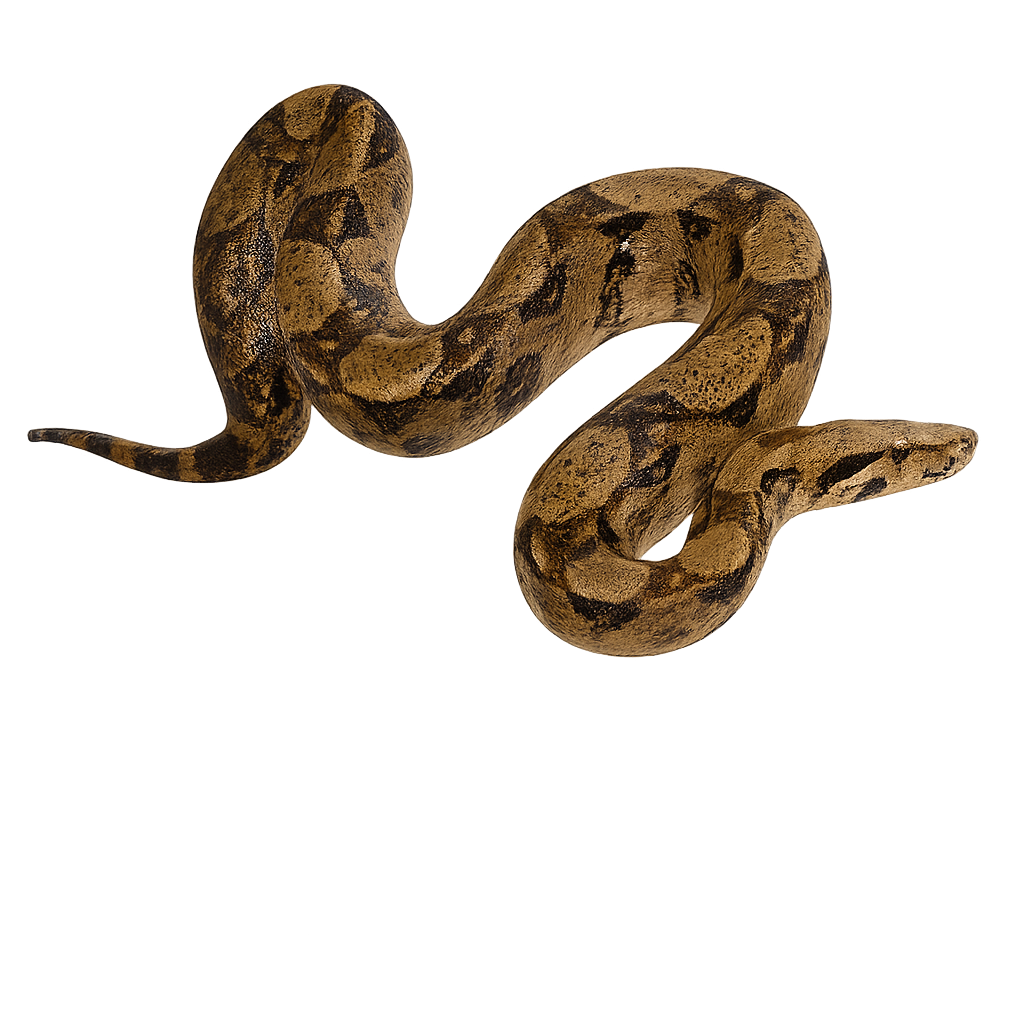
The Boa constrictor, also known as the Emperor Boa, is a medium to large-sized snake, easily recognized by its smooth scales and complex pattern of brown and golden spots and bands. It primarily inhabits the tropical forests of Central and South America, where it hides in foliage or tree trunks, using its climbing skills to hunt and conceal itself. This non-venomous snake is a constrictor, meaning it kills its prey by wrapping around it tightly before swallowing it whole.
The Boa constrictor is generally a solitary animal, and while it is an effective predator, it primarily feeds on small mammals, birds, and occasionally reptiles. It is also popular in captivity, but like many reptiles, it is threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.
The Musk Ox is a large herbivorous mammal, easily recognized by its thick brown fur that protects it from the freezing temperatures of the Arctic. This robust animal, with curved horns and a massive build, primarily inhabits the cold regions of Canada, Greenland, Alaska, and Norway. The Musk Ox feeds on woody plants, lichens, and mosses, which it finds in Arctic and sub-Arctic zones. It forms social groups to protect itself from predators and extreme weather conditions.
Adapted to harsh environments, the Musk Ox is an extremely resilient animal, capable of surviving extremely low temperatures due to its dense coat. However, it remains vulnerable to climate change, habitat loss, and human disturbances, which threaten its population.
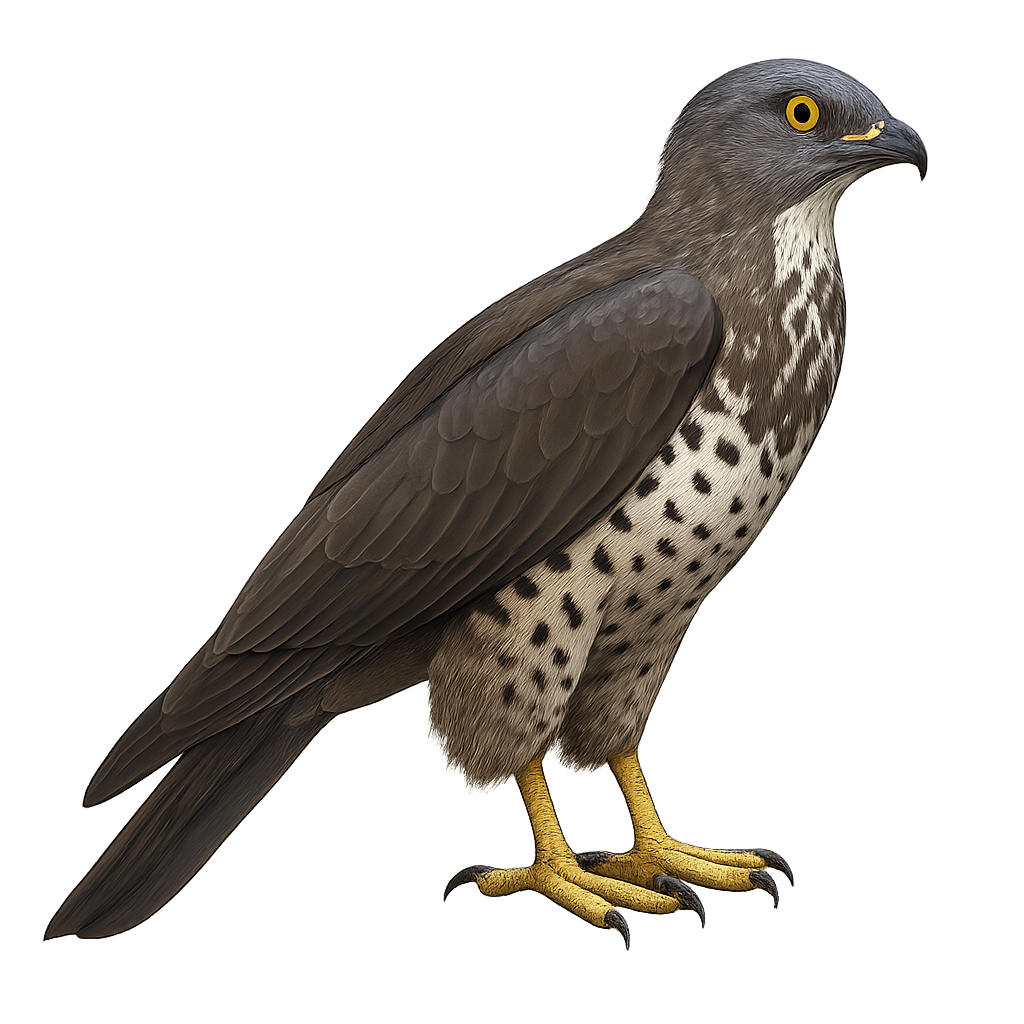
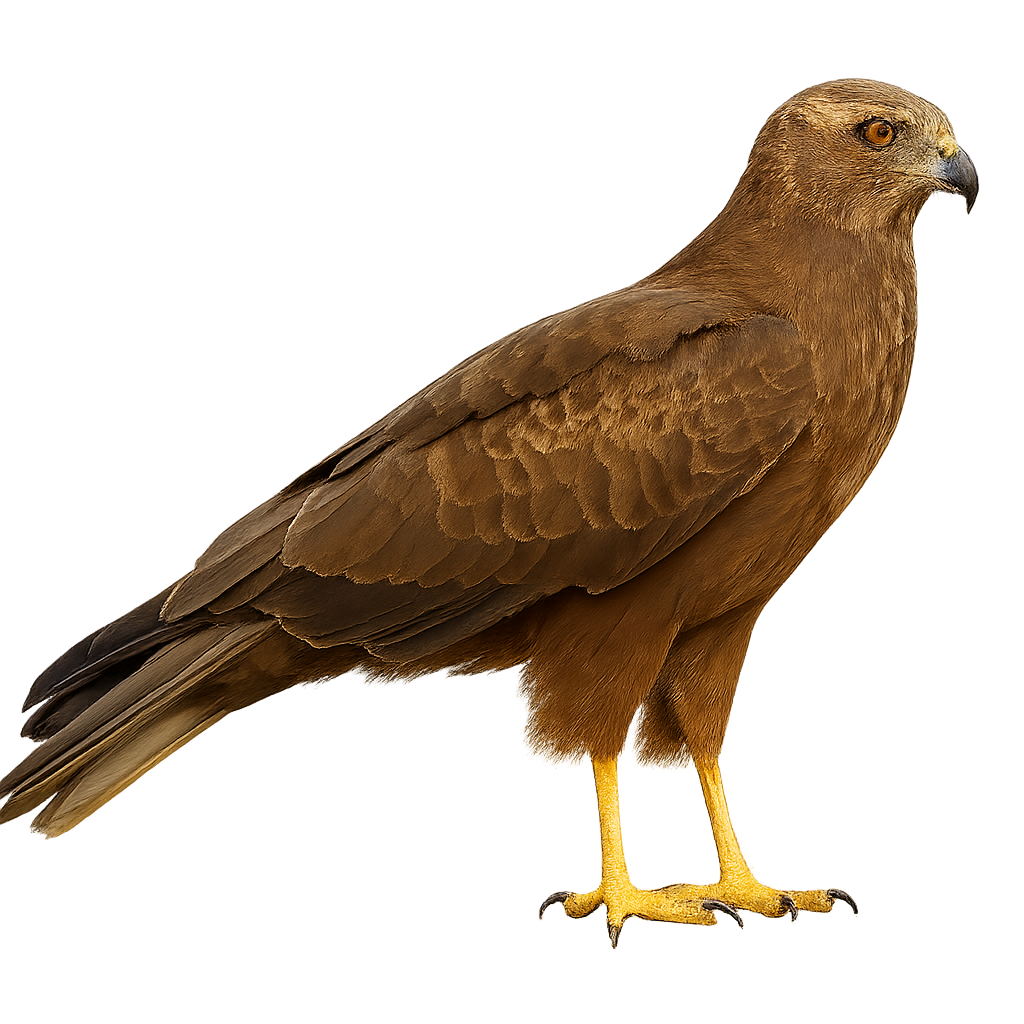
The Honey Buzzard is a medium-sized diurnal raptor, easily recognizable by its plumage marked with light and dark brown patterns and its slender build. It primarily inhabits open forests, hedgerows, and wooded areas in Europe and Asia, and feeds mainly on larvae of bees, wasps, and small insects, which it captures by flying above beehives or attacking the nests of social insects.
This raptor uses its powerful talons and curved beak to extract larvae from the nests. The Honey Buzzard is also known for its ability to undertake long migratory flights, leaving its breeding grounds in Europe to travel to warmer regions in North Africa for the winter. While the population remains stable in many areas, the Honey Buzzard may be threatened by habitat loss and the reduction in insect populations on which it relies.
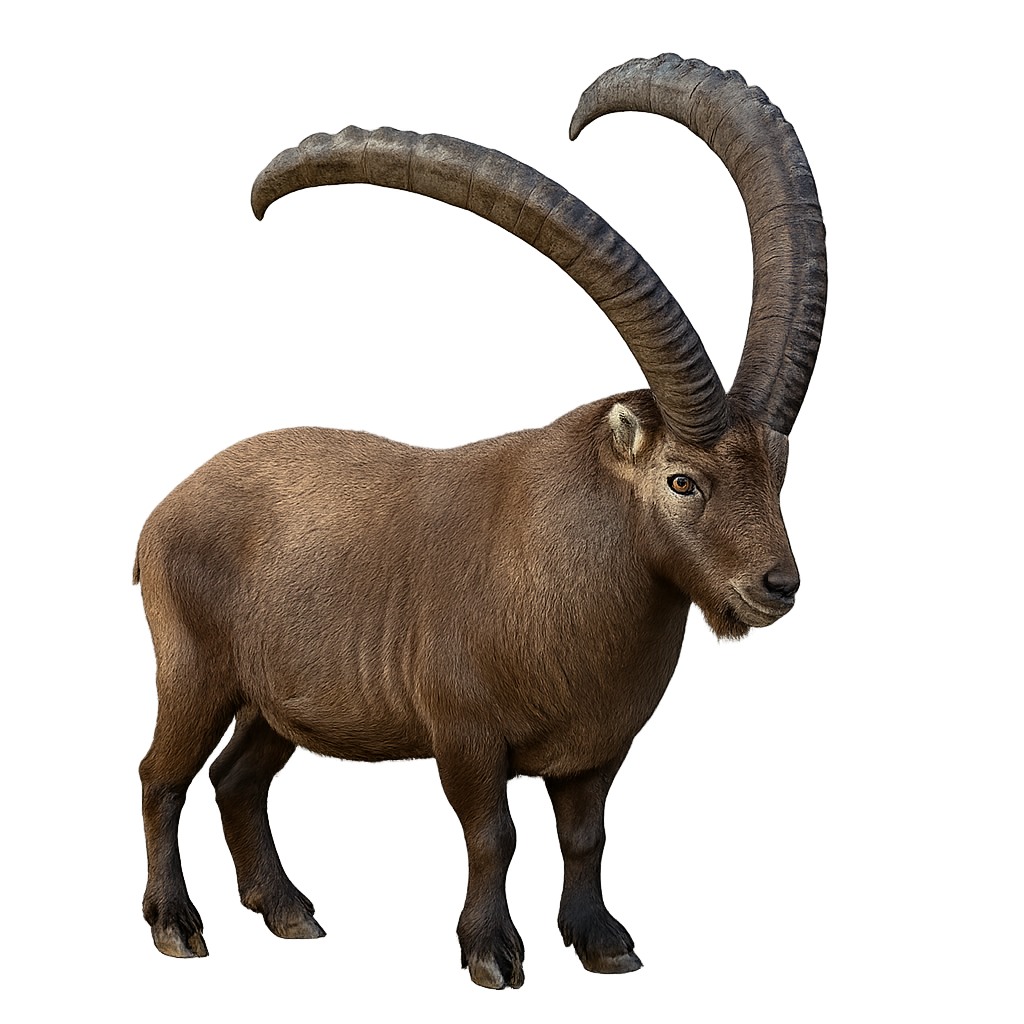
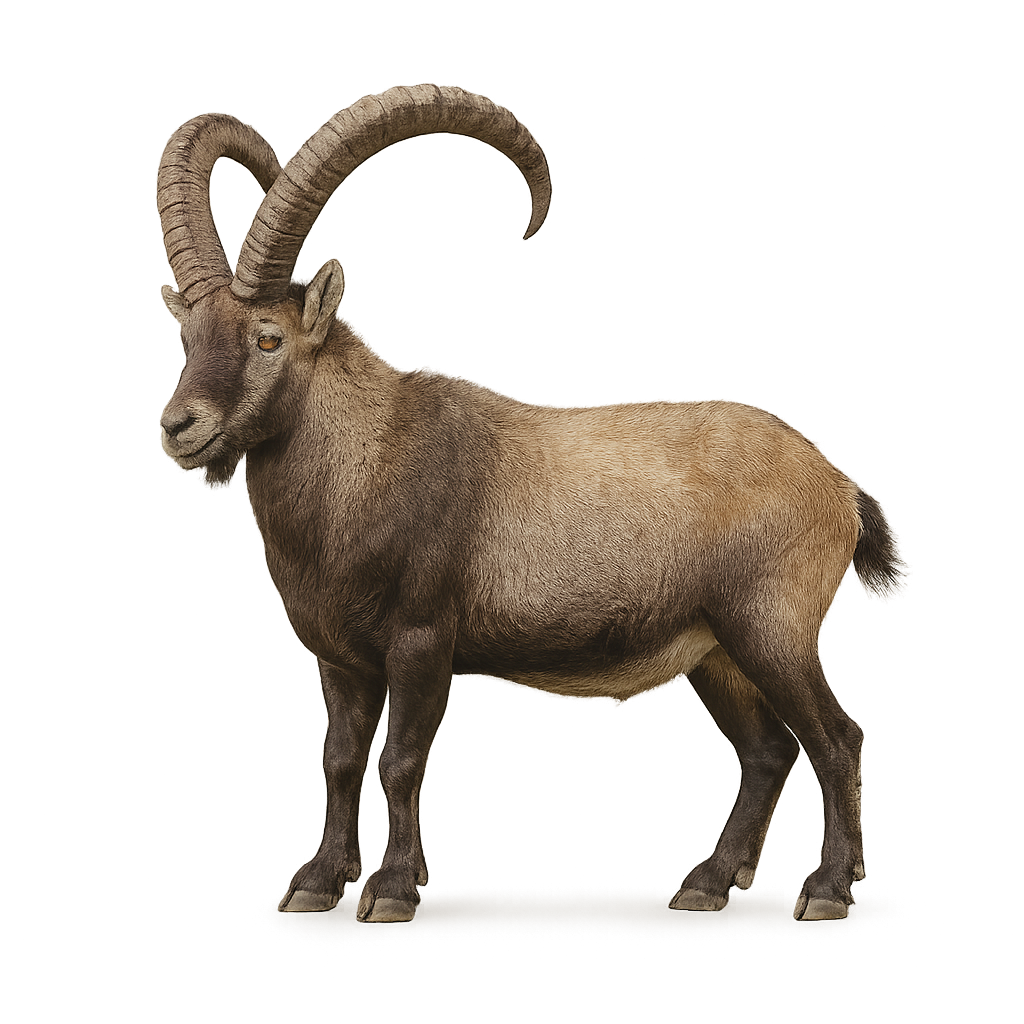
The Siberian Ibex, also known as the Asiatic Ibex, is a majestic wild goat species that lives in the rocky mountains of Central Asia, particularly in Russia, Kazakhstan, China, and Mongolia. This imposing animal, with long, curved horns and a dense coat that protects it from harsh winters, typically inhabits the steep slopes of high-altitude mountains.
Herbivorous, the Siberian Ibex primarily feeds on alpine vegetation, grasses, and woody plants. It is particularly agile, capable of moving across rugged terrain and leaping between rocks with ease. While it was once heavily hunted for its valuable horns and meat, conservation efforts have helped stabilize its population, although the Siberian Ibex remains vulnerable due to habitat loss and poaching.
The Alpine Ibex is a large herbivorous mammal, easily recognized by its long, curved horns and light brown or grayish coat. It primarily inhabits the rugged mountains of the Alps, southern Europe, and some mountainous regions of the Middle East. The Alpine Ibex feeds on alpine vegetation, grasses, and woody plants, and it is particularly adapted to life at high altitudes due to its great agility on rocky terrain and its thick coat.
This animal is social and lives in family groups, although adult males, called "ibex", form separate groups. After nearly disappearing in the early 20th century due to overhunting, conservation programs have helped stabilize its population. However, it remains vulnerable to habitat loss and human disturbances.
The Iberian Ibex is a large herbivore native to the mountains of the Iberian Peninsula, primarily in the mountain ranges of the Pyrenees and the Sierra de Gredos in Spain. It is easily recognizable by its massive, backward-curved horns and brown and gray coat. This ibex lives in rocky, steep terrain, where it feeds mainly on grasses, woody plants, and alpine vegetation.
The Iberian Ibex is a social animal that forms family groups consisting of females and young, while adult males, called "ibex," form separate groups. The species nearly went extinct in the 20th century due to overhunting, but thanks to conservation efforts, its population has been restored in several regions of Spain. However, the Iberian Ibex remains vulnerable to habitat loss and human disturbances.
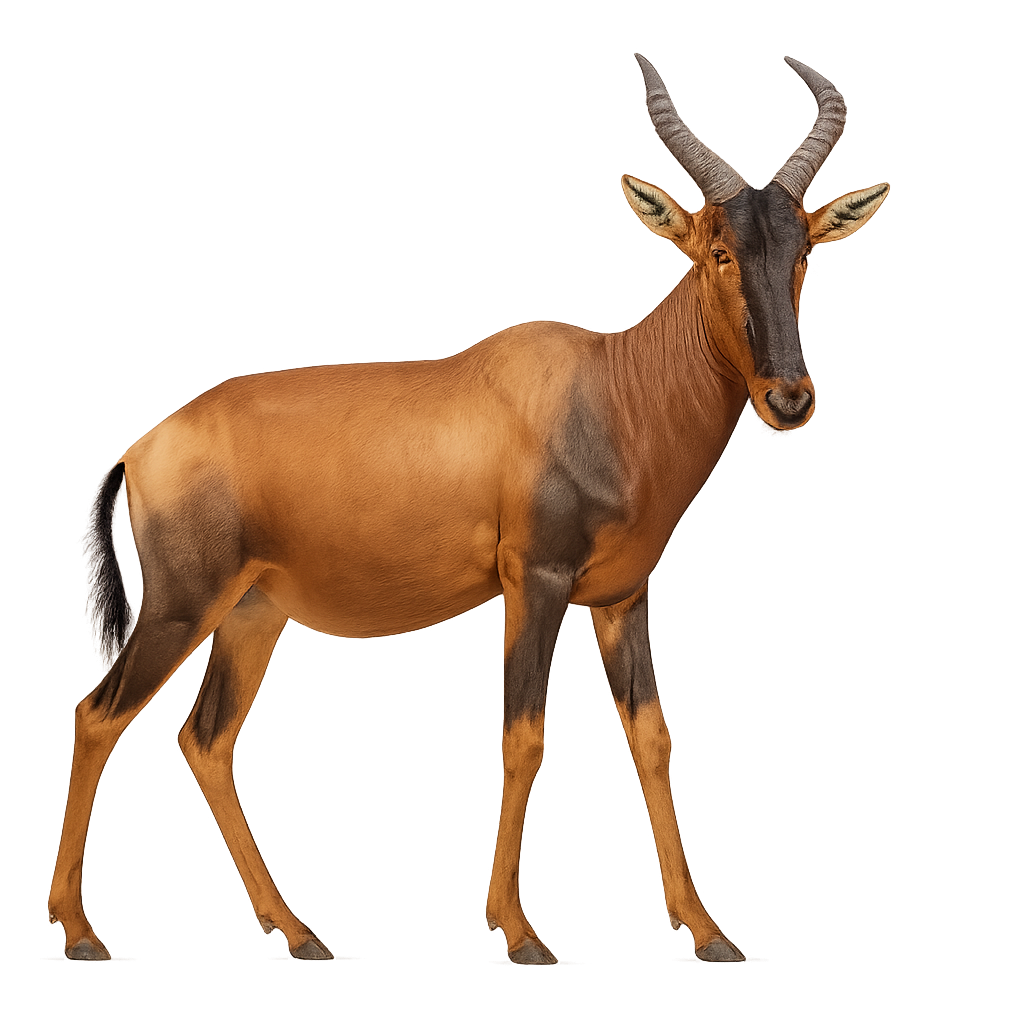
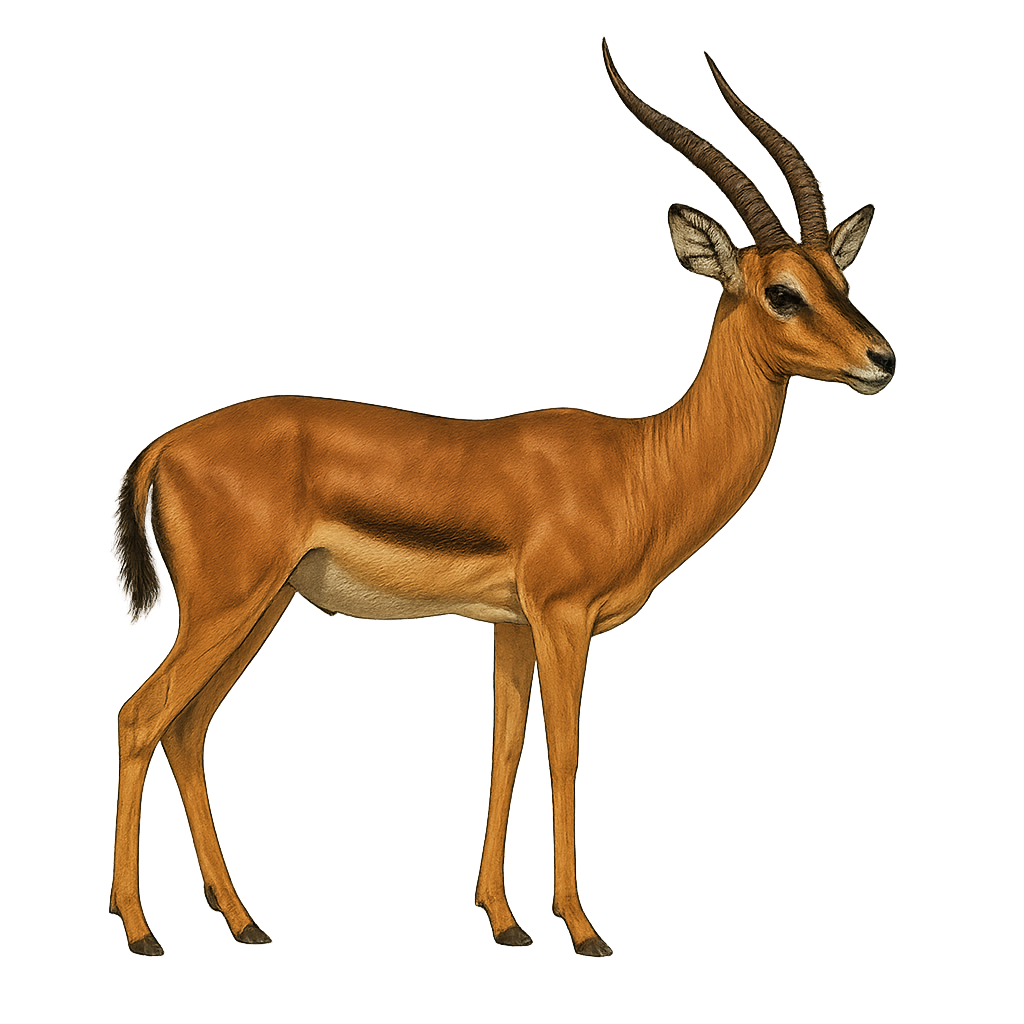
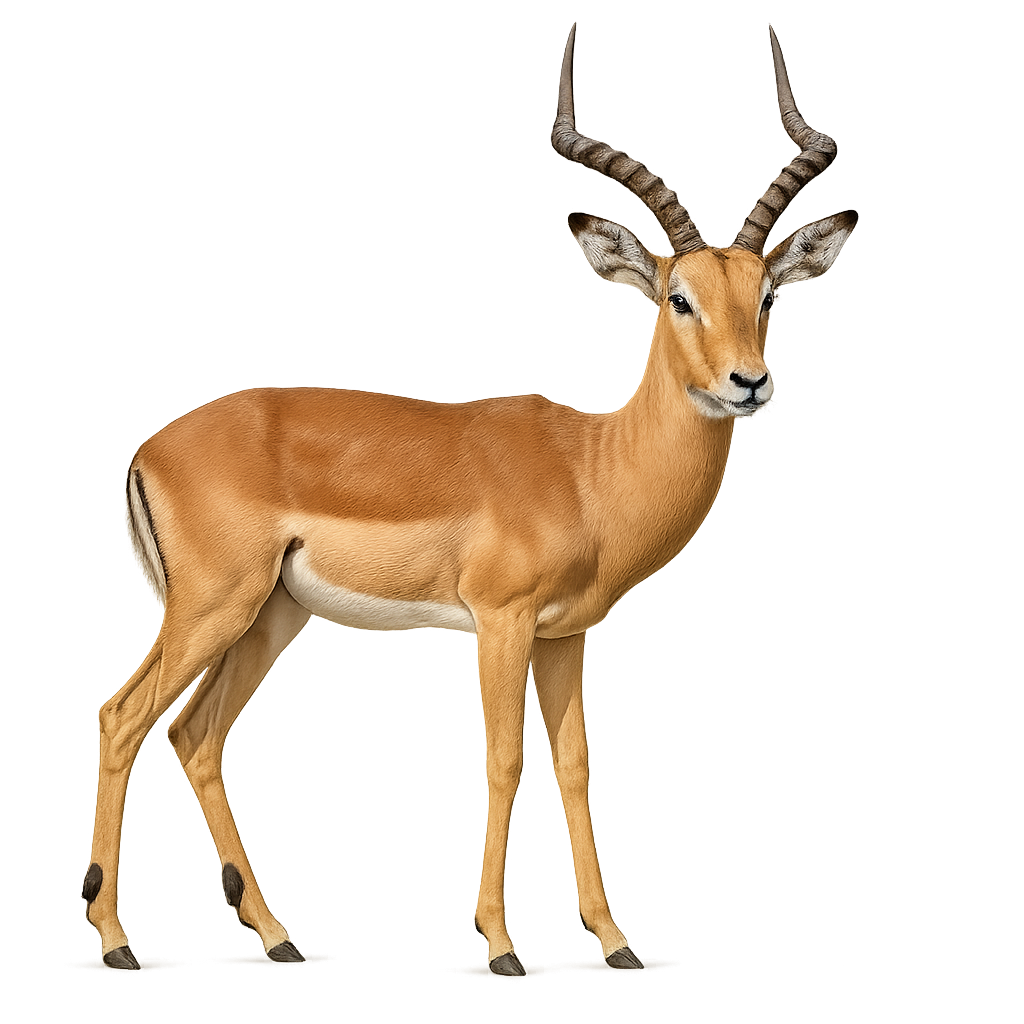
The Hartebeest is a medium-sized antelope, easily recognized by its slender body, long legs, and slightly curved horns. It primarily inhabits the savannas and open plains of North and West Africa, where it forms large herds. The Hartebeest feeds mainly on grasses and low vegetation, and it is particularly well adapted to life in arid and semi-arid environments.
This species is mainly active at dawn and dusk, avoiding the intense heat of the day. The Hartebeest is threatened by habitat loss due to agriculture and hunting, and although conservation efforts have been made, its population remains vulnerable. It is listed as "Near Threatened" on the IUCN Red List.
The African Buffalo is one of the largest and most powerful herbivorous mammals on the African continent, easily recognizable by its massive body, impressive horns, and dark coat. It primarily inhabits the savannas, grasslands, and open forests of sub-Saharan Africa. This social animal moves in large herds, sometimes composed of hundreds of individuals, which offer protection from predators through the collective strength of the group.
The African Buffalo is a strict herbivore, feeding mainly on grasses and woody vegetation. Although it has a rather calm temperament, it can become extremely aggressive when threatened, and its physical strength makes it a formidable opponent for predators. Despite being a secondary predator, it is vulnerable due to hunting and habitat loss, although conservation efforts have helped stabilize some populations.
Montagu's Harrier is a medium-sized diurnal raptor, easily recognizable by its light gray plumage on the top and white underside, as well as its long, narrow wings and light flight. It primarily inhabits open areas such as grasslands, cultivated fields, and steppe regions, where it hunts small mammals, birds, and insects. This raptor flies low over the ground searching for prey, often gliding or making wide circles.
Montagu's Harrier is particularly active during the breeding months, where it can be seen flying in pairs, sometimes forming small colonies. Migratory, it leaves its breeding grounds in Europe to head to North Africa during the winter. While its population is declining in some areas due to habitat loss and intensified agriculture, conservation efforts are underway to stabilize its numbers.
The Marsh Harrier is a medium-sized raptor, easily recognized by its brownish-green plumage and slender build. It primarily inhabits wetlands, marshes, and reed beds in Europe, Asia, and North Africa. This diurnal bird hunts small mammals, birds, and insects, which it captures by flying low over the reeds or circling slowly.
The Marsh Harrier is particularly active in spring and summer during the breeding season. Males and females often fly in tandem, searching for food to feed their young. Migratory, it leaves its breeding grounds in Europe to head to North Africa during the winter. While its population remains relatively stable in some areas, the Marsh Harrier faces threats related to habitat loss and pollution in wetland areas.
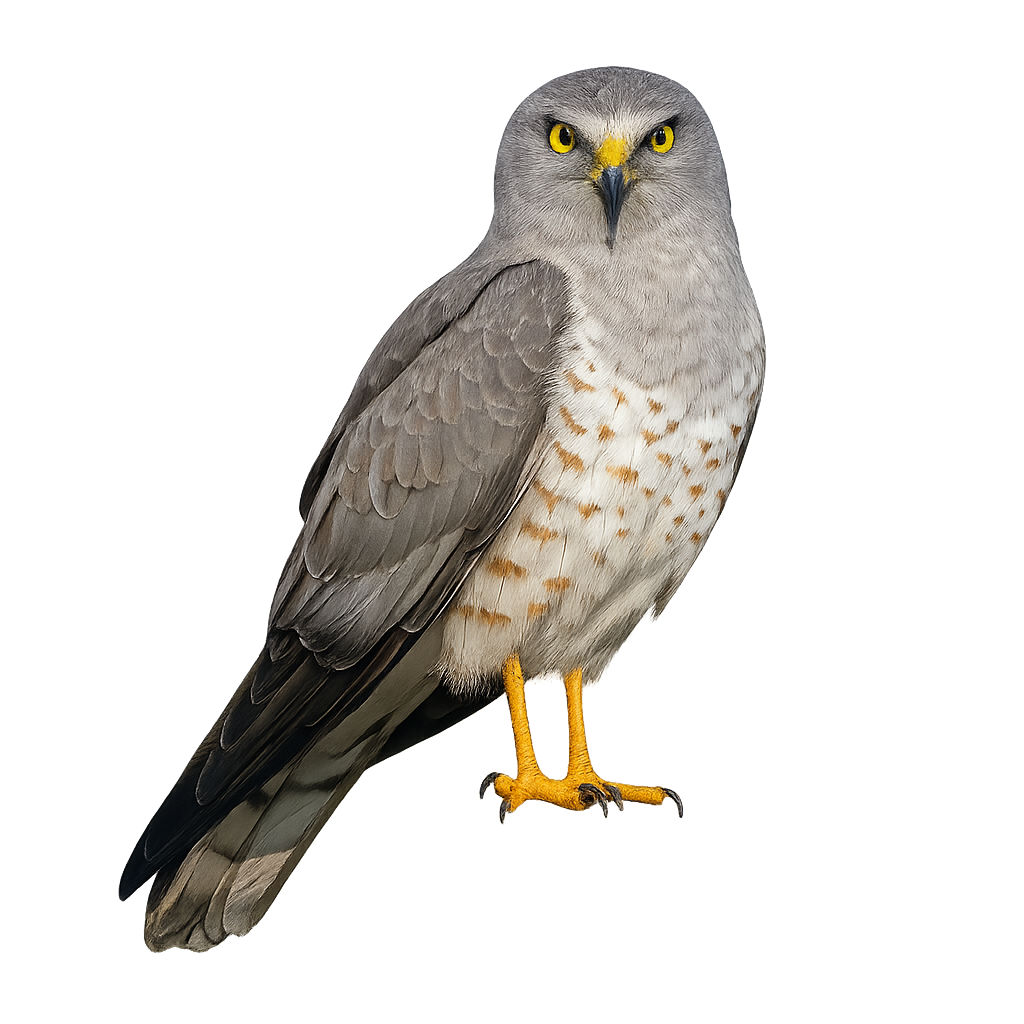
The Northern Harrier is a medium-sized raptor, easily recognizable by its gray and brown plumage, with distinct markings on its wings and a slightly rounded head. This diurnal bird primarily inhabits open areas such as grasslands, cultivated fields, and marshes, mainly in Europe and Asia. The Northern Harrier hunts small mammals, birds, and insects, which it captures by flying low, often making wide circles in search of prey.
This raptor is migratory, leaving its breeding grounds in Europe to head to North Africa during the winter. The Northern Harrier is also known for its majestic flight, which makes it easily identifiable. Although its population is declining in some areas due to habitat loss and human disturbances, conservation efforts are underway to help stabilize its populations.
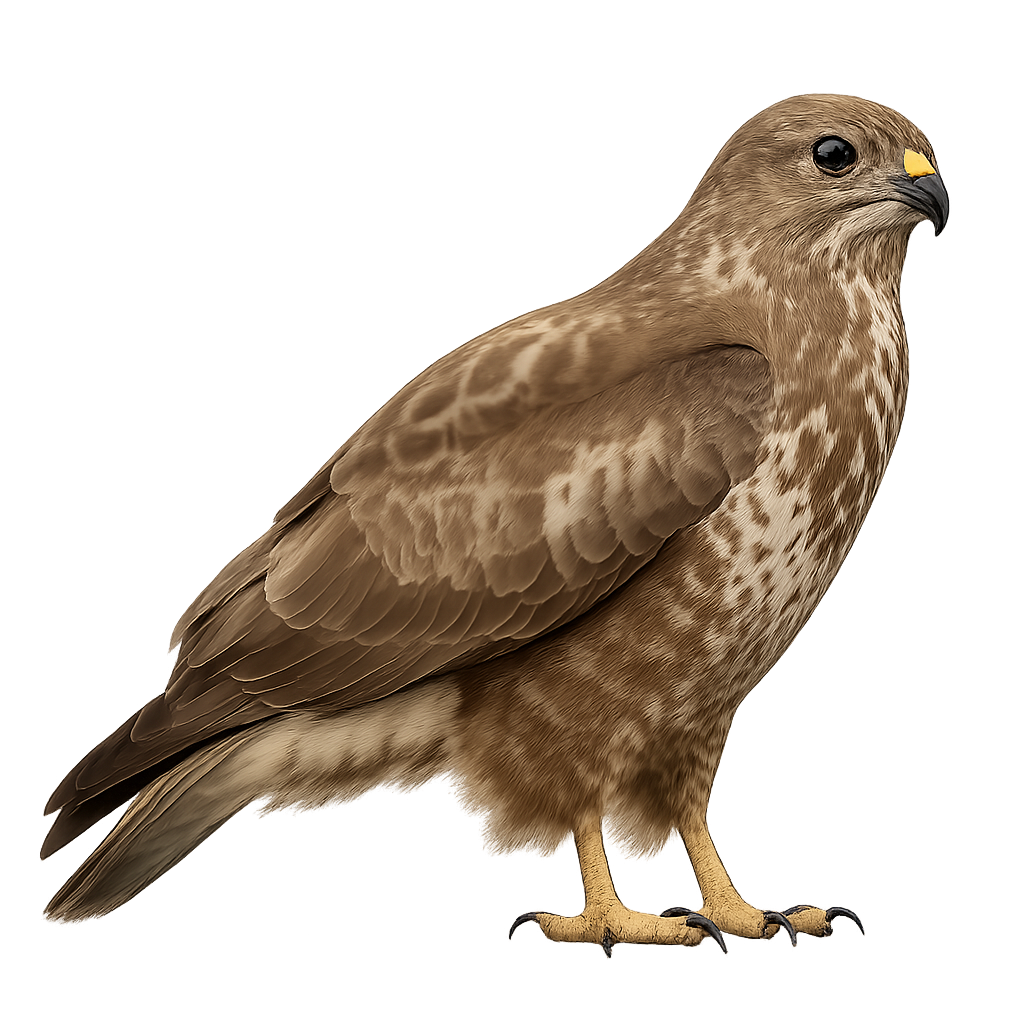
The Common Buzzard is a medium-sized diurnal raptor, easily recognizable by its often spotted and banded brown and white plumage, which gives it a particularly variable appearance from one individual to another. It primarily inhabits open forests, hedgerows, and agricultural landscapes in Europe, Asia, and North Africa. The Common Buzzard feeds on small mammals, birds, and occasionally insects, which it hunts on the ground, often perched on a tree or pole, waiting for the right moment to swoop down on its prey.
This raptor is known for its characteristic flight, often soaring in the sky in wide circles. The Common Buzzard is also a migratory bird, leaving some of its breeding grounds in Europe to migrate to warmer regions during the winter. While the population of the Common Buzzard is stable in many areas, it can be affected by habitat loss and human persecution.
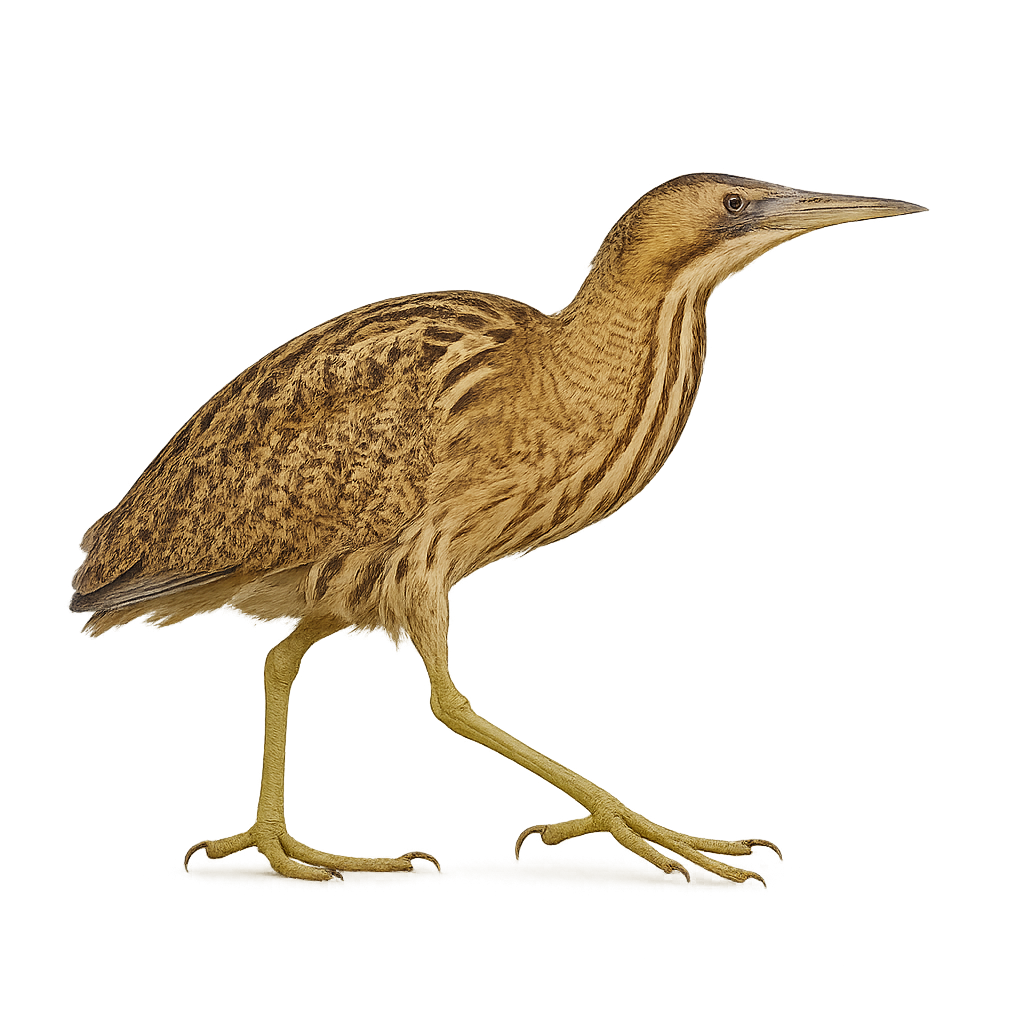
The Great Bittern is a large, secretive heron, easily recognized by its brown spotted and striped plumage, which allows it to blend perfectly into the reeds and vegetation of wetland areas where it lives. This nocturnal and solitary bird primarily inhabits marshes, ponds, and reed beds in Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It feeds mainly on fish, amphibians, and small birds, which it hunts by silently creeping through aquatic plants or standing still to wait for its prey.
The Great Bittern is an excellent master of camouflage, using its plumage to conceal itself in its environment, making it difficult to observe. Migratory, it leaves its breeding grounds to travel to Africa during the winter. While it is listed as "Near Threatened" on the IUCN Red List, it remains vulnerable to habitat loss due to wetland drainage and urbanization.
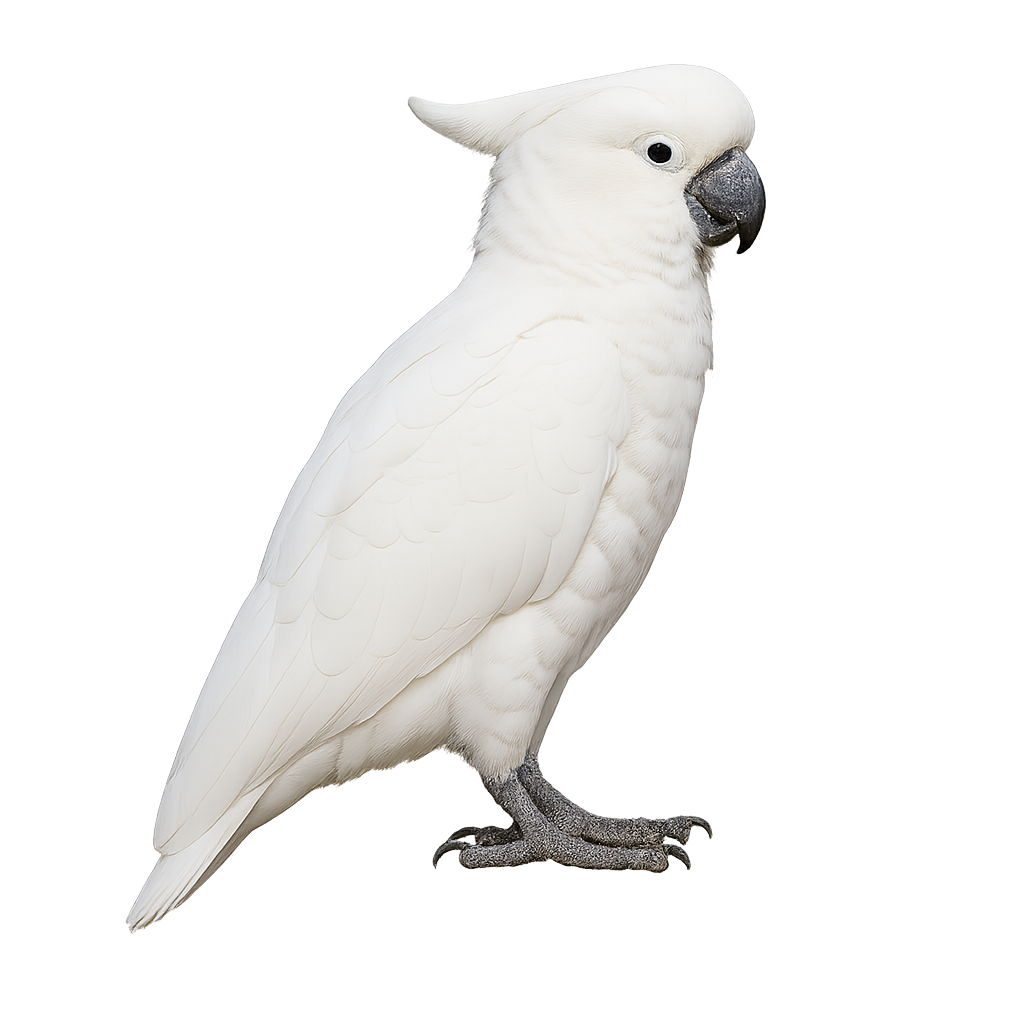
Cockatoos are exuberant and colorful birds, known for their spectacular crests and fascinating social behavior. These birds are native to Australia, New Guinea, and neighboring islands. Their plumage, often white with brightly colored accents on the crest or tail, makes them particularly attractive. They are also famous for their intelligence and ability to mimic sounds, including human speech, making them popular as pets.
Cockatoos live mainly in forests, savannas, and coastal areas. They are social birds that form often noisy groups, spending their days searching for food, perching, and interacting with other members of their group. Although some species of cockatoos are protected due to habitat loss and poaching, they remain an iconic symbol of exotic birds.
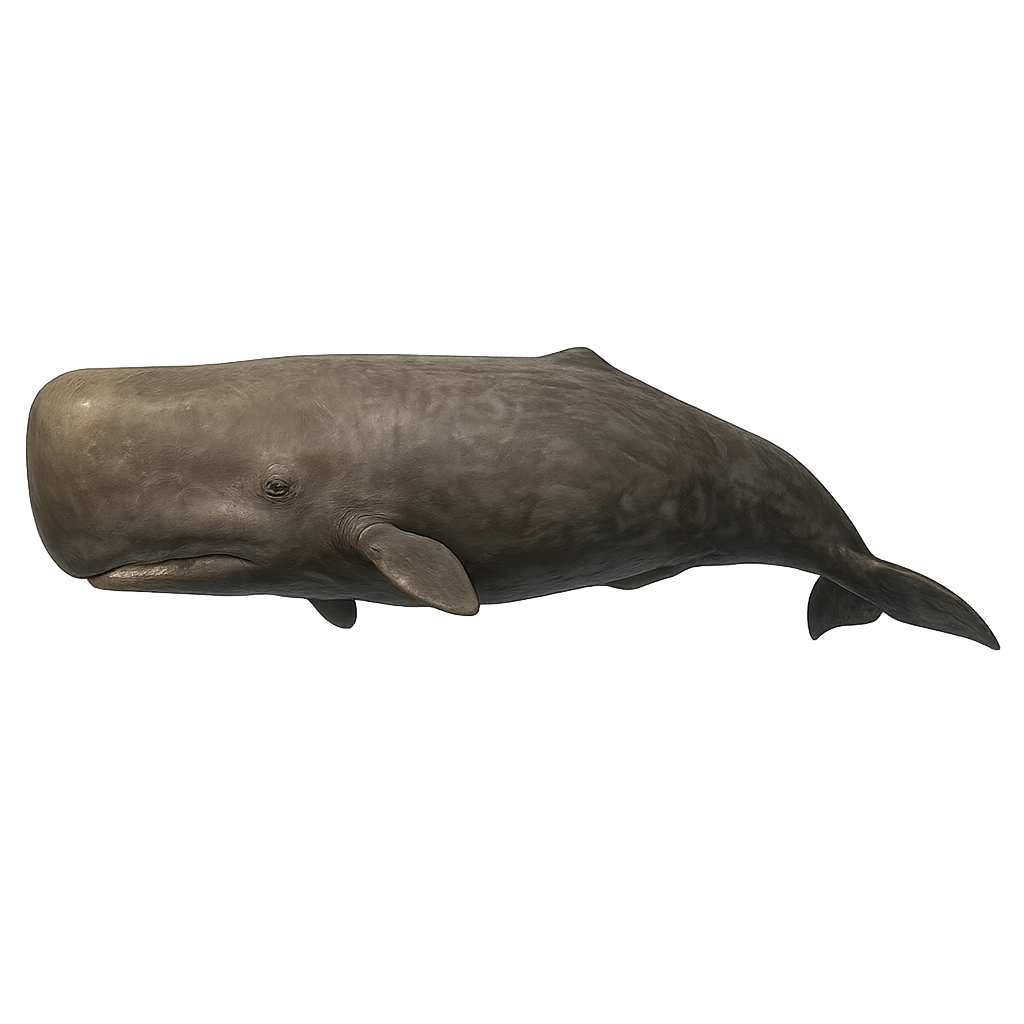
The Sperm Whale is the largest of the toothed cetaceans and the largest living marine predator today. It is easily recognizable by its massive head, which makes up about one-third of its total body length, and its streamlined body. This cetacean, which can reach up to 20 meters in length and weigh several dozen tons, is a deep-sea creature, primarily feeding on squid, including giant squids, which it hunts at extreme depths.
The Sperm Whale is known for its long migrations, traveling thousands of kilometers between breeding grounds in the tropics and feeding areas in colder waters. Although it was intensively hunted for its oil and blubber in past centuries, it remains a protected species. The Sperm Whale also plays a crucial role in the marine ecosystem by regulating prey populations and maintaining the balance of food chains.
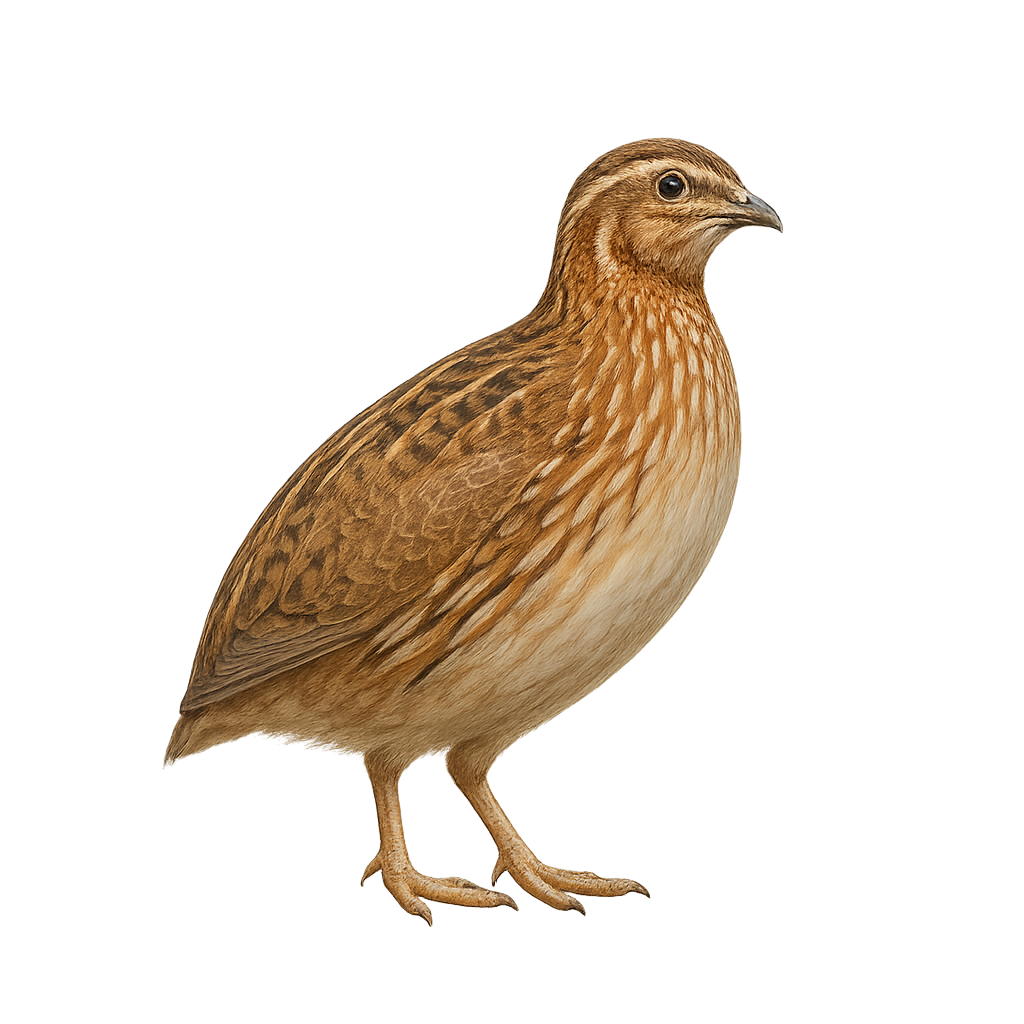
The Common Quail is a small, ground-dwelling bird, easily recognizable by its striped brown plumage and small size. It primarily inhabits fields, meadows, and open agricultural areas, where it blends perfectly into the vegetation. This bird is mostly terrestrial, spending much of its time running through tall grasses rather than flying. When it does take flight, it is usually quick and short, a strategy to escape predators.
The Common Quail is migratory, leaving its breeding grounds in Europe and Asia to travel to Africa during the winter. Its population is declining in some areas due to habitat loss, intensified agriculture, and hunting. Despite these threats, conservation efforts have been implemented to stabilize local populations.
The Spectacled Caiman is a reptile of the alligator family, primarily found in rivers, swamps, and lakes of tropical Central and South America. It is recognizable by its green-gray skin and smaller size compared to other crocodilians, typically reaching 2 to 3 meters in length. The Spectacled Caiman feeds mainly on fish, amphibians, small mammals, and birds, which it captures with its powerful jaws.
This semi-aquatic animal spends much of its life in the water, where it hunts and hides in the vegetation along the shores to avoid predators. While the Spectacled Caiman is generally discreet, it can become dangerous if threatened. Its population is stable, although the species is sometimes threatened by illegal hunting and habitat loss.
The Yellow-casqued Hornbill is a characteristic bird of the open forests and savannas of sub-Saharan Africa. It is easily recognizable by its large curved bill, adorned with a bright yellow casque that gives it a distinctive appearance. Despite its massive size, the bill is lightweight and hollow, allowing this bird to fly with agility despite its size. Its plumage is primarily black and white, with yellow accents around the bill and casque.
The Yellow-casqued Hornbill is primarily frugivorous, feeding on fruits, berries, and insects found in trees. It is often seen in pairs or small groups, moving from branch to branch and emitting loud and distinct calls. While it is relatively widespread in its habitat, it may be threatened by deforestation and habitat loss due to agricultural expansion.
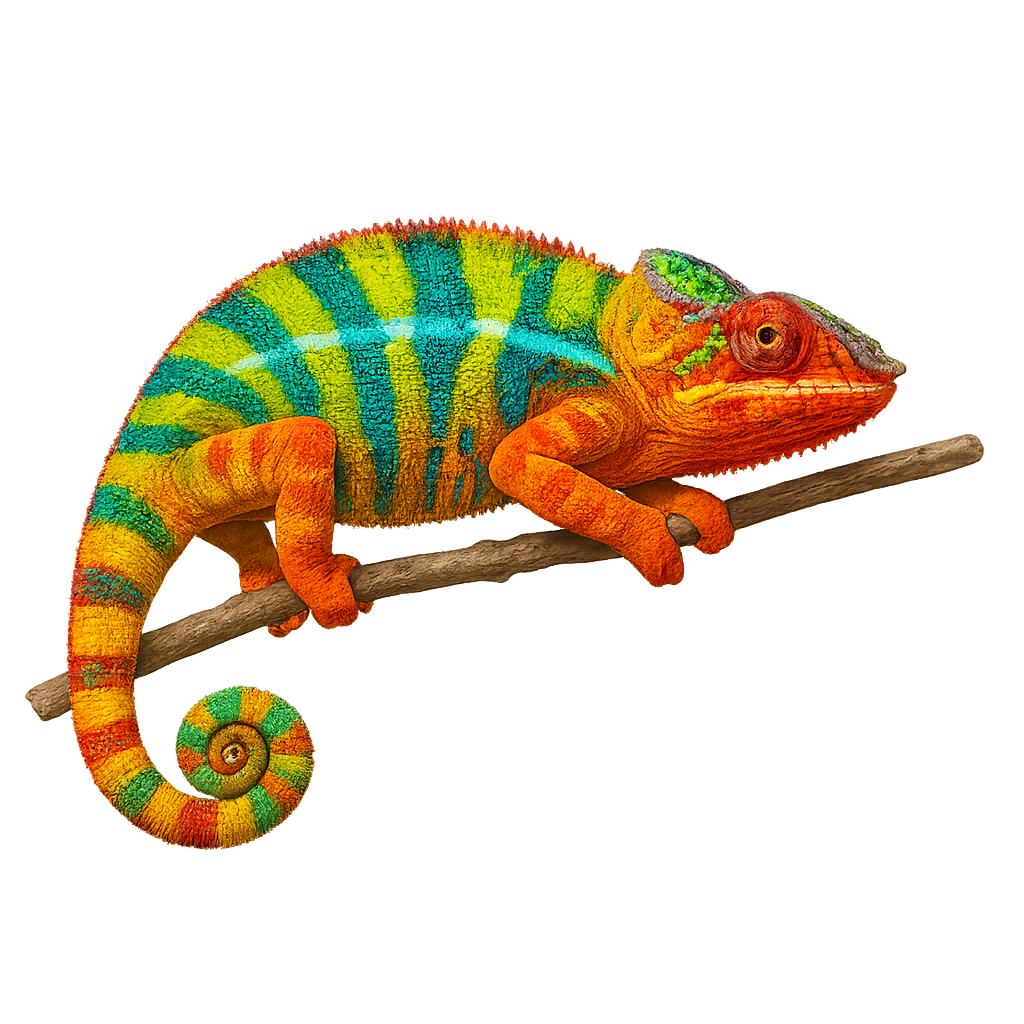
The Panther Chameleon is an iconic species from Madagascar, famous for its vibrant colors and impressive patterns that vary depending on its mood and environment. This chameleon is primarily arboreal, living in the humid tropical forests of the island, where it hides among branches and foliage. It is also known for its ability to change color, an adaptation that helps it camouflage but is also used during fights between males or to attract a female. Although generally calm, it can become more active during the breeding season.
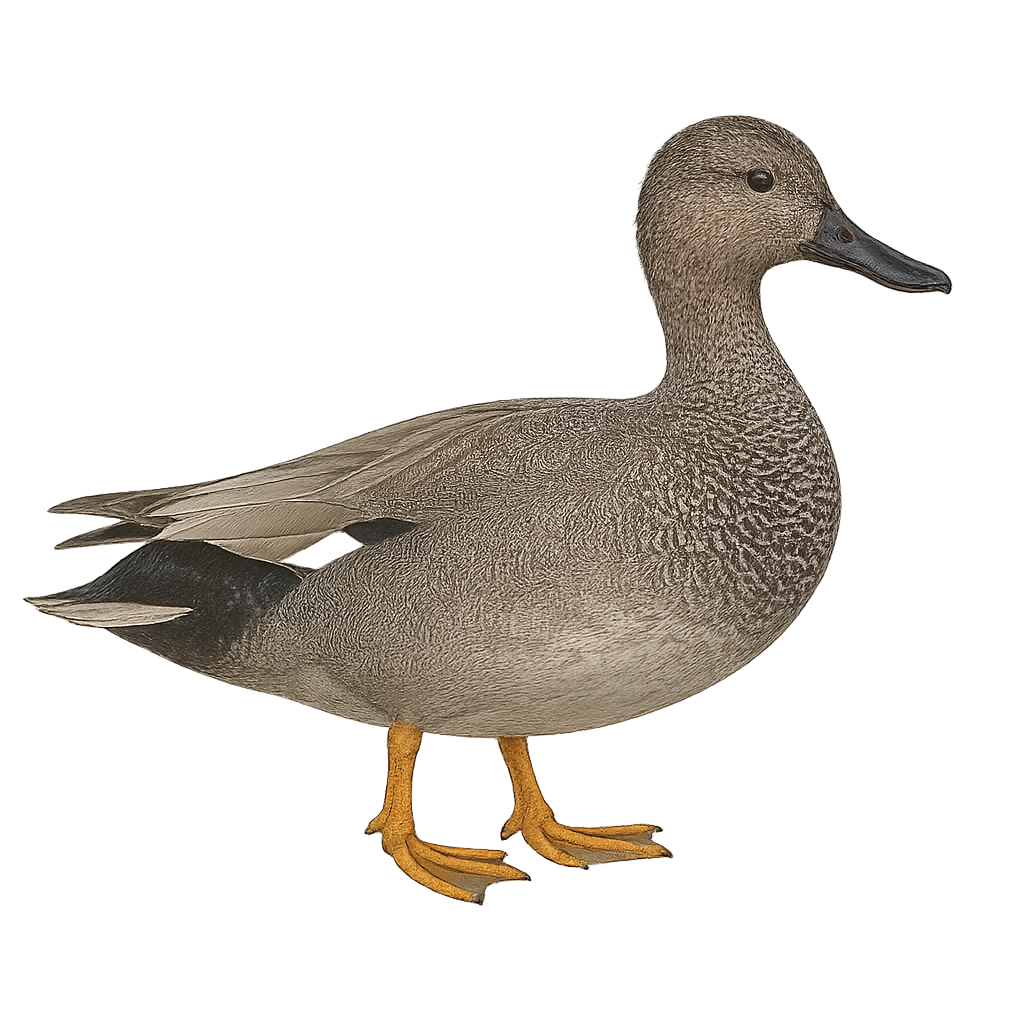
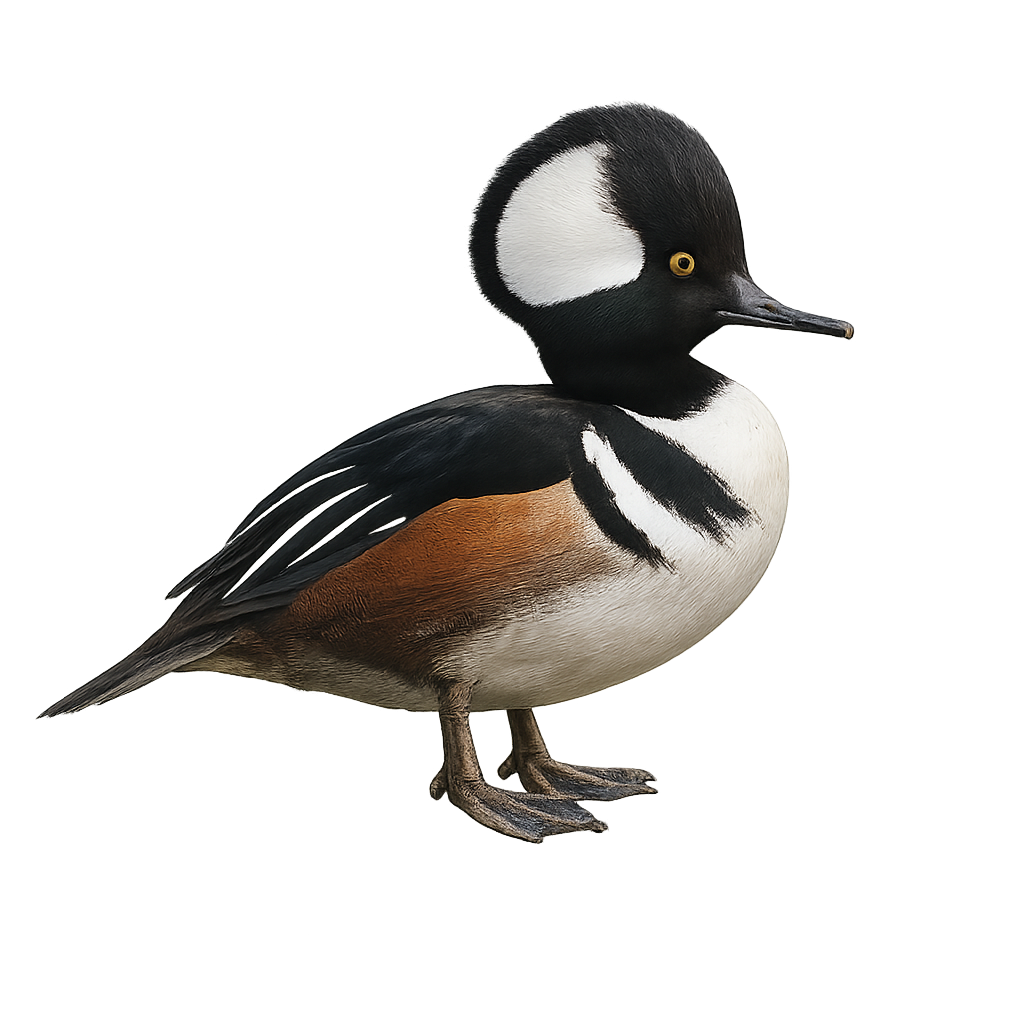
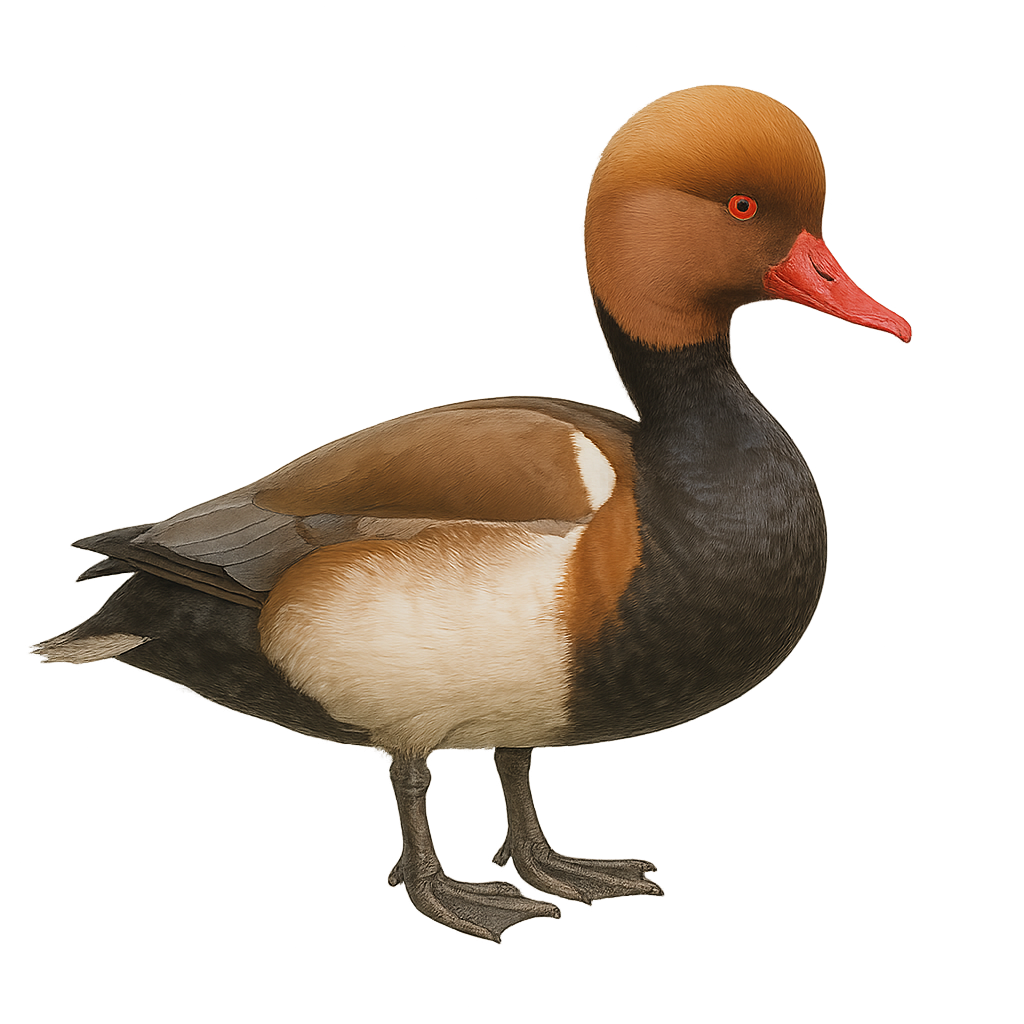
The Gadwall is a medium-sized dabbling duck, measuring between 46 and 56 cm in length with a wingspan of 78 to 90 cm. The male has finely patterned gray plumage with a distinctive white wing patch visible in flight, a black rump, and a dark bill. The female is mottled brown with an orange-edged dark bill. This species inhabits wetlands such as marshes, ponds, lakes, and flooded meadows rich in aquatic vegetation. It feeds mainly on leaves, stems, and seeds of aquatic plants, but also consumes aquatic invertebrates, especially during the breeding season. The Gadwall is a partial migrant, breeding in Eurasia and North America, and wintering in more southern regions. Although listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, it is sensitive to wetland degradation and pollution.
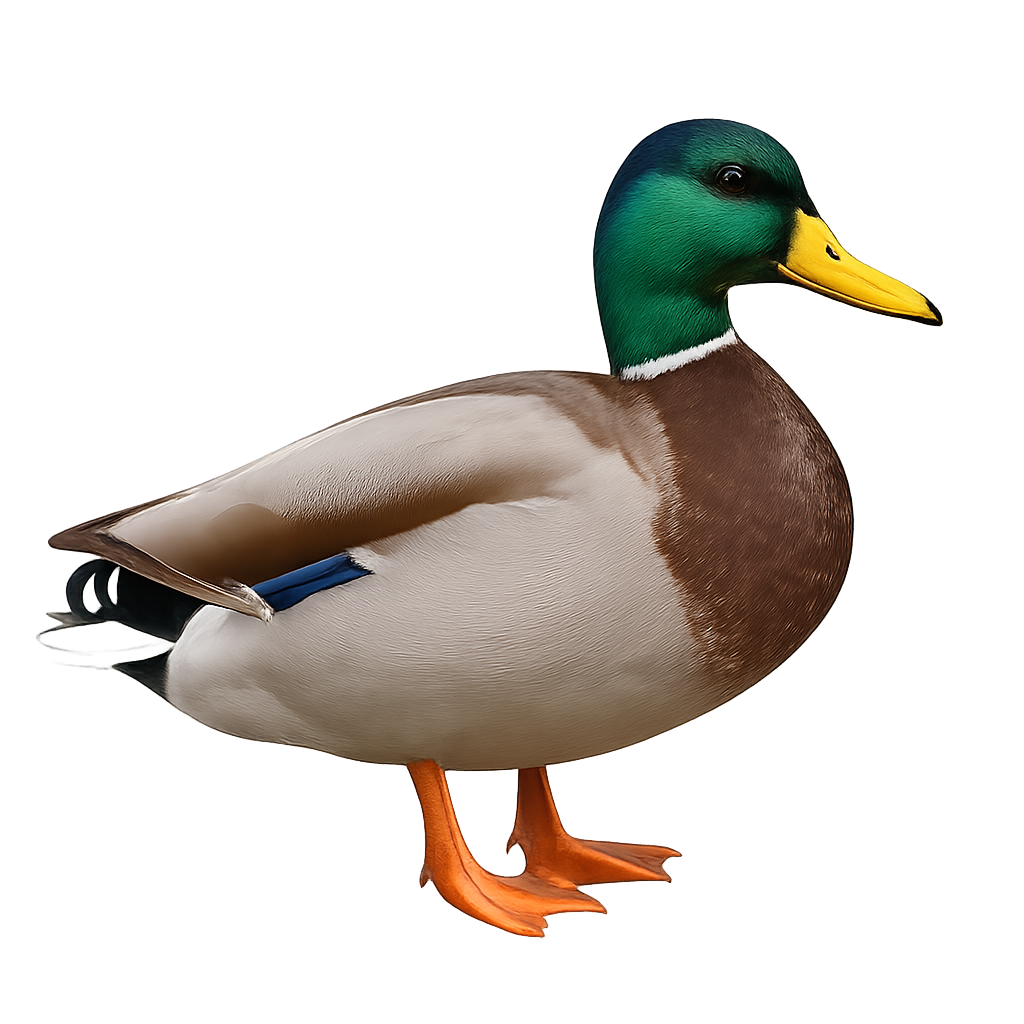
Anas platyrhynchos is a medium-sized duck species, measuring between 50 and 65 cm in length, with a wingspan of 81 to 98 cm. The male is distinguished by its iridescent green head, white neck, and brown-roux body, while the female is brown-speckled, aiding in camouflage. They primarily inhabit freshwater wetlands such as ponds, lakes, slow rivers, and marshes. They feed on a wide variety of plant and animal matter, including seeds, roots, insects, and small fish. Reproduction occurs in spring, with the female building a ground nest near water, where she typically lays 8 to 13 eggs. Incubation lasts about 27 to 28 days, and ducklings are capable of swimming and feeding themselves shortly after hatching. A very widespread species, it is classified as Least Concern by the IUCN.
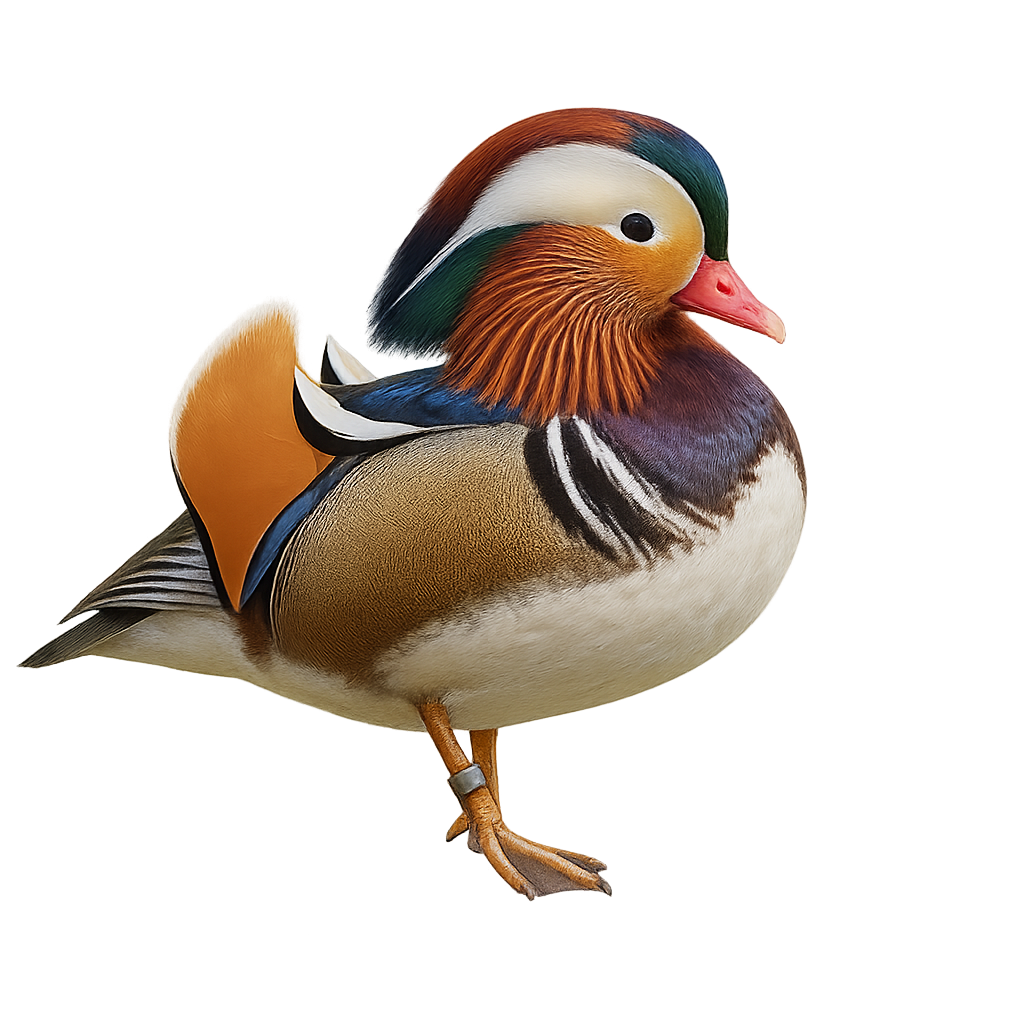
The Mandarin Duck is a spectacular waterfowl, easily recognizable by its vibrant and colorful plumage, particularly in the male. The male displays an impressive mix of bright colors, including orange, blue, and green, with a distinctive crest on the head and feathers on the sides of the neck that resemble scales. The female, more subdued, has brown plumage with subtle white accents around the eyes and bill.
Native to East Asia, the Mandarin Duck is now widely distributed in Europe and North America, often seen in parks and gardens around bodies of water. This duck prefers calm waters in lakes, ponds, and rivers, where it feeds mainly on seeds, fruits, insects, and small crustaceans. Although the Mandarin Duck is not considered endangered, its natural habitat can be threatened by pollution and the loss of wetland areas.
The Northern Pintail is a migratory species of duck, easily recognizable by its slender body and long neck, which gives it an elegant and distinctive silhouette. The male during the breeding season has a colorful plumage, with a green head, brown body, and long bill. The female, on the other hand, has more subdued plumage, brown speckled, adapted for camouflage.
This duck primarily inhabits wetland areas, such as marshes, ponds, and rivers, where it feeds on aquatic vegetation, seeds, and insects. The Northern Pintail is a long-distance migrant, leaving its breeding grounds in Europe and Asia to head to Africa or the Middle East during the winter. Although still fairly widespread, the species is threatened by the loss of its natural habitat due to wetland drainage and intensified agriculture.
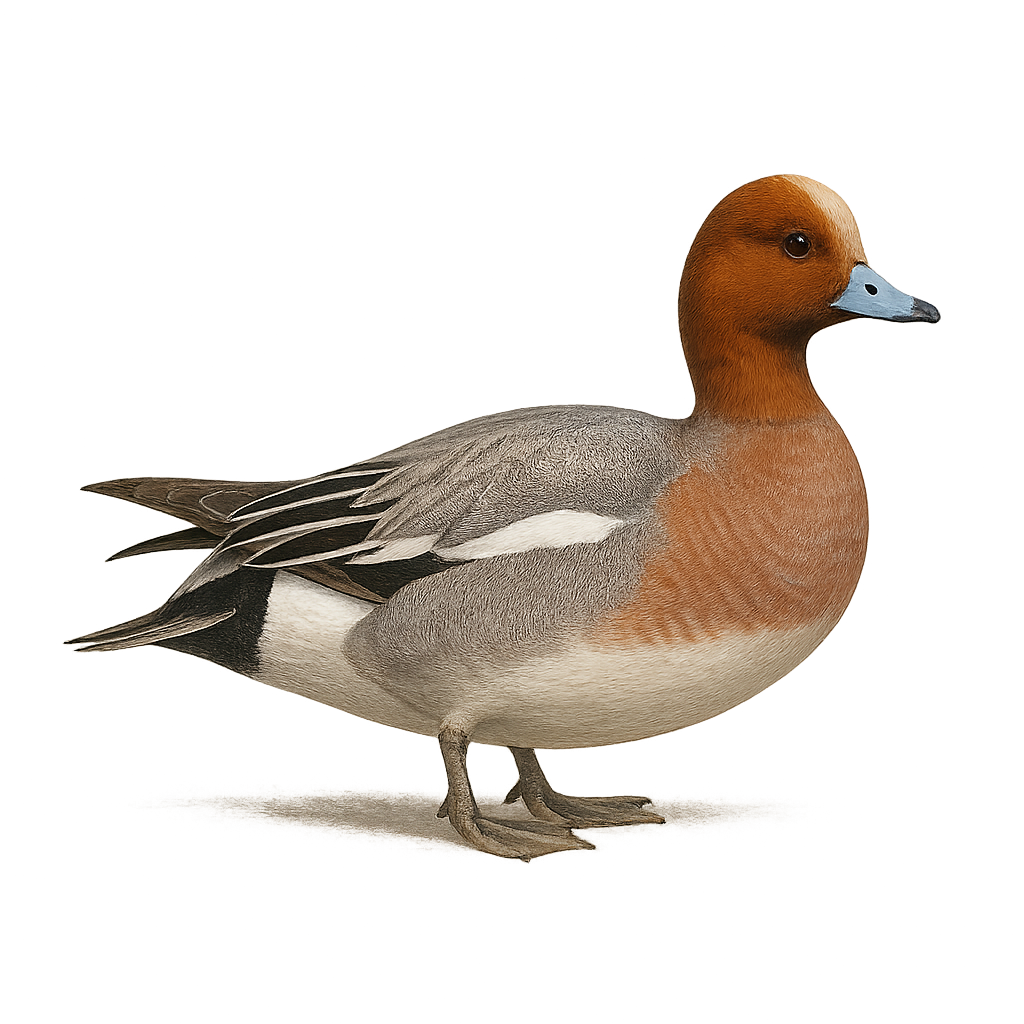
The Eurasian Wigeon is an elegant waterfowl, easily recognizable by its distinctive plumage and characteristic whistle. The male, during the breeding season, has colorful plumage with a dark green head, light brown body, and a white stripe running across its neck. The female is more subdued, with speckled brown plumage, adapted for camouflage. This duck gets its name from the whistling sound it makes during its movements and social interactions.
The Eurasian Wigeon primarily inhabits wetlands, such as lakes, ponds, and marshes, where it feeds on aquatic plants, seeds, and insects. It is a long-distance migratory bird, leaving its breeding grounds in Europe to travel to warmer regions in Africa or the Middle East during the winter. While its population remains generally stable, it faces threats related to habitat loss and water pollution.
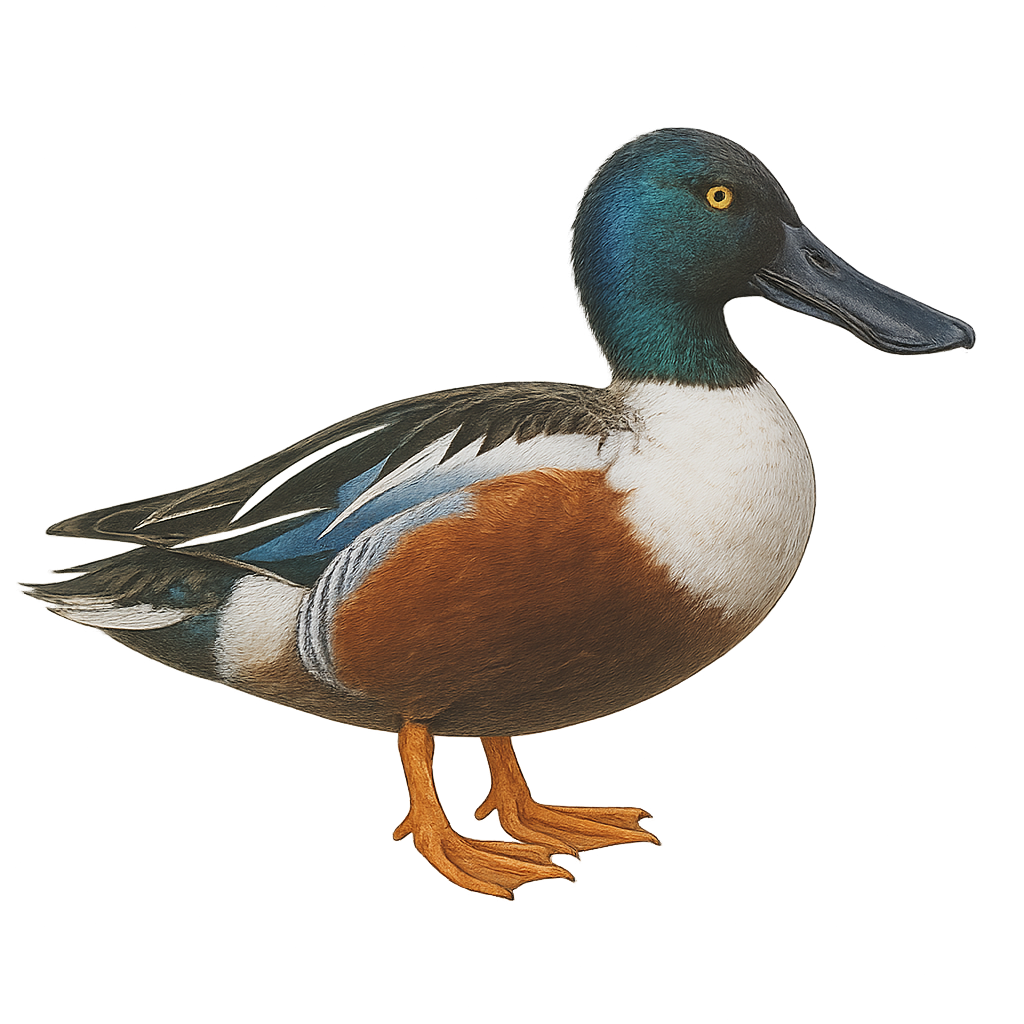
The Northern Shoveler is a medium-sized dabbling duck, measuring between 44 and 56 cm in length with a wingspan of 70 to 85 cm. The breeding male features an iridescent dark green head, white chest, chestnut flanks, and a large spatula-shaped bill. The female has mottled brown plumage and a similarly shaped bill. This species inhabits shallow wetlands, such as marshes, ponds, and floodplain meadows rich in aquatic vegetation. It feeds by filtering water with its specialized bill, consuming primarily plankton, aquatic insects, crustaceans, mollusks, and seeds. Migratory, the Northern Shoveler breeds in Europe and Asia, wintering in Africa, India, and Southeast Asia. Although listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, it is sensitive to wetland degradation.
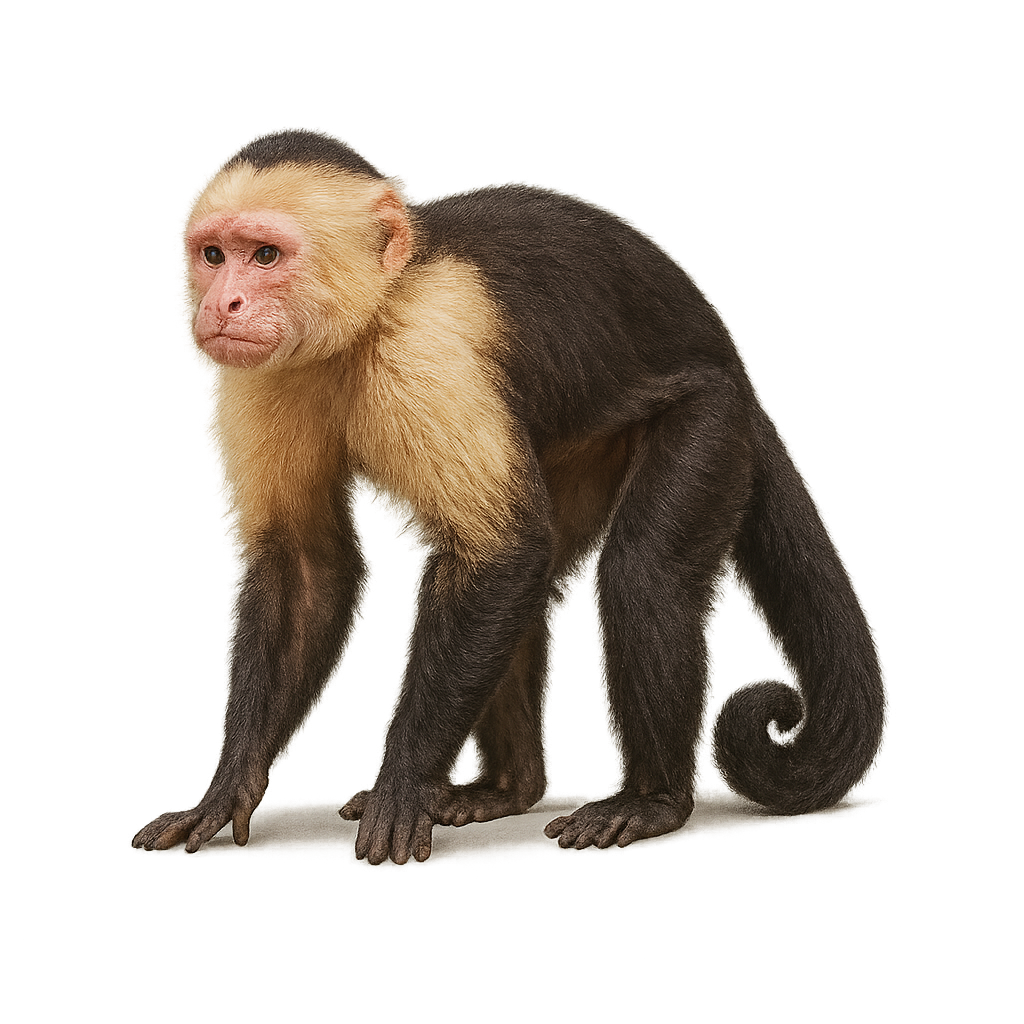
The White-faced Capuchin is a small, intelligent, and social monkey, easily recognizable by its pale face, framed by darker fur, and its agile, slender body. This primate lives in the tropical forests of Central and South America, primarily inhabiting the canopy, where it feeds on fruits, seeds, insects, and occasionally small vertebrates.
White-faced Capuchins are highly social animals, living in family groups or bands of up to twenty individuals. They are known for their great learning ability and curious behavior, often used in behavioral studies due to their intelligence and problem-solving skills. Unfortunately, like many other primate species, they are threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.
The Capybara is the largest rodent in the world, easily recognizable by its massive body and short, light brown fur. This semi-aquatic mammal primarily inhabits wetland areas of South America, near rivers, lakes, and swamps. The Capybara is an excellent swimmer and spends much of its time in the water, where it feeds mainly on aquatic grasses, plants, and fallen fruits.
Naturally social, the Capybara lives in large groups of 10 to 20 individuals, often organized around a social hierarchy. The groups spend a lot of time grooming each other and protecting each other from predators. Although it is a calm and docile animal, the Capybara is threatened by the loss of its natural habitat due to urbanization and pollution of rivers. However, its population remains relatively stable, and it is often seen in protected areas.
The Caracal is an elegant feline, easily recognizable by its pointed ears adorned with tufts of black fur. It has a short tawny coat that allows it to blend into the dry, rocky environments where it lives, primarily in savannas, steppes, and semi-desert areas in Africa and Western Asia. This agile and fast predator primarily hunts birds, small mammals, and reptiles, often catching prey by leaping great heights to snatch them in mid-air.
The Caracal is a solitary and territorial hunter. It uses its long back legs to make impressive jumps, capable of reaching up to three meters high. While the species is relatively widespread, it faces threats due to habitat loss and poaching. The Caracal is protected in several regions, and its population is monitored.
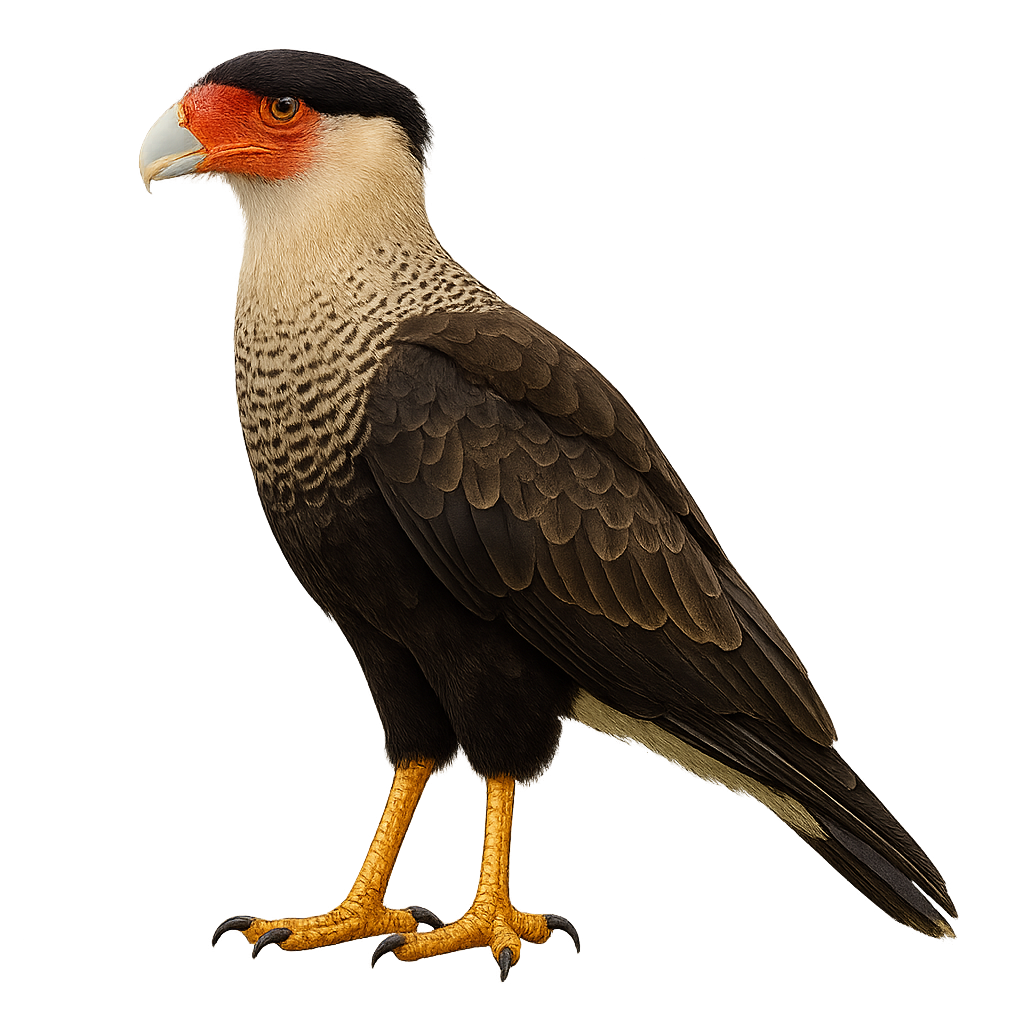
The Northern Caracara is an imposing bird of prey, easily recognizable by its distinctive black and white plumage, with a bright orange head and a powerful beak. This raptor, often mistaken for an eagle due to its behavior and size, is an opportunistic scavenger, feeding primarily on animal carcasses, but it can also hunt live prey, such as small mammals and reptiles.
The Northern Caracara primarily inhabits open areas such as savannas, grasslands, and roadside habitats, where it spends its time scouring the ground for food. It is well adapted to life in varied environments, notably in the southern United States, Mexico, Central America, and South America. Although its population is relatively stable, the species is sometimes threatened by habitat destruction and illegal hunting.
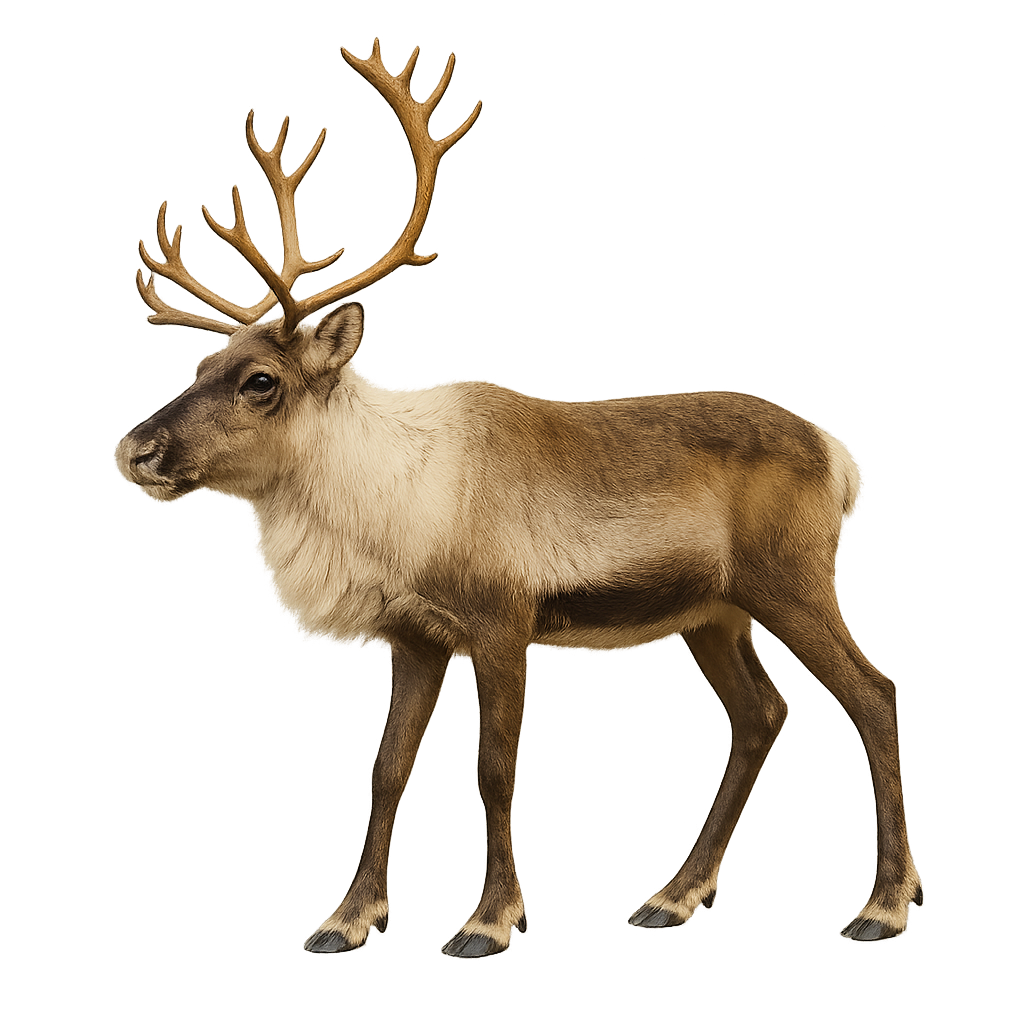
The Caribou, or Reindeer in Europe, is a large cervid adapted to cold and northern environments. It is easily recognizable by its distinctive antlers, which are present in both males and females, a unique trait among cervids. Its thick, woolly coat, typically brown with lighter shades on the belly and neck, allows it to survive in the harshest climates. Caribou populations are found primarily in arctic and subarctic regions, including Iceland, where they were introduced and have thrived in the mountainous and tundra landscapes.
The Caribou is a migratory species, undertaking long seasonal migrations to find food resources. It primarily feeds on lichens, grasses, and tundra plants, which it digs out from under the snow during the winter. The Caribou plays a crucial role in its ecosystem by affecting vegetation and serving as prey for large carnivores such as wolves. However, it is threatened by climate change and habitat loss.
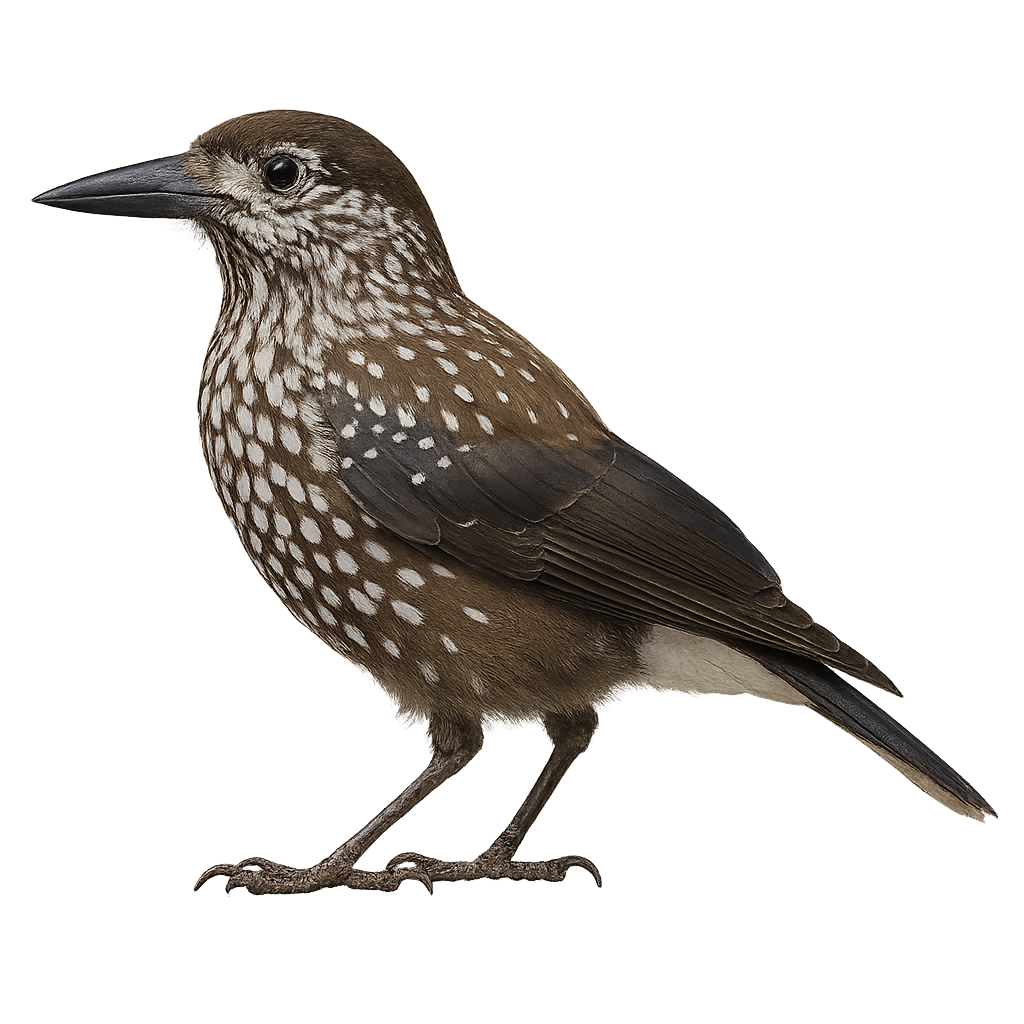
The Spotted Nutcracker is a medium-sized bird, easily recognizable by its spotted black and white plumage, which helps it blend perfectly into the coniferous forests where it lives. This passerine is primarily found in the mountainous regions of Europe and Asia, where it mainly feeds on pine seeds and other fruits, which it hides in tree crevices to consume later, a behavior that makes it an excellent food gatherer. The Spotted Nutcracker is also a migratory bird, although it may sometimes remain in colder areas during the winter.
This crow is known for its great intelligence and curious behavior, and it plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by dispersing tree seeds, thus promoting forest regeneration. While the population of this bird is generally stable, it may be threatened by the destruction of forest habitats, particularly in areas where coniferous forests are reduced by logging.
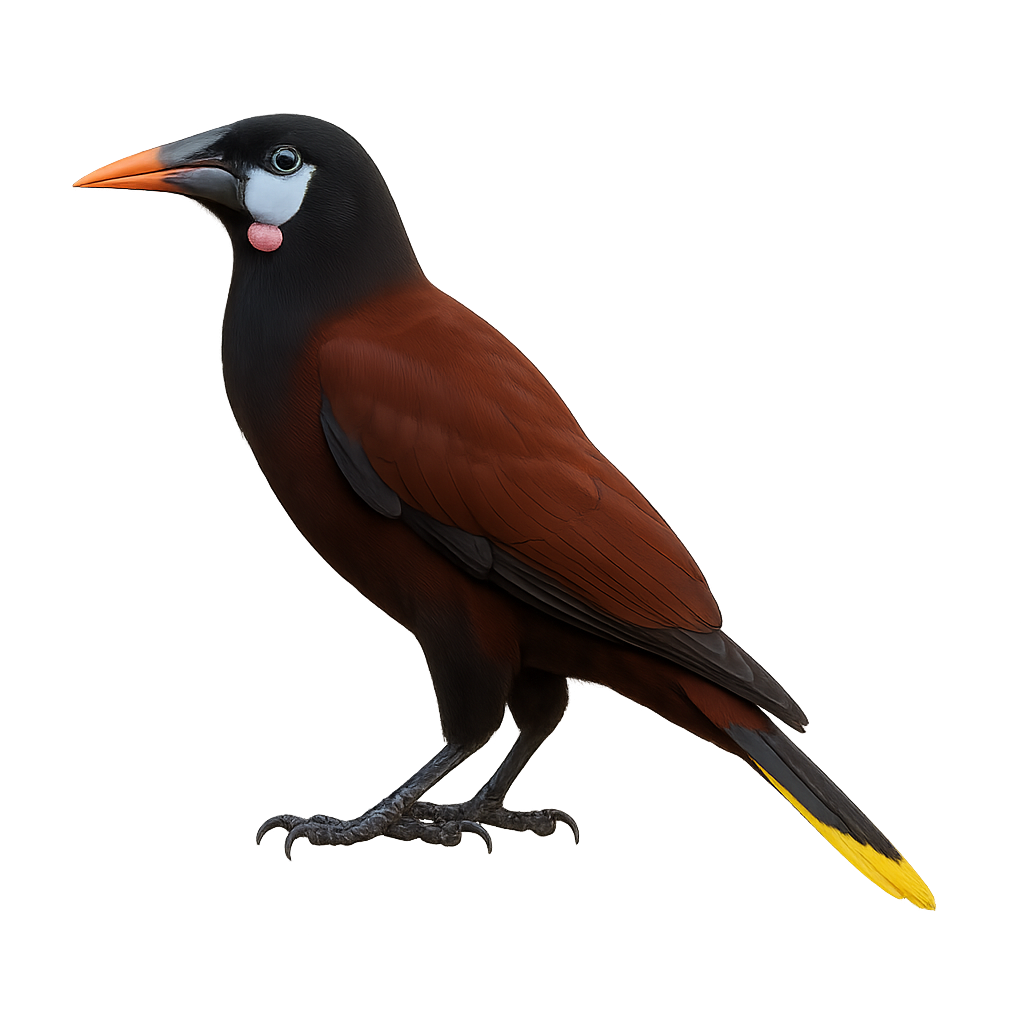
The Montezuma Oropendola is an exotic and colorful bird, easily recognizable by its vibrant plumage, which blends shades of black, yellow, and red. This large bird belongs to the Icteridae family and primarily inhabits the tropical forests and wooded areas of Mexico and Central America. It is especially famous for its long tail feathers, giving it a striking and elegant silhouette.
The Montezuma Oropendola is a social bird that lives in groups, often consisting of several individuals. It feeds primarily on fruits, seeds, and small insects, which it finds in trees and climbing plants. It is also known for its suspended nests, which it constructs with great skill in the trees. While its population remains generally stable, it may be threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.
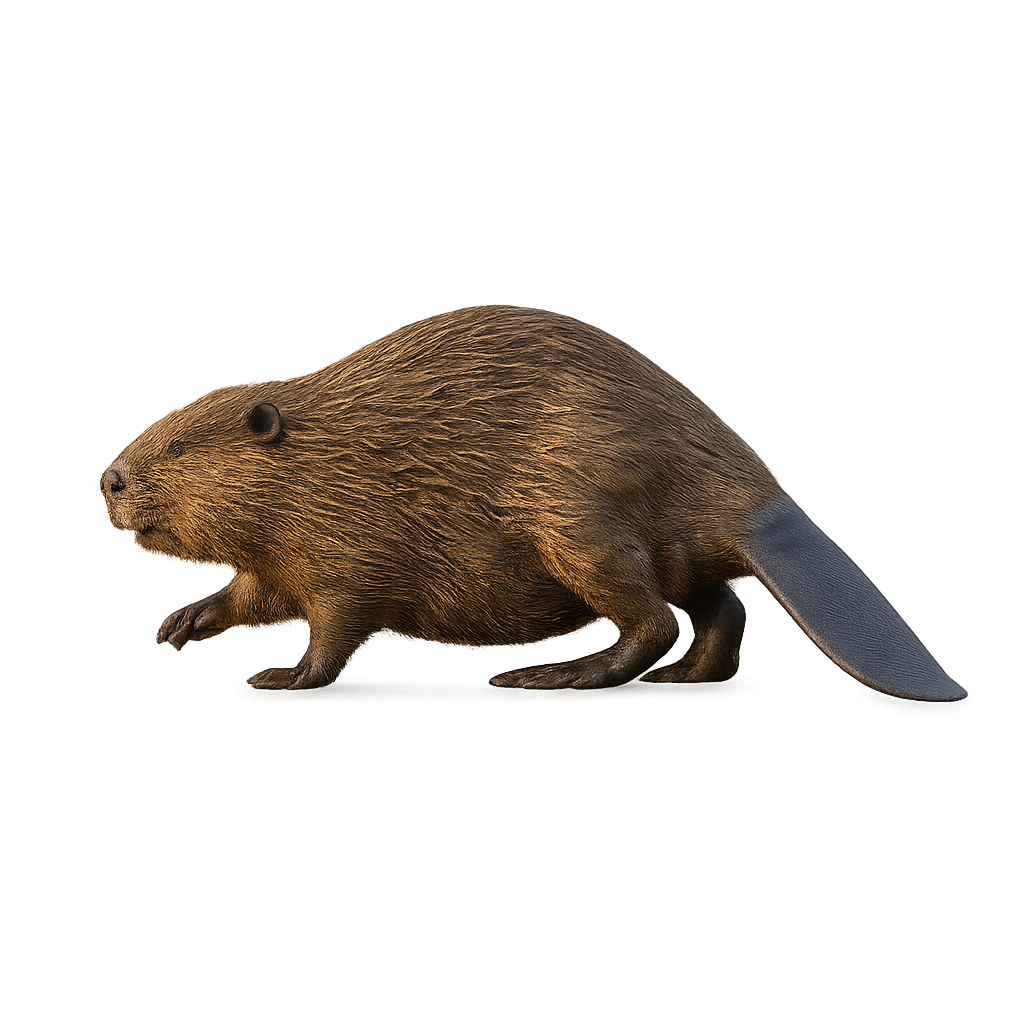
The American Beaver is a large, semi-aquatic rodent famous for its construction skills and its ability to modify its environment. It is easily recognizable by its wide head, large orange incisors, and its flat, scaly tail. The American Beaver primarily lives in rivers, lakes, and wetlands, where it builds dams and lodges using branches, tree trunks, and mud to create safe, stable habitats.
This rodent is an excellent swimmer and spends much of its life in the water, where it feeds mainly on bark, roots, and young tree shoots. The American Beaver plays a crucial role in its ecosystem by altering waterways, creating ponds and wetlands that are beneficial to many other species. However, it is sometimes threatened by habitat loss due to urbanization and water management.
The European Beaver is a large, semi-aquatic rodent renowned for its exceptional ability to alter its environment. This rodent is easily identifiable by its brown fur, large orange incisors, and flat, scaly tail. It primarily inhabits rivers, lakes, and wetlands, where it builds dams to create ponds and wetlands that serve as refuges. The European Beaver is an excellent swimmer, capable of staying underwater for several minutes to move or escape danger.
It feeds mainly on bark, roots, and young tree shoots. In addition to its ability to modify waterways, the European Beaver plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by promoting the regeneration of wetland areas, which benefits many other animal species. Although its population was historically threatened by hunting and habitat loss, conservation efforts have stabilized its numbers, and the species is now protected in many regions.
The Sunbittern is a medium-sized bird, about 43 cm long, known for its striking wing patterns that resemble eyespots. When threatened, it fans out its wings like a butterfly or stylized sun to startle predators. It has a long beak, slender neck, and thin legs adapted to walking along rivers and streams. Found in Central and South America, it inhabits shaded riverbanks and humid forests at moderate elevations. Solitary and elusive, it feeds on small fish, aquatic insects, and invertebrates. While not currently endangered, it is vulnerable to habitat loss and water pollution.
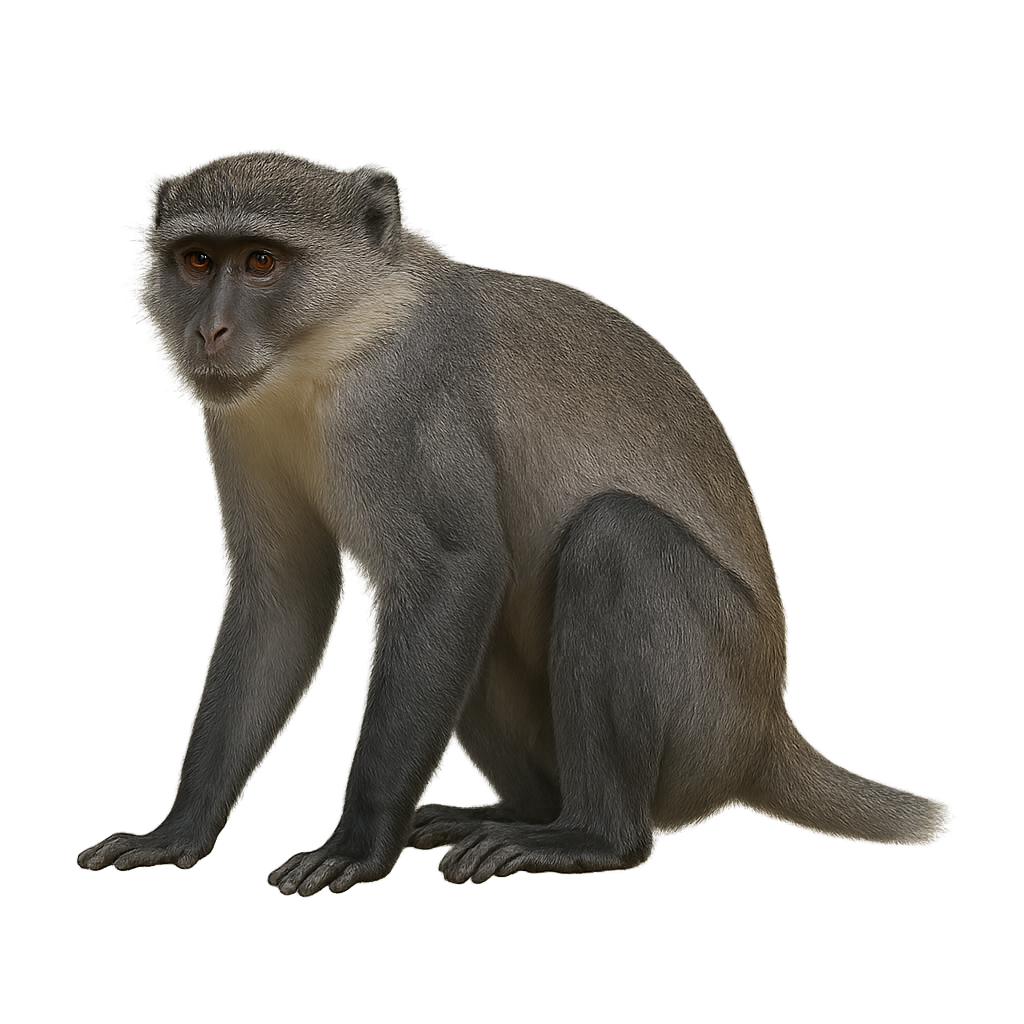
The Diademed Monkey is a primate of the Cercopithecidae family, native to the tropical forests of Central Africa, primarily in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Uganda, and Kenya. This monkey is recognizable by the crest of hair on the top of its head, forming a 'diadem,' from which it gets its name. The Diademed Monkey is a social animal living in groups and feeds primarily on fruits, leaves, and insects. It is also known for its complex vocalizations and marked social behaviors, communicating with other group members to establish relationships and organize movements.
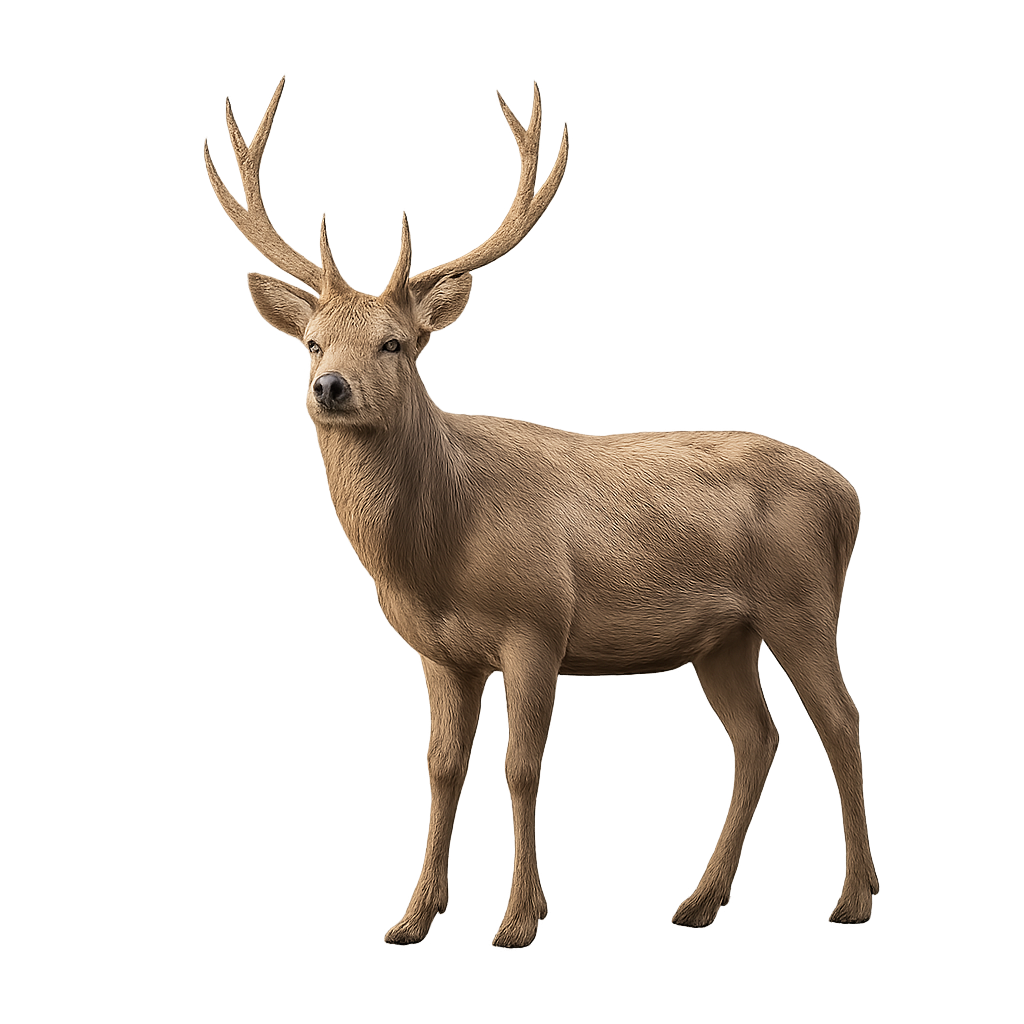
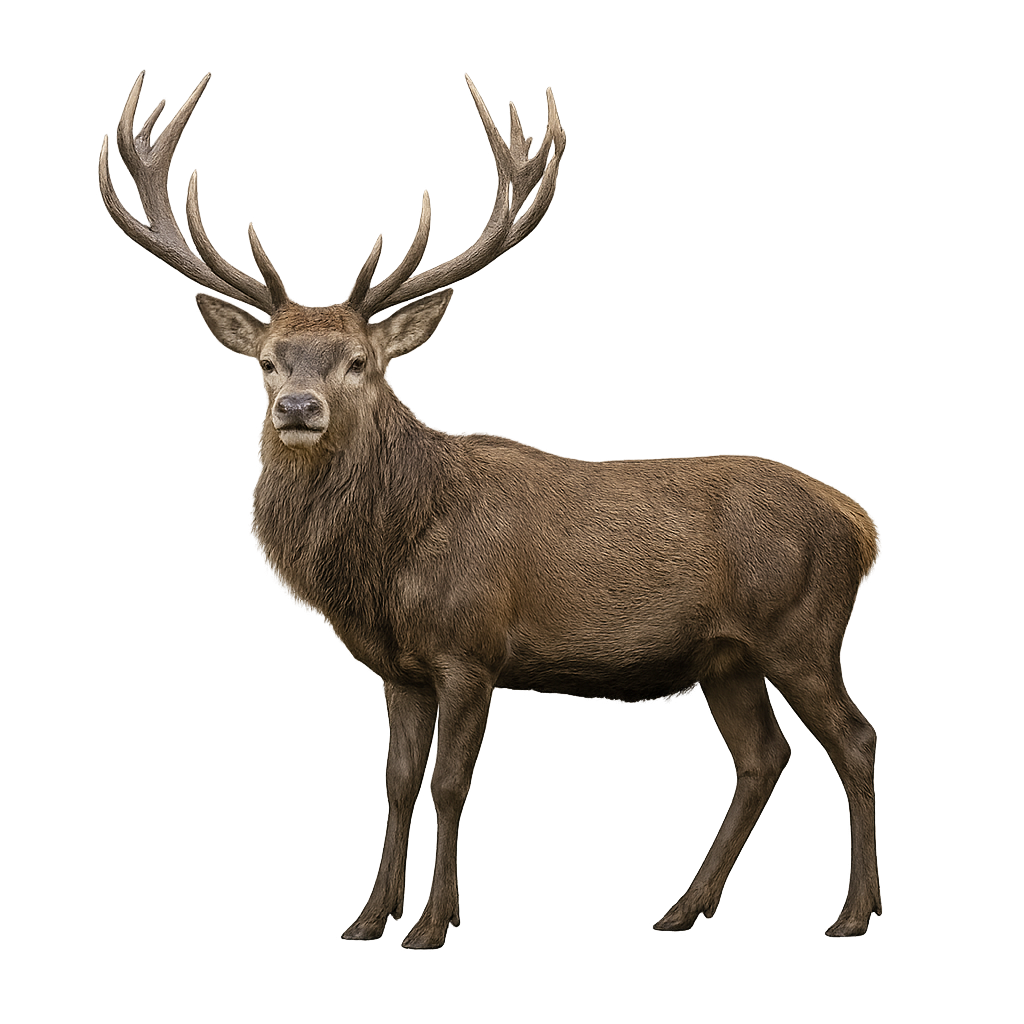
The Kashmir Stag, also known as the Hangul, is a majestic species primarily found in the mountains of the Himalayas and Kashmir. This deer is easily recognizable by its dense, woolly coat, which helps it withstand the cold temperatures of high altitudes. It has impressive antlers, which can grow to a considerable size in adult males. The females, on the other hand, are generally smaller and do not have antlers.
This deer inhabits high-altitude forests, alpine meadows, and mountainous regions covered in snow. It feeds primarily on herbaceous vegetation, foliage, and young shoots. The Kashmir Stag is a relatively shy and discreet animal, often living in small groups or family units. While its population remains relatively stable, it faces threats such as habitat loss due to deforestation and poaching, especially for its antlers.
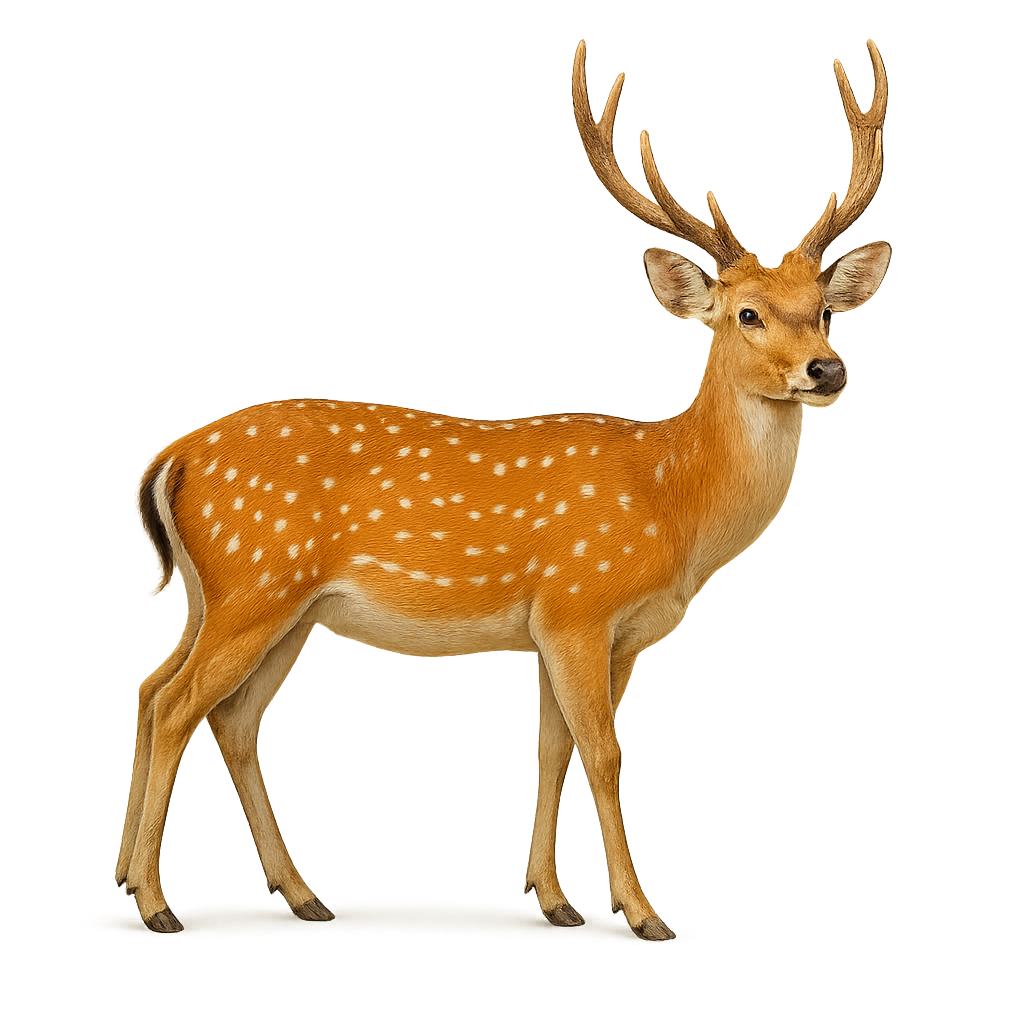
The Sika Deer is a medium-sized cervid, native to East Asia, that is distinguished by its spotted coat, especially visible in young individuals and females. Its coat ranges from light brown to reddish, often sprinkled with small white spots that help it blend into its forested environment. The Sika Deer has antlers that, although smaller than those of the Red Deer, are well-developed in adult males. It primarily inhabits deciduous and coniferous forests, as well as mountainous areas.
The Sika Deer is an herbivore, feeding mainly on herbaceous plants, young shoots, and leaves. It is a social animal, living in groups, especially during the breeding season. Outside of this period, Sika Deer may be more solitary or live in small family units. While its population remains stable in certain regions, the Sika Deer is sometimes considered an invasive species in other parts of the world, particularly in Europe, where it has been introduced and can compete with local species.
The Black-backed Jackal, also known as the silver-backed jackal, is a small canid native to Africa, particularly found in savannas and open grasslands. It is distinguished by its grayish coat with a black stripe running along its back, hence the name "black-backed". This coat helps it blend effectively into its environment. The Black-backed Jackal has a slender body and relatively long legs, allowing it to run at high speeds.
An opportunistic carnivore, it primarily feeds on small mammals, birds, insects, and carrion, but it can also eat fruits and plants. Although it is a solitary animal, the Black-backed Jackal can occasionally be seen in small groups, especially during the breeding season. While its status is not particularly threatened, it faces competition from other predators and the loss of its natural habitat.
The Striped Jackal is a small canid found primarily in Africa, inhabiting savannas, open forests, and mountainous regions. It is distinguished by the dark stripes along its flanks, which give it a unique appearance among other jackals. Its coat is typically brown-gray, with lighter markings on the belly and underside of the legs, helping it blend into its natural environment.
The Striped Jackal is an opportunistic carnivore, feeding on small mammals, insects, fruits, and sometimes carrion. While it is primarily solitary, it can occasionally be seen in small groups while foraging for food. A skilled hunter, it uses strategies to capture its prey. Like many canids, it faces threats such as habitat loss and competition with other predators, but its population remains relatively stable.
The Golden Jackal is a small canid found primarily in South Asia, the Middle East, and Southeastern Europe. It is easily recognizable by its golden fur, which ranges from pale yellow to golden brown, allowing it to blend into the landscapes of grasslands, open forests, and savannas. The Golden Jackal has a more slender body and relatively long legs compared to other jackals, enabling it to be an excellent runner.
Opportunistic by nature, the Golden Jackal feeds on a wide variety of prey, ranging from small mammals and birds to fruits and carrion. Although often solitary or in small family groups, the Golden Jackal can occasionally be seen in larger groups while foraging for food. It is also known for its varied vocalizations and skilled hunting behavior. While its population remains relatively stable, it faces threats such as habitat loss and human conflict.
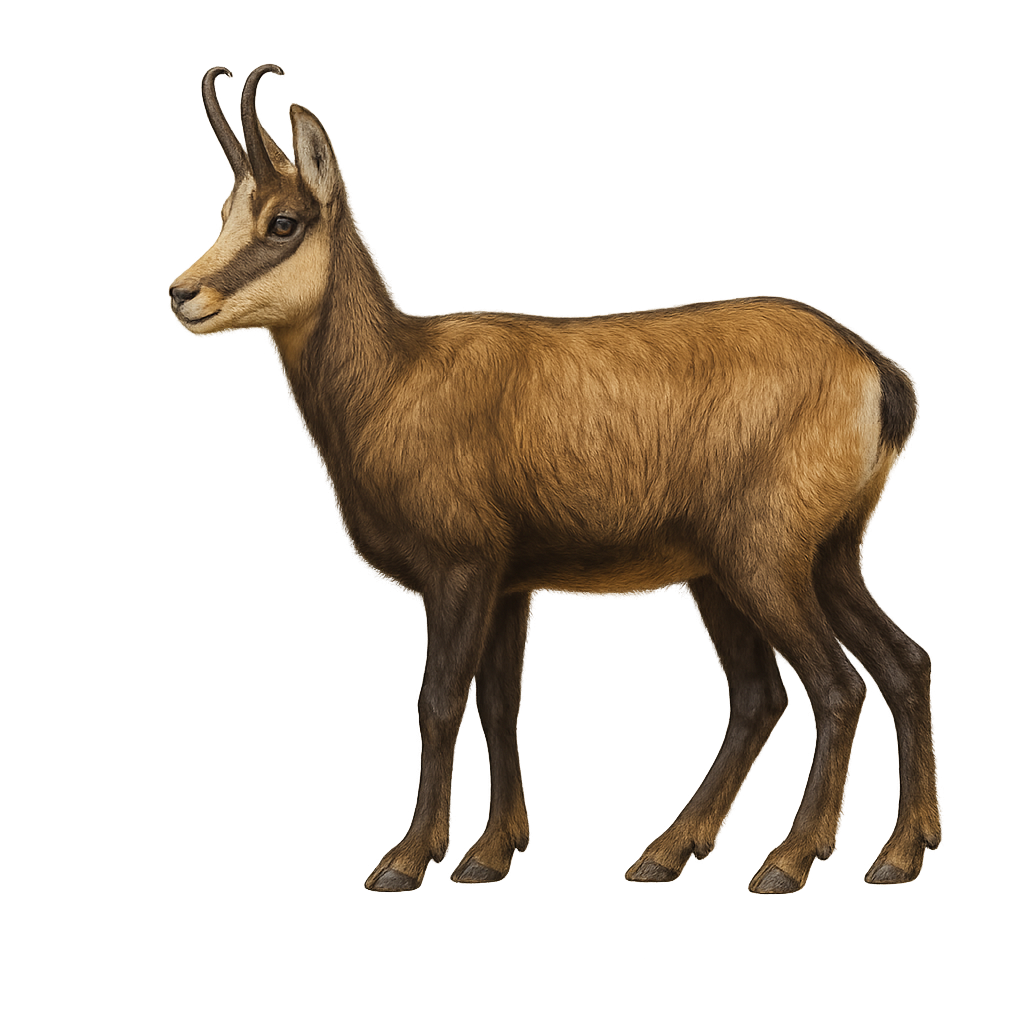
The Alpine Chamois is an elegant and agile ungulate, well adapted to the mountainous environments of the Alps, Pyrenees, and other mountain regions of Europe. It is distinguished by its reddish-brown coat in the summer, which becomes more gray and thicker in the winter, helping it endure the cold temperatures. The Alpine Chamois has small, curved horns, present in both males and females, but larger in adult males.
This ruminant primarily inhabits rocky slopes, mountain forests, and alpine meadows, where it feeds mainly on herbaceous vegetation, mosses, and lichens. The Alpine Chamois is an excellent climber, able to move with agility over steep and rocky terrain. It is usually solitary or lives in small family groups, but may also gather in larger herds during the winter. Although its population is stable in many areas, the Alpine Chamois remains vulnerable to hunting and human disturbances in its mountainous habitats.
The African Golden Cat is a rare and mysterious small feline, characterized by its silky golden coat and pointed ears adorned with tufts of black hair. This medium-sized cat primarily inhabits the forests and savannas of West Africa, where it preys mainly on birds, small mammals, and reptiles. Its golden coat, which gives it its name, is perfect for camouflaging in tall grasses and foliage.
The African Golden Cat is a discreet and solitary hunter, primarily active at dawn and dusk. Although it is rare and difficult to observe due to its nocturnal habits, it plays an important role in regulating prey populations. The species is threatened by habitat loss and poaching, although conservation efforts are in place to protect this elusive feline.
The African Wildcat is a small, discreet, and nocturnal feline, primarily found in desert regions, savannas, and open forests of North and Sub-Saharan Africa. It is often compared to the domestic cat but has a more uniform coat, typically sandy or gray-brown, with light markings on the head and paws. Its eyes are large, adapted for nocturnal vision, and its ears are pointed, enhancing its wild appearance.
This cat is a solitary hunter, feeding mainly on small mammals, birds, and insects. Although shyer than its domestic cousin, it plays an essential role in regulating prey populations in its habitat. It is also known as the ancestor of the domestic cat, which was domesticated from this species around 10,000 years ago. While the African Wildcat is still relatively widespread, it is threatened by habitat loss and human conflict.
The Scottish Wildcat is a rare and endemic subspecies of the European Wildcat, primarily found in the mountains and forests of Scotland. It is recognizable by its dense, thick coat, which ranges from gray-brown to brown with characteristic dark markings on the head, legs, and tail. Smaller and stockier than the domestic cat, the Scottish Wildcat has slightly rounded ears and a sharp gaze, allowing it to blend perfectly into its wooded and hilly environment.
This cat is a discreet and solitary hunter, primarily active at night, feeding on small mammals, birds, and occasionally insects. It is also an excellent climber and can often be seen in trees or rocky areas. The Scottish Wildcat is considered an endangered species due to habitat loss, hybridization with domestic cats, and poaching. Conservation programs are in place to protect this unique subspecies and preserve its habitats.
The European Wildcat is a small, nocturnal, and discreet feline, often considered the ancestor of the domestic cat. It has a thick coat, typically gray-brown with dark stripes, which allows it to blend into its forested environment. Its size and behavior make it an agile and efficient hunter, primarily active at dusk. The European Wildcat has pointed ears and a slender body, with relatively long legs that allow it to move easily in varied environments, such as deciduous forests and mountainous regions.
This solitary cat feeds mainly on small mammals, birds, and insects, hunting them stealthily. While its population remains stable in some regions, it faces threats, including habitat loss, hybridization with domestic cats, and poaching. Conservation efforts are in place to protect this species, which is considered an important part of the forest ecosystem.
The Greenshank is a large species of wader, distinguished by its long bill and slender legs. It has a gray-brown plumage marked with lighter spots and a slightly speckled head, which helps it blend into the muddy and marshy environments of wetlands and shorelines. This wader is especially known for its characteristic calls, a loud barking cry, which is how it gets its name. It primarily inhabits wetlands, estuaries, and shorelines where it feeds on small invertebrates, worms, and crustaceans found by probing in the mud.
The Greenshank is a migratory bird that travels long distances between its breeding grounds in Europe and its wintering sites in Africa and Asia. Although its population remains relatively stable, it faces threats from the loss of wetland habitats and pollution. The species is protected in some areas where it is found.
The Redshank is a medium-sized wader with distinctive plumage that changes with the seasons. During the breeding season, the male displays vibrant colors, with a black head and reddish chest, while the female has more subdued tones. Outside the breeding season, both sexes adopt a more muted plumage, often gray-brown with shades of white and black. The Redshank is primarily found in wetlands, estuaries, and lakeshores, where it feeds on small invertebrates, aquatic insects, and occasionally worms and crustaceans.
This migratory bird is known for its long-distance migration, between its breeding grounds in northern Eurasia and its wintering areas in southern Asia and North Africa. While its population remains generally stable, the Redshank is vulnerable to threats such as habitat destruction, pollution, and hunting. The species is protected in some areas where it is found.
The Green Sandpiper is a medium-sized wader, easily recognizable by its green-brown plumage with mottled patterns and its white tail, which gives it its name. During the breeding season, males display more colorful plumage, with iridescent green tones and white markings on the wings and tail. Outside of the breeding season, both sexes adopt a more uniform plumage, often olive-brown with shades of white and gray.
The Green Sandpiper is primarily found in wetlands, marshes, estuaries, and lake shores, where it feeds on small aquatic invertebrates, insects, and crustaceans that it uncovers while probing in the mud. While this species is migratory, it does not travel as long distances as some other waders, primarily moving between Central Europe and its wintering sites in North Africa. The Green Sandpiper remains generally stable, but it faces threats from the loss of its wetland habitats and pollution.
The Common Redshank is a medium-sized wader, easily recognizable by its long red legs and straight bill. Its plumage is typically gray-brown with shades of white on the belly and dark markings on the back and wings. During the breeding season, it displays brighter colors, especially on the head and chest, which become duller outside of this period. This wader is often seen in wetlands, marshes, estuaries, and lake shores, where it feeds mainly on small invertebrates, insects, and worms found by probing in the mud.
The Common Redshank is a migratory bird that travels between its breeding grounds in Northern Europe and its wintering sites in Africa and Asia. While its population remains generally stable, the Common Redshank faces threats from habitat loss and pollution. It is sometimes considered a vulnerable species in certain regions.
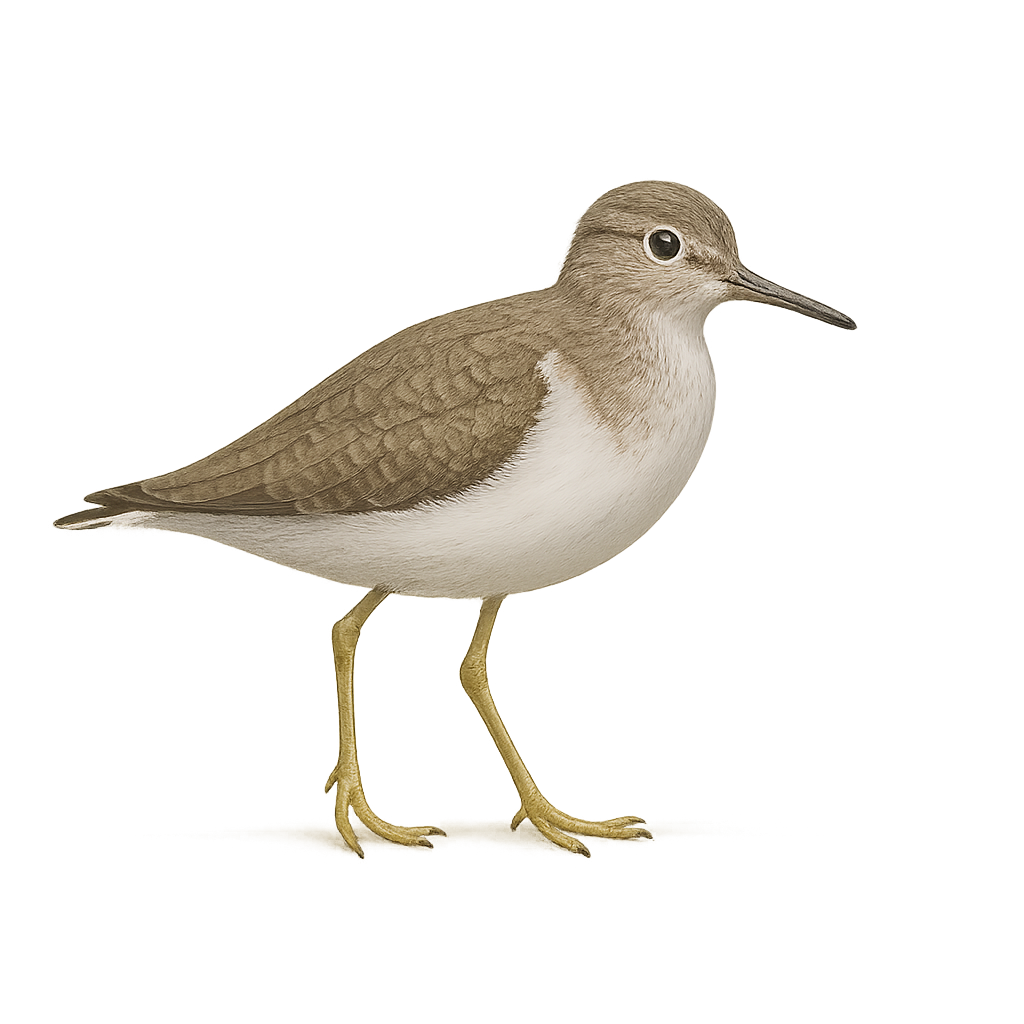
The Common Sandpiper is a small, agile, and active wader, easily recognizable by its light brown plumage, speckled with darker spots, and its long, slender legs. It is also distinguished by its short, straight bill and its energetic and nervous behavior. It is commonly found along riverbanks, estuaries, marshes, and lakes, where it hunts by running along the shores, capturing small insects, worms, and crustaceans found in the mud and shallow water.
This migratory bird typically breeds in temperate regions of Europe and Asia and migrates to North Africa for the winter. While the population of the Common Sandpiper remains stable in many regions, the species is threatened by the loss of wetland habitats and the effects of climate change, which alters aquatic ecosystems. The species is protected in some areas where it is found.
The Marsh Sandpiper is a medium-sized wader, easily identifiable by its plumage marked with gray-green and white, with darker patterns on the wings and head. During the breeding season, it displays brighter colors, with shades of vibrant green and distinct markings. Outside the breeding season, its plumage is more subdued, generally gray-brown and more muted. This wader is primarily observed in shallow wetlands such as marshes, lagoons, and estuaries, where it feeds on aquatic invertebrates, small fish, and occasionally worms.
The Marsh Sandpiper is a migratory bird that travels relatively short distances between its breeding grounds in Eastern Europe and its wintering sites in North Africa and Asia. While its population remains stable in some regions, it is threatened by the loss of its wetland habitats and water pollution. The species benefits from protections in areas where it is found, but it remains vulnerable in certain regions due to urbanization and intensive agriculture.
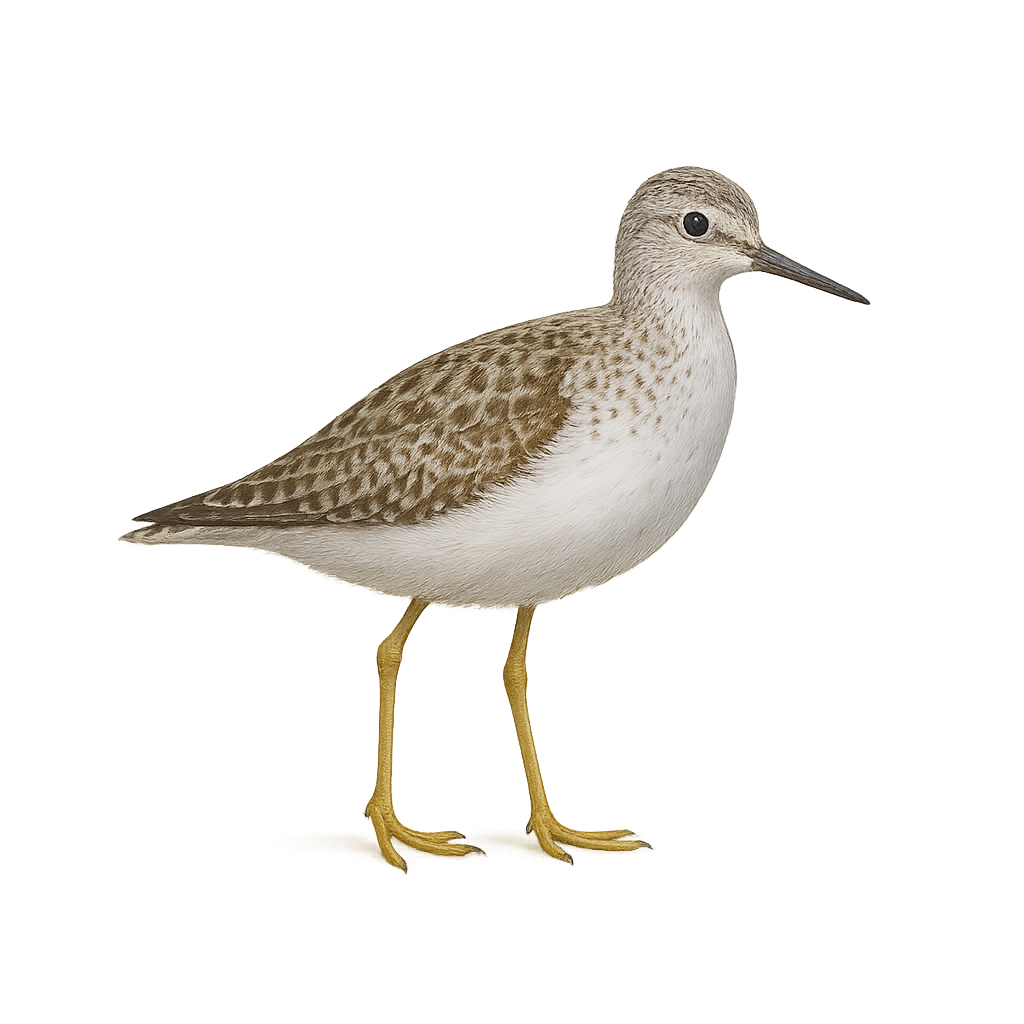
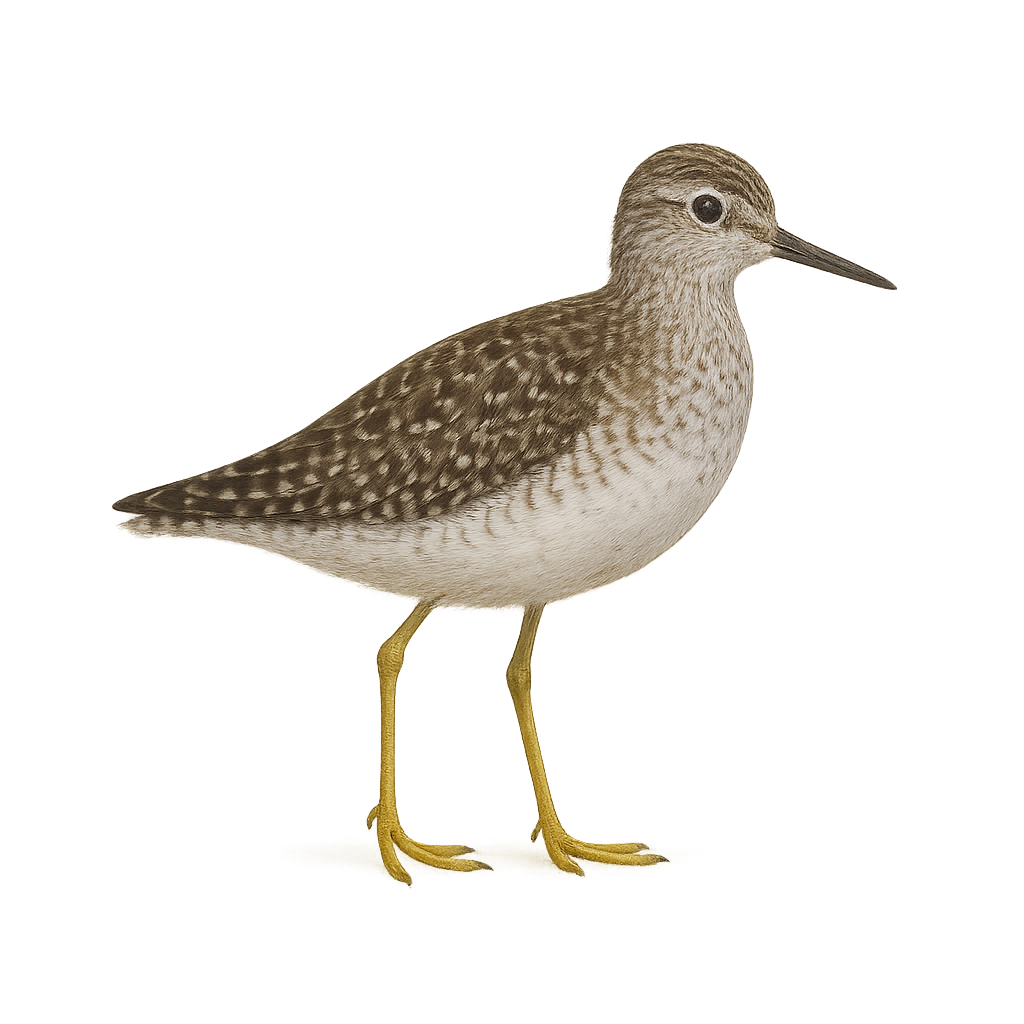
The Wood Sandpiper is a medium-sized wader, recognizable by its elegant plumage that ranges from gray-green to white, with dark markings on the wings and sometimes a marbled head. This wader is primarily found in wet forests and marshy areas, where it feeds on small invertebrates, worms, and occasionally small fish, which it catches by probing in the mud and shallow water.
During the breeding season, the male displays brighter colors, notably a darker head plumage and iridescent green shades on its back. Outside the breeding season, the Wood Sandpiper has a more subdued and uniform plumage, often gray-brown. As a migratory bird, it travels between its breeding grounds in Northern Europe and its wintering sites in Africa and Asia. Although its population remains relatively stable, the Wood Sandpiper faces threats from the loss of wetland habitats and pollution.
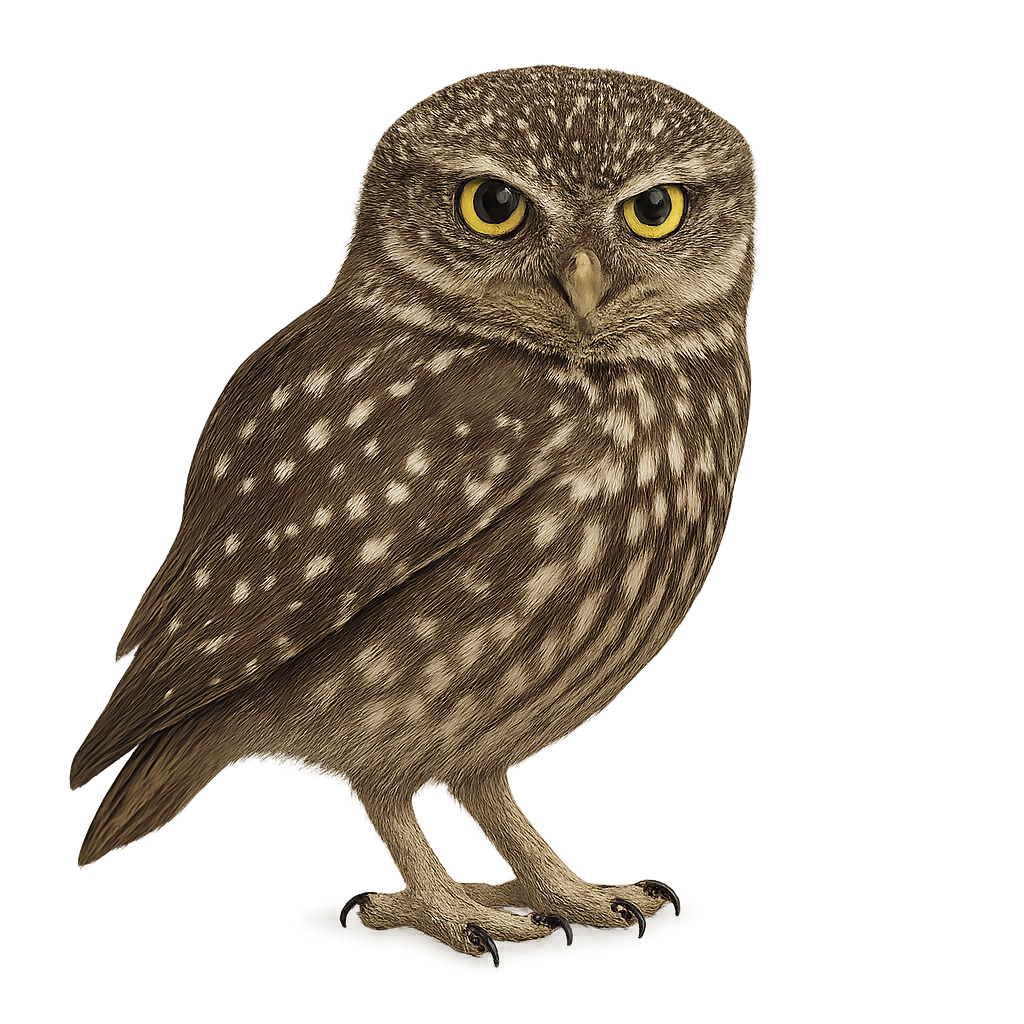
The Little Owl is a small, distinctive owl, easily recognizable by its large yellow eyes and its generally gray-brown plumage marked with white spots. It has a stocky body and a round head, without the ear tufts typical of other owls. The Little Owl is often found in open areas such as fields, orchards, and agricultural sites, where it frequently perches on stones, posts, or low trees.
This nocturnal predator feeds mainly on small mammals, insects, and reptiles, which it hunts primarily at night. Although its population remains relatively stable in many parts of Europe, the Little Owl is threatened by habitat loss and changes in agricultural practices. The species benefits from some protections and is often associated with conservation efforts aimed at preserving its open habitats.
The Eurasian Pygmy Owl is the smallest owl in Europe, easily recognized by its tiny size and large, piercing yellow eyes. It has gray-brown plumage, with white markings on the chest and abdomen, and dark spots on its head. It has a stocky body and a small, round head, without the ear tufts found in other owls. This nocturnal predator primarily inhabits coniferous forests, where it hides in tree cavities or old nests to rest during the day.
The Eurasian Pygmy Owl primarily hunts small birds, insects, and rodents, which it captures at dawn or dusk. While its population remains relatively stable in some regions of Northern and Eastern Europe, it is threatened by deforestation and disruption of its habitats. This owl is protected by conservation measures aimed at preserving its coniferous forests and nesting sites.
The Mountain Goat is a robust mammal well adapted to life in the rugged mountains and rocky terrain of North America. This herbivore is easily recognizable by its white or cream-colored coat, which helps it blend into the snow and rocks. Its legs are specially adapted for climbing, with wide and rigid hooves that provide excellent traction on steep slopes.
The Mountain Goat feeds primarily on herbaceous plants, lichens, and moss, which it finds in rocky slopes and alpine meadows. While it is often perceived as a hardy species, it faces threats from habitat loss, poaching, and diseases transmitted by domestic animals. The population of Mountain Goats is closely monitored, and efforts are underway to protect this iconic species of the mountains.
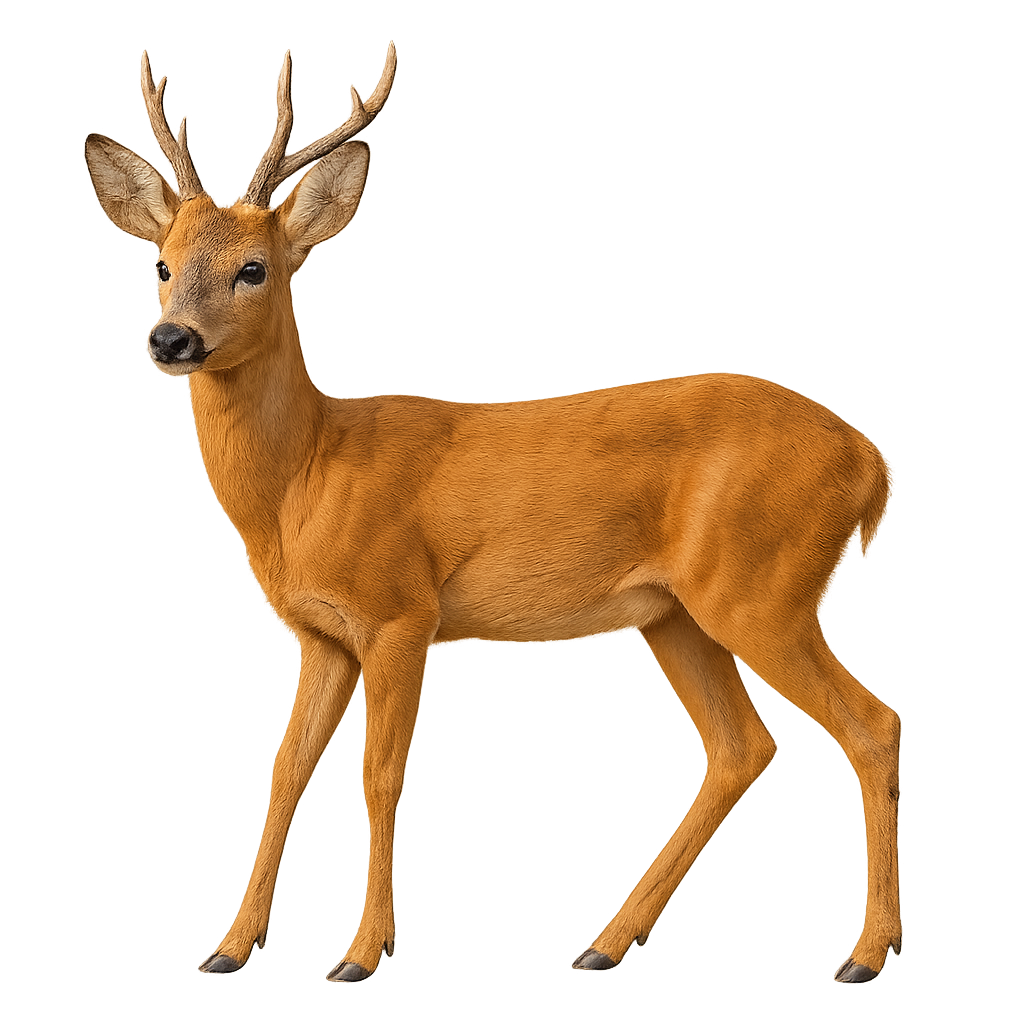
The Roe Deer is an elegant, small cervid, recognizable by its slender figure and long legs. It has a coat that changes with the seasons: reddish-brown in summer, becoming more gray-brown in winter. Males carry antlers, which grow back each year and are generally smaller than those of other cervids. The Roe Deer primarily lives in forests, wooded areas, and heathlands, where it hides during the day and becomes more active at dusk and night, particularly for feeding.
Its diet is varied, consisting of leaves, fruits, young shoots, and bark. While it is generally discreet and solitary, it can sometimes be seen in small groups, especially in winter. The Roe Deer is an agile and fast animal, capable of covering large distances in a short time when threatened. While its population remains relatively stable, it faces threats from hunting and habitat loss.
The Siberian Roe Deer, also known as the Asian Roe Deer, is a slightly larger species of cervid compared to the European Roe Deer. It is easily recognizable by its darker coat, ranging from brown to gray, with white markings around the mouth and belly. Males carry antlers that, while smaller than those of other large cervids, are still distinct and visible. This species primarily inhabits coniferous forests and wooded areas of Siberia, Central Asia, and Mongolia, where it hides during the day and becomes more active at dusk and night.
The Siberian Roe Deer is an herbivore, primarily feeding on vegetation, including young shoots, leaves, fruits, and bark. It is known for its great agility and speed, allowing it to move easily through the rugged terrain of its habitat. While its population remains stable in some regions, it is threatened by deforestation, hunting, and habitat fragmentation.
The African Wild Dog is an exceptional social predator, easily recognized by its unique spotted coat, which ranges in color from yellow-orange to black, with irregular markings. It has large, rounded ears and an expressive face. This carnivore primarily lives in organized packs, which allow it to effectively hunt large mammals such as gazelles and impalas. Their hunting strategy is based on cooperation, speed, and endurance, with long and energetic chases.
The African Wild Dog is also known for its social behavior, with pack members maintaining strong bonds through vocalizations, play, and grooming rituals. Unfortunately, this species is endangered due to habitat loss, illegal hunting, and conflicts with humans. It is a protected species, and efforts are underway to preserve remaining populations in wildlife reserves.
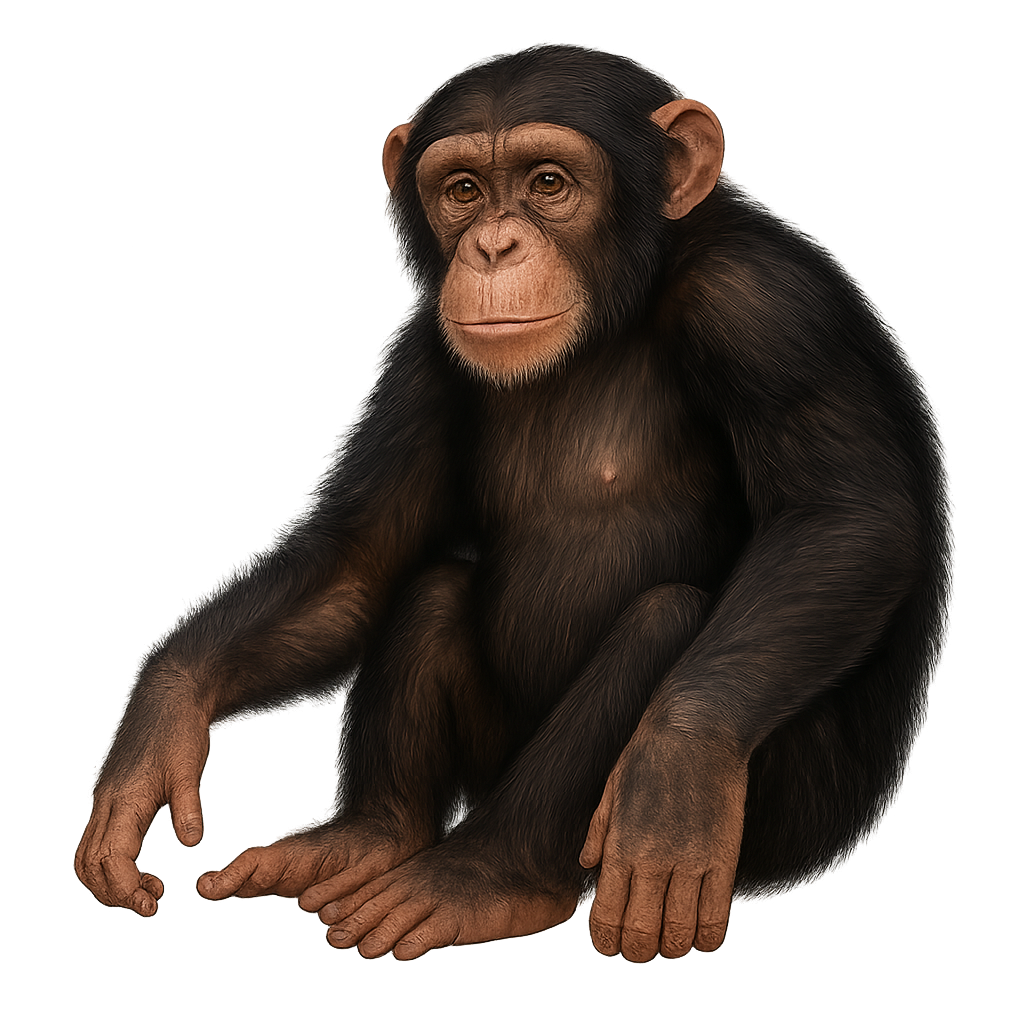

The Chimpanzee is one of humans' closest relatives, sharing about 98% of its DNA with humans. This large primate is easily recognizable by its expressive face, dark or brown skin, and sharp eyes. It has a powerful body, although it is smaller and less robust than other large primates like the gorilla. The Chimpanzee primarily inhabits tropical forests and savannas in West and Central Africa, where it forms complex social groups, called communities, which can include several dozen individuals.
An omnivore, the Chimpanzee feeds on a wide range of foods, including fruits, leaves, insects, and sometimes meat. It is also known for its use of tools, such as sticks to extract termites or stones to crack nuts. This primate has exceptional intelligence, capable of solving complex problems, communicating in sophisticated ways, and adopting cultural behaviors. However, it is threatened by deforestation, poaching, and habitat loss, leading to a decline in its wild populations. The chimpanzee is classified as an endangered species.
The Long-tailed chinchilla is a small rodent native to the mountains of South America, particularly the Andes. It is known for its extremely soft and dense fur, which helps protect it from the cold in its natural high-altitude habitat. Although its fur is an asset for survival, it is also the primary reason for the animal's hunting, although it is now protected. The Long-tailed chinchilla is a nocturnal and climbing animal, feeding primarily on plants, seeds, and fruits. It is active at night and spends the day hidden in crevices or burrows.
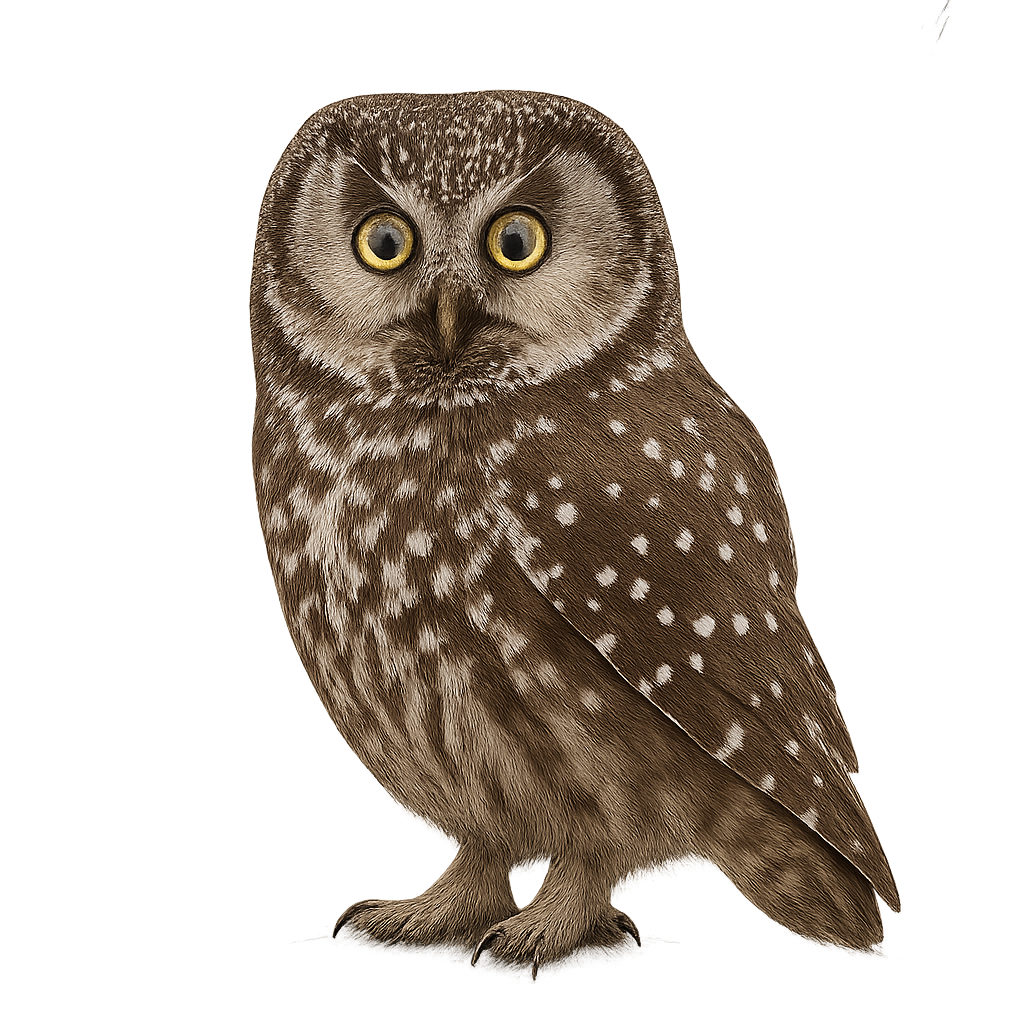
Tengmalm's Owl is a small nocturnal raptor, easily recognized by its small size and large, piercing yellow eyes. It has gray-brown plumage with characteristic white markings on the head, wings, and back. Its ears are very inconspicuous, and its face is surrounded by a pale facial disc. This owl primarily inhabits coniferous forests, dense wooded areas, and mountains, where it hides in tree cavities or abandoned nests of other birds.
Tengmalm's Owl mainly hunts small mammals, birds, and insects, which it catches at night by flying silently through the forests. It is particularly active during the breeding season, when it emits characteristic calls to attract its mate. Although it is relatively discreet and often difficult to observe, Tengmalm's Owl is protected in some areas, though its population is threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.
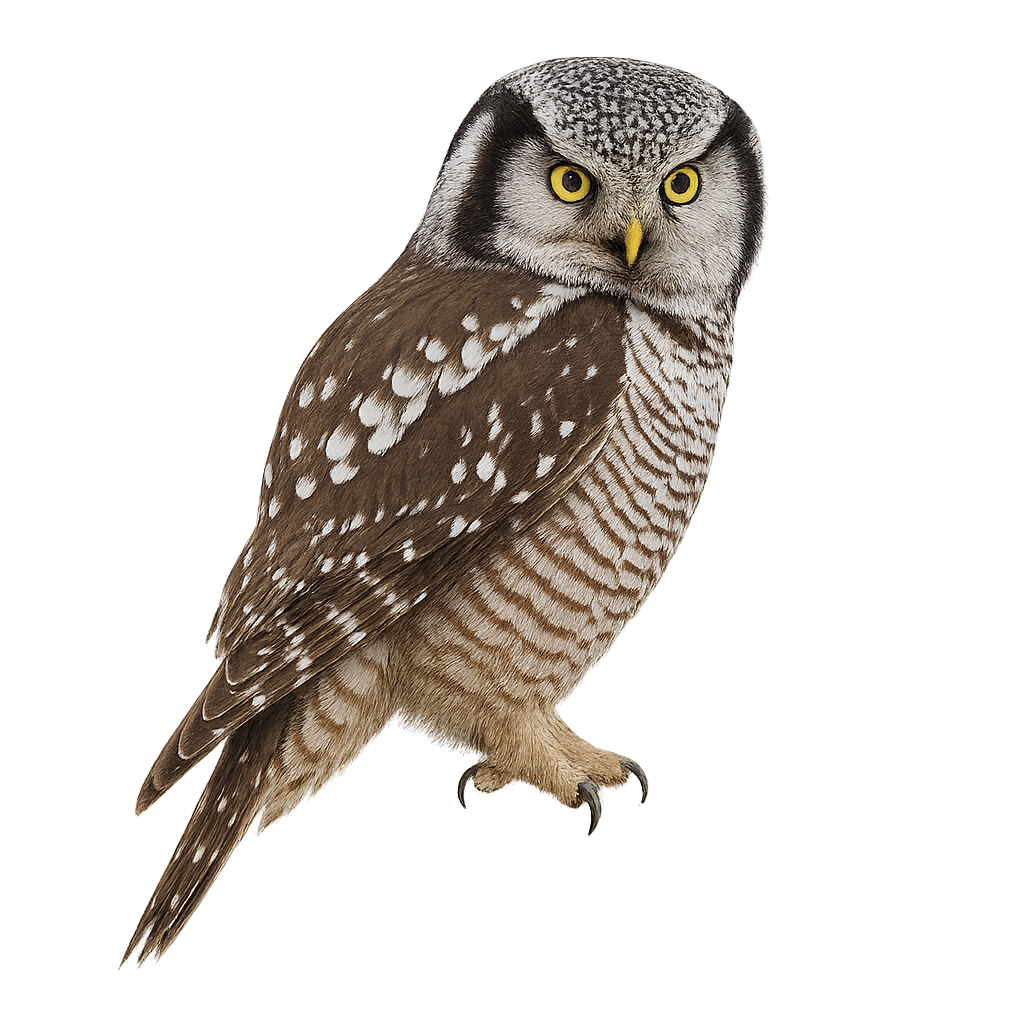
The Northern Hawk Owl is a unique nocturnal raptor, easily recognized by its large yellow eyes and its plumage marked with white and gray-brown patterns. It has a slender build with a round head, small size, and broad wings adapted for silent flight. It is primarily found in coniferous forests of northern regions, particularly in wooded areas of North America, Northern Europe, and Russia.
This raptor primarily hunts small mammals, birds, and insects, which it catches with its silent flight skills. The Northern Hawk Owl is also known for its ability to hunt during the day if necessary, especially during the breeding season. It is a relatively discreet bird, often feeding near open areas where it can spot its prey. While its population remains stable in some regions, it is threatened by deforestation and the loss of its natural habitat. It is protected in many areas to preserve its coniferous forests.
The Tawny Owl is one of the most common owls in Europe, easily recognized by its round face forming a facial disc and its large, piercing black eyes. Its plumage is typically brown, with irregular white spots on the belly and back. It has a stocky body, broad wings, and silent flight, which is suited to its nocturnal hunting. This nocturnal raptor primarily inhabits broadleaf and mixed forests, as well as lowland wooded areas.
The Tawny Owl primarily hunts small mammals like rodents, as well as birds, insects, and worms. It uses its ability to fly silently to capture its prey, often in open areas like clearings, forest edges, or fields. It is also known for its characteristic calls, a deep, melodious "hoo-hoo." While its population remains stable in many parts of Europe, the Tawny Owl can be affected by habitat loss, light pollution, and human disturbances.
The Great Grey Owl is a large nocturnal raptor, easily recognizable by its broad facial disc and piercing yellow eyes. Its plumage is primarily gray and brown, with lighter markings on the belly and wings. It has a massive build, a round head, and long wings that allow it to fly silently. This raptor primarily inhabits boreal forests and northern regions of Europe, Asia, and North America.
The Great Grey Owl primarily hunts small mammals, such as hares, rodents, and birds. It has a remarkable ability to locate its prey with its keen hearing and silent flight. It is a solitary owl, preferring dense forests where it can hide during the day. While its population remains generally stable, it is threatened by deforestation, habitat loss, and human disturbances. It is protected in many areas to ensure the preservation of its forest habitats.
The Barred Owl is a large nocturnal raptor, easily identifiable by its circular face forming a facial disc and its large yellow eyes. Its plumage is primarily gray-brown, marked with dark streaks on the head, back, and wings, from which it gets its name. This owl has a robust, stocky body, with broad wings and silent flight, perfectly suited to its nocturnal hunting in forests.
It primarily inhabits mixed and deciduous forests, especially in regions of North America. The Barred Owl hunts small mammals like rodents, birds, and occasionally insects, which it captures using its ability to fly silently. It is a solitary predator, hiding during the day in tree cavities or abandoned nests of other animals. While its population remains stable, the Barred Owl is vulnerable to disturbances in its natural habitat, such as deforestation and urbanization. It is protected in many regions to preserve its forest habitats.
The White Stork is a large bird easily recognized by its slender silhouette, bright white plumage, and long red legs. It has a long pointed beak, which it primarily uses to capture prey in wetlands, meadows, and fields. This migratory bird travels thousands of kilometers each year, migrating from Eastern and Central Europe to Africa for the winter.
The White Stork primarily feeds on small mammals, amphibians, insects, and small birds, which it captures with its great ability to walk and forage through grass or mud. While it is a solitary bird during breeding, it gathers in large colonies during migrations. Although its population remains stable in many parts of Europe, it faces threats from habitat loss, hunting, and human disturbances. Conservation efforts are underway to protect this iconic species.
The Black Stork is a large bird with dark, glossy plumage, characterized by its slender silhouette and long red legs and beak. Its plumage is primarily black, with a slight greenish tint and a metallic sheen on the wings and back. This migratory raptor is distinguished from its cousin, the White Stork, by its more discreet behavior and preference for wilder habitats. It primarily inhabits dense forests, wetlands, and mountainous areas of Eastern and Southeastern Europe and Asia.
The Black Stork primarily feeds on fish, amphibians, and small mammals, which it catches with its long beak while moving silently near rivers and lakes. Unlike the White Stork, it prefers isolated habitats, avoiding human areas. Its population has long been in decline due to deforestation, illegal hunting, and disturbance of its breeding habitats. However, conservation efforts have helped stabilize its populations in some regions.
The White-throated Dipper is a small aquatic bird, easily recognized by its dark plumage, compact body, and characteristic posture, often seen bobbing on rocks at the edge of streams. It has brownish plumage on its back and a white chest, with a short, powerful beak. This small bird is perfectly adapted to aquatic life, thanks to its webbed feet that allow it to swim and dive underwater in search of food.
The White-throated Dipper primarily feeds on aquatic insects, larvae, and small fish, which it captures by diving into rivers and streams. It is capable of swimming underwater and moving along the riverbed to search for prey. Although this bird is generally solitary, it can be observed in clear river or stream habitats, primarily in Europe and Asia. While it is generally not threatened, it can be impacted by water pollution and the disruption of its natural habitats.
The Short-toed Snake Eagle is a large diurnal raptor, easily recognized by its white and light gray plumage, powerful beak, and large, wide, rounded wings. It is primarily found in open areas, steppes, light forests, and hills across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. This raptor is distinguished by its unique hunting habits: it feeds almost exclusively on snakes, which it spots using its keen eyesight.
The Short-toed Snake Eagle mainly preys on snakes, including vipers and grass snakes, which it captures by attacking them in flight or grabbing them on the ground. Once it has captured its prey, it kills it with a powerful beak strike before devouring it. Due to its specialized diet, it is often seen in habitats where snake populations are abundant. Although its population remains relatively stable, it is threatened by habitat loss, human disturbance, and illegal hunting in certain regions.
The European Pond Turtle is a medium-sized freshwater turtle, measuring between 12 and 20 cm in length. Its carapace is oval, slightly domed, dark brown to blackish, with yellow spots. The plastron is yellow with dark spots. The feet are webbed, adapted for swimming. This species inhabits stagnant or slow-flowing waters, such as ponds, marshes, and slow rivers, with dense aquatic vegetation. It is omnivorous, feeding on small aquatic invertebrates, fish, amphibians, and plant matter. Reproduction occurs in spring, with the female laying 8 to 10 eggs in loose, sunny soil. Incubation lasts about 80 to 110 days, with hatchlings emerging in late summer or the following spring. Listed as Near Threatened by the IUCN, the European Pond Turtle is protected in many European countries.
The Coati is a mammal belonging to the raccoon family, easily recognized by its long ringed tail and elongated snout shaped like a trunk. Its fur is typically light brown to reddish-brown, with darker markings on the face and back. This small carnivore is known for its great agility, especially in trees where it moves with ease in search of food. It primarily inhabits tropical and subtropical forests in Central and South America.
The Coati is omnivorous and feeds on a wide variety of foods, including fruits, insects, small vertebrates, and eggs. It is often seen in family groups, especially females, while adult males tend to live alone. Although the Coati is a relatively adaptable animal, it is threatened by deforestation, hunting, and habitat loss. It plays an important role in seed dispersal and regulating populations of insects and small animals.
The White-nosed Coati is a mammal from the raccoon family, easily recognized by its distinctive white snout that contrasts with its reddish-brown fur. It has a long, ringed tail that it uses to maintain balance while moving through trees. This small carnivore is primarily found in the tropical and subtropical forests of Central America, Mexico, and the southern Costa Rica, where it lives in social groups, often led by a dominant female.
Omnivorous, the White-nosed Coati feeds on fruits, insects, small vertebrates, eggs, and even small mammals. Its social lifestyle is marked by complex interactions within its family groups. Although its population remains relatively stable in certain protected areas, it is still threatened by deforestation, hunting, and habitat disruption. Conservation efforts aim to protect the forest areas of this agile and adaptable animal.

Hummingbirds, members of the Trochilidae family, are small birds exceptionally known for their ability to hover in place due to their rapid and agile wing beats. These birds are characterized by their iridescent plumage, which varies from green and blue to red and purple, depending on the species. Their small size and high energy make them easily recognizable. Hummingbirds are primarily found in tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas, from Canada to the southern parts of South America.
They primarily feed on nectar that they gather from flowers, using their long slender beak and extendable tongue to reach the food. In addition to nectar, they also consume insects and spiders for protein. Due to their high metabolism, they must feed frequently throughout the day. Hummingbirds play a key role in pollinating flowering plants, thus contributing to the biodiversity of their habitats. While their population is generally stable, some species are threatened by habitat loss and climate change.
The Ruby-throated Hummingbird is one of the most iconic species of hummingbirds in North America, easily recognizable by the bright red color of its throat, which gives it its name. This small bird has bright metallic green plumage on its back and a white chest. It has a long, slender beak and an extendable tongue that it uses to extract nectar from flowers. In addition to nectar, it also consumes insects and spiders for protein.
The Ruby-throated Hummingbird is a migratory bird, covering long distances between its breeding range in North America and its wintering grounds in Central America. It is known for its rapid and agile flight, capable of hovering in place by beating its wings up to 80 times per second. While its population remains generally stable, it is threatened by habitat loss due to urbanization and climate change, which affect food resources and breeding conditions.
The Coppery-headed Emerald is a small hummingbird endemic to Costa Rica, measuring about 8 cm. The male is notable for his metallic coppery crown, bright green throat, and white underparts. The female is duller in color, with a bronzy head and pale throat. It inhabits humid mid-elevation forests, woodland edges, and flower-rich gardens. This hummingbird feeds on nectar from various flowers and catches small insects. It is threatened by deforestation, as its range is very restricted.
The Scintillant Hummingbird is one of the smallest birds in the world, measuring about 6.5 cm in length. The male has bronze-green upperparts, a bright reddish-orange throat, and a rufous tail with black bars. The female is more subdued, with a buffy throat spotted with green and rufous flanks. This species is endemic to Costa Rica and western Panama, inhabiting forest edges, coffee plantations, and gardens between 900 and 2500 meters elevation. It feeds primarily on nectar from small flowers, such as sages, and supplements its diet with small insects for protein. Although listed as Least Concern, deforestation could threaten its habitats.
The Guereza Colobus is a large primate belonging to the family Cercopithecidae, easily recognized by its distinctive black and white fur. It has a white mane around its face, white limbs, and a long, bushy tail that helps it stabilize in the trees. Its black body is contrasted by tufts of white fur along the sides and back, making it one of the most elegant primates of the forest. It primarily lives in the tropical and subtropical forests of East Africa, spending most of its time in the trees.
The Guereza Colobus is primarily herbivorous, feeding on leaves, fruits, seeds, and flowers. With its specialized stomach, it can digest tough, fibrous leaves that other animals cannot consume. It lives in social groups led by a dominant male and is generally very calm, moving gracefully and agilely through the forest canopy. Although its population remains stable in some protected areas, it faces threats due to deforestation and hunting, causing some populations to be classified as vulnerable.
The Colugo, also known as the flying lemur, is a small tree-dwelling mammal native to Southeast Asia. While not a true lemur, it is often called so due to its gliding abilities, which it performs using a thin membrane of skin that connects its limbs to its body. This gliding allows it to move efficiently from tree to tree in search of food, primarily consisting of leaves, fruits, and flowers. The Colugo is a nocturnal and rather discreet animal, using its dense fur and camouflage to blend into the forest environment.
The Ruff is a medium-sized wader bird, easily recognizable by its colorful plumage and relatively large size for a bird in its family. The male is particularly distinctive during the breeding season, with vibrant plumage ranging from brown and white to red and orange, and a large ruff that surrounds its head. Outside the breeding season, the male loses its bright colors and presents a more subdued plumage similar to the female.
This wader inhabits wetlands, marshes, and riverbanks across Europe and Asia. During the breeding season, males engage in spectacular courtship displays to attract females, including throat inflations and dances. The Ruff primarily feeds on small invertebrates and aquatic plants. It migrates south for the winter. While its population remains relatively stable, it is threatened by habitat loss due to the draining of wetlands and pollution.
The Macaroni Cormorant is a large aquatic bird, easily recognized by its slender silhouette, glossy black plumage, and the tuft of feathers on top of its head, which gives it its name. It has a long, pointed beak, perfectly adapted to catching fish, which it captures by diving underwater. Macaroni cormorants are often seen on rocky coastlines, islands, or along marine shores, where they form large breeding colonies.
This cormorant primarily feeds on fish, but also consumes crustaceans and mollusks. It is an exceptional diver, capable of diving to considerable depths to hunt its prey. Although its population remains relatively stable, it is threatened in certain regions by habitat disruption, water pollution, and competition with other fishing birds. It is mainly found in the Mediterranean and along certain Atlantic coasts of Europe.
The Lovely Cotinga is a tropical bird notable for its vibrant plumage. The male displays a brilliant turquoise blue with a deep purple throat and chest, while the female has more subdued grayish-brown plumage with scaly patterns. This species inhabits lowland humid forests and woodland edges in Central America, from southern Mexico to Costa Rica. Primarily frugivorous, it plays a crucial role in seed dispersal. Although globally listed as "Least Concern," deforestation poses a threat to its natural habitats.
The European Water Snake is a non-venomous species of snake, easily recognized by the distinct black or brown collar-like markings around its neck. Its body is typically olive or brown, with lighter patterns on the back and sides. This snake typically measures between 50 and 100 cm long, although it can sometimes reach up to 1.5 meters in rare cases.
The European Water Snake primarily inhabits wetland areas, such as lake shores, rivers, and marshes. It is highly agile and spends most of its time hunting fish, amphibians, and small reptiles, which it captures by diving or swimming. Though mainly terrestrial, it is also an excellent swimmer. The species is protected in some areas due to habitat loss. The European Water Snake plays an important role in regulating amphibian populations and controlling small aquatic animals.
The Common European Water Snake is a non-venomous snake species, easily recognized by the distinctive black patch that forms a collar around its neck. It is typically olive green to gray in color, with lighter patterns on the belly and small black spots on the back. It can grow up to 1.5 meters in length, although the average size is around 1 meter.
This snake primarily inhabits wetland areas, such as lake shores, marshes, and rivers, where it primarily hunts fish, amphibians, and small reptiles. It is a very good swimmer and spends much of its time in the water, using its diving skills to capture prey. While it is fairly common, it may be threatened by the destruction of its natural habitats, pollution, and illegal collection. The Common European Water Snake is protected in several regions of its range.
The Aesculapian Snake is a non-venomous, long and slender snake that can reach up to 2 meters in length. Its coloration ranges from olive green to brown, with smooth scales and a metallic sheen. It inhabits temperate forests, hedgerows, fallow lands, and rocky areas, often near human settlements. It is diurnal and arboreal, primarily feeding on small mammals, birds, lizards, and eggs. Reproduction occurs in spring, with 2 to 18 eggs laid and incubated for 6 to 10 weeks. Protected species in Europe, it is listed as Least Concern by the IUCN.
The Western Whip Snake is a slender snake that can reach up to 1.60 m in length. Its coloration is dark, black or dark green, speckled with yellow spots forming transverse bars at the front of the body and longitudinal lines towards the rear. The belly is light, yellow or greenish-white. Juveniles have a more uniform grayish to beige hue with distinctive head patterns. It inhabits dry and sunny environments, such as hedgerows, fallow lands, forest edges, and rocky areas, from plains up to 1900 m altitude. Diurnal and agile, it primarily feeds on small vertebrates: rodents, lizards, amphibians, and sometimes other snakes. Reproduction occurs in spring, with 5 to 15 eggs laid in June-July, incubated for 6 to 8 weeks. Protected species in Europe, it is vulnerable to habitat destruction and road traffic.
The Viperine snake is a non-venomous semi-aquatic snake, typically measuring between 50 and 90 cm, with a distinct head and round pupils. Its back features a dark zigzag pattern on a gray, brown, or greenish background, and its belly is yellow or reddish with black spots. It inhabits humid environments such as rivers, ponds, and lakes, where it primarily hunts fish, amphibians, and tadpoles. Reproduction occurs in spring, with 2 to 26 eggs laid in loose soil. This species is protected in Europe and is listed as Least Concern by the IUCN.
The Eurasian Curlew is a large wader, easily recognizable by its long, down-curved bill and gray-brown plumage with dark speckling. This wader has a slender silhouette, long legs, and broad wings. It measures about 50 to 60 cm in length, with a wingspan of 90 to 105 cm. During the breeding season, the Eurasian Curlew has brighter and more contrasting plumage, but it becomes more subdued during winter, with duller tones.
The Eurasian Curlew primarily feeds on earthworms, invertebrates, and small crustaceans, which it captures in marshy areas, wet meadows, or along riverbanks. It is mainly observed in coastal areas or estuaries, where it forages by probing the ground for food. Although it is migratory, the Eurasian Curlew breeds mainly in Europe and winters in North Africa and southern Europe. It is currently classified as vulnerable due to habitat loss and disturbances in its breeding areas.
The Whimbrel is a medium-sized wader, easily recognized by its long, finely curved bill and its brown-gray plumage with lighter speckling on the belly. It measures about 40 to 50 cm in length and has a wingspan of about 70 to 85 cm. Unlike the Eurasian Curlew, it is more subtle in its behavior and colors, making it a bird that is often less visible despite its size.
This wader primarily inhabits coastal areas, estuaries, and mudflats, where it primarily feeds on small invertebrates, worms, and mollusks, which it captures from sandy or muddy soils at low tide. During migration, the Whimbrel can travel long distances, moving from its breeding grounds in Northern Europe to the coasts of West Africa. While it is considered a species of concern in some areas, it is primarily threatened by habitat loss and human disturbance.

The Coyote is a medium-sized canine, very similar to the wolf but smaller and more agile. Its fur varies from gray to light brown, with a face often marked by black traits, a white chest and belly, and dark legs. The Coyote is easily recognizable by its pointed muzzle, relatively large ears, and bushy tail. It typically stands between 60 and 80 cm at the shoulder, with a total length of 75 to 90 cm for the body, excluding the tail.
This canine is an opportunistic feeder, primarily hunting small mammals such as rodents, rabbits, and sometimes birds, but it can also eat fruits and carrion. Highly adaptable, the Coyote inhabits a wide variety of environments, ranging from prairies and deserts to urban areas, and it is particularly active at dusk and during the night. Unlike other predators, the Coyote often hunts alone or in small groups. Although its population is stable across much of its range, it is sometimes seen as a nuisance in certain areas and faces threats from hunting and habitat loss.
The Squacco Heron is a small heron, easily recognizable by its head adorned with long white feathers that form a sort of mane, which gives it its name. Its plumage is primarily beige and white, with brown or gray shades on the wings and back, and a short, thick beak. This heron measures about 45 cm in length, with a wingspan of approximately 80 cm. It is often observed in wetland areas such as marshes, riverbanks, and ponds, where it primarily hunts small fish, aquatic insects, and crustaceans.
The Squacco Heron is a migratory bird found primarily in the Mediterranean regions, but its population is declining due to habitat loss and water pollution. Although it is a rather discreet and solitary bird, it can sometimes be seen in small groups during the breeding season. This heron has a characteristic hunting behavior, walking slowly in shallow water where it probes the ground with its beak.
The Desert Horned Frog is an amphibian species found in the dry, sandy regions of South America, particularly in Argentina, Paraguay, and Uruguay. This toad is easily recognized by the large 'horns' above its eyes, giving it an imposing appearance. It is primarily terrestrial and often hides in the sand or under dead leaves to protect itself from the daytime heat. This frog is a voracious predator, using its large mouth to capture prey as large as small mammals or other amphibians. It is primarily nocturnal and waits until nightfall to hunt.
The Suriname Toad is a fascinating amphibian species, known for its unique appearance and extraordinary reproductive behavior. This flat and wide toad is often called the 'birthing toad' because of the way it carries its eggs on its back, where the tadpoles develop until they are ready to hatch. It primarily lives in slow-moving waters and swamps in the tropical forests of South America, particularly in Colombia, Venezuela, Suriname, and Guyana. Its flat body allows it to hide easily in aquatic substrate, and it is primarily nocturnal. Its skin is a brownish-green, and its appearance allows it to blend perfectly into its aquatic environment.

The American Crocodile, also known by the scientific name Crocodylus acutus, is a large reptile distinguished by its impressive size and broad distribution. It can reach lengths of 6 to 7 meters, although some individuals can exceed this size. Its body is covered with green to gray scales, often speckled with darker patches, which help it blend perfectly into the brackish waters and marshlands of its habitats. The American crocodile primarily lives in coastal and estuarine areas, where it feeds on fish, birds, and small mammals. It is an opportunistic hunter and can occasionally capture large prey when they venture too close to the water. This reptile is semi-aquatic and spends a significant amount of time in the water, but it is also capable of moving on land. Regarding migration, the American crocodile is relatively sedentary, although it can travel long distances along the coast depending on environmental conditions. It is listed as vulnerable due to habitat loss and intensive hunting for its skin. Potential Threats: habitat loss due to coastal development and water pollution, illegal hunting for its skin and meat.
The Marsh Crocodile, also known by the scientific name Crocodylus palustris, is a medium-sized reptile that can reach about 4 to 5 meters in length. Its body is typically olive to brown, with darker patterns that allow it to effectively blend into the swamps, rivers, and lakes of its habitat. This crocodile is primarily carnivorous and feeds on fish, birds, and small mammals, but it can also hunt larger animals when they venture too close to the water. The Marsh Crocodile is known for its patience and discretion when hunting, often remaining still for hours before seizing its prey. In terms of distribution, it is found in the Indian subcontinent, particularly in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka. Although primarily sedentary, it can move short distances in search of new habitats. This species is listed as vulnerable due to habitat loss and hunting for its skin. Major threats include the draining of swamps, water pollution, and conflicts with human communities.
The Nile Crocodile is one of the most formidable and largest species of crocodiles, capable of reaching up to 5 meters in length. It primarily lives in rivers, lakes, and swamps in Africa and is an opportunistic predator, mainly hunting fish, birds, and mammals that approach the shores. This crocodile is also known for its territorial behavior, with males often dominating large aquatic areas. Its powerful body and rough skin allow it to blend into its environment, facilitating its stealthy hunting strategy. While primarily aquatic, the Nile Crocodile sometimes ventures onto land to bask in the sun.
The Whooper Swan, also known by the scientific name Cygnus cygnus, is a large species of swan that can reach a wingspan of 2 to 2.5 meters, making it one of the largest swans in Europe and Asia. Its plumage is entirely white, except for the bright orange skin covering its bill. The Whooper Swan is primarily a migratory bird that lives in wetlands, lakes, and marshes. It feeds mainly on aquatic plants, but can also consume seeds and roots. During the breeding season, the Whooper Swan prefers freshwater lakes and ponds, where it builds floating nests. The migration of the Whooper Swan is particularly notable, as it travels long distances between its breeding grounds in Northern Europe and its wintering areas in Western Europe, Central Asia, and China. While its status is currently stable, the Whooper Swan can be threatened by habitat loss due to the draining of wetlands and water pollution. It is also vulnerable to illegal hunting and human disturbances.

The Fallow Deer, also known by the scientific name Dama dama, is a medium-sized cervid native to Europe and Asia Minor. It stands between 90 and 120 cm tall at the withers and can weigh between 30 and 100 kg, depending on sex and environment. Its coat, usually brown or gray, is spotted with white during the summer season, helping it blend into its forest habitat. The Fallow Deer primarily inhabits forests and woodlands, where it feeds on a variety of vegetation, including grasses, leaves, fruits, and bark. It is also known for its habit of moving in herds, often forming separate groups of males or females. The Fallow Deer is a ruminant herbivore that is primarily active at dawn and dusk. Although it is mostly sedentary, it can travel long distances in search of food or new habitats. During the breeding season, males fight for females, producing characteristic sounds such as roars. This species is listed as of least concern, but it can be threatened by habitat loss and excessive hunting.
The White-fronted Damalisque is a medium-sized antelope, recognizable by its reddish-brown coat and the distinctive white band that crosses its forehead, which gives it its name. It stands between 1.30 and 1.50 meters tall at the withers and weighs between 50 and 70 kg. This mammal primarily inhabits open savannas, grasslands, and semi-desert areas, preferring open terrain where it can graze on grasses, leaves, and stems. It is well adapted to heat and drought, thanks to its short coat and behavior of seeking shade during the hottest parts of the day. The White-fronted Damalisque lives in small groups, often consisting of females and young, while adult males usually live alone or in small groups. It is mainly active in the morning and late afternoon, when it is easier to feed while avoiding the heat of the day. While the species is currently in good health, it faces threats such as illegal hunting, habitat loss due to human expansion, and competition with livestock for food resources.
The Common Damalisque is a medium-sized antelope, recognizable by its reddish-brown or gray-brown coat, with distinctive white markings on the legs and belly. It stands about 1.10 to 1.30 meters tall at the withers and weighs between 45 and 70 kg. This mammal primarily inhabits the savannas and open grasslands of East Africa, notably in Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. It mainly feeds on grasses and herbaceous plants but can also consume leaves and fruits when grass resources are limited. The Common Damalisque is known for its social behaviors, typically living in groups of females and young, while adult males are often solitary or form small groups. During the breeding season, males fight to defend their territory and access females. While it is currently listed as of least concern, the Common Damalisque faces threats such as habitat loss due to agriculture and urban expansion, as well as hunting for its meat and skin.
The White-beaked Dolphin is a small cetacean from the Delphinidae family, easily recognizable by its white beak and distinctive markings on its body. It typically measures between 1.5 and 2.5 meters in length and weighs between 70 and 150 kg. This dolphin primarily inhabits the cold and temperate waters of the North Atlantic, particularly around Iceland, Greenland, and the North American coasts. It primarily feeds on fish and cephalopods, using group hunting techniques to capture its prey. The White-beaked Dolphin is often seen in small groups or families, and it is known for its complex social behaviors, including group play and acrobatic leaps. This dolphin has a lifespan of about 20 to 30 years in the wild. Although the species is not currently endangered, it faces threats from pollution, underwater noise, and ship collisions. Managing its marine habitats is crucial for the preservation of this species.
The Common Dolphin is a medium-sized cetacean, easily recognizable by its streamlined body and distinctive beak. It typically measures between 2 and 2.5 meters in length and weighs between 100 and 150 kg. This dolphin is widely distributed in temperate and tropical waters, particularly in the Mediterranean, the Atlantic, and the seas around Asia. The Common Dolphin primarily feeds on fish, cephalopods, and sometimes small crustaceans, hunting in highly coordinated groups. Its social structure is complex, with groups ranging from a few individuals to several hundred, depending on environmental conditions and the availability of food resources. It is also known for its acrobatic behaviors, such as jumping and group play, and is often seen following boats. While this species is not currently endangered, it faces threats from pollution, disturbances caused by human activities at sea, and bycatch in fishing nets.
The Dendrobate, belonging to the Dendrobatidae family, is a small frog known for its bright colors and toxic behavior. These frogs typically measure between 2 and 6 centimeters in length and are easily recognizable by their shiny, colorful skin, which can be yellow, blue, red, or green, depending on the species. They are primarily found in the humid tropical forests of Central and South America. Their diet consists of insects, small arthropods, and occasionally small worms. Dendrobates are known for their toxic secretions, which serve as defense against predators. These toxins mainly come from their diet, particularly ants and beetles that contain alkaloids. Dendrobates are also both terrestrial and aquatic creatures, typically laying their eggs in humid places, where their tadpoles develop in small pools of water or decaying leaves. Although fascinating, Dendrobates are vulnerable to habitat loss due to deforestation and pollution.
The Golden Poison Dart Frog is a small, vibrant, and colorful frog from the Dendrobatidae family. This species typically measures between 2 and 3 centimeters in length and is easily recognized by its golden skin, often speckled with black. It primarily inhabits the humid tropical forests of Central and South America, particularly in Costa Rica and Panama. The Golden Poison Dart Frog feeds mainly on small insects, ants, and mites. It is known for its toxicity, which comes from its diet, particularly from certain ants and beetles that contain alkaloids. These toxins serve as a defense mechanism against predators. This species is also known for its social behaviors and vocalizations during the breeding season. The eggs of the Golden Poison Dart Frog are laid on the forest floor, and the tadpoles develop in small pools of water or on decaying leaves. While this species is not currently endangered, it is threatened by deforestation and the destruction of its natural habitat.

The Strawberry Poison Dart Frog is a small, vibrant, and colorful frog from the Dendrobatidae family. This species typically measures between 2 and 3 centimeters in length and is easily recognizable by its bright red or orange color, sometimes speckled with blue or black, hence its name "strawberry." It is primarily found in the humid tropical forests of Central America, particularly in Costa Rica and Panama. Its diet mainly consists of ants, spiders, and other small arthropods, which it primarily captures from the forest floor. The bright coloration of its skin is an indicator of its toxicity, which comes from alkaloids found in its diet, particularly ants. These toxins serve as protection against predators. During the breeding season, the Strawberry Poison Dart Frog lays its eggs on the forest floor or in humid areas where the tadpoles develop, often in small pools of water or tiny puddles. While this species is not in immediate danger, it is threatened by deforestation, habitat loss, and pollution.
The Dendrobates tinctorius, also known as the Blue Poison Dart Frog, is a vibrant species of toxic frog native to the humid tropical forests of South America, primarily in Guyana, Brazil, and Suriname. This frog is easily recognizable by its bright blue color, which serves as a warning to predators of its toxicity. Dendrobates tinctorius are primarily insectivorous and feed on small insects. Their bright color comes from the toxins of the insects they consume in their natural habitat. In captivity, they are not toxic as their diet changes. This frog is also known for its discreet behavior and primarily nocturnal habits.
The Golden poison dart frog, also known as the Terrible Dart Frog, is considered one of the most toxic animals in the world. Native to the tropical forests of Colombia, this small frog is distinguished by its bright yellow color, which serves as a warning to predators of its toxicity. It derives its toxin from its diet, primarily consisting of insects found in its natural habitat. These frogs are not toxic in captivity as their diet changes. Despite its toxicity, it has been used by some cultures to poison the tips of their arrows, earning it the name 'poison dart frog.'
The Tasmanian Devil is a medium-sized carnivorous marsupial, easily recognized by its black fur and white patches on its chest and hips. It measures about 50 cm in length, with a tail of 25 cm, and weighs between 5 and 10 kg. This nocturnal predator is found exclusively on the island of Tasmania, where it primarily feeds on small mammals, birds, insects, and carcasses of dead animals. The Tasmanian Devil is known for its aggressive feeding behavior, often making growling and screaming noises. It is also a solitary animal, only coming together during breeding or when it finds a large carcass. While this species plays an important scavenging role in its ecosystem, it is now threatened by a devastating infectious disease, Devil Facial Tumour Disease (DFTD), which has significantly reduced its population. Habitat loss and vehicle collisions also pose threats to its survival.
The Thorny devil is a fascinating lizard native to the deserts of Australia. Its skin is covered with sharp spines that allow it to camouflage effectively among rocks and desert vegetation. It primarily feeds on ants, which it captures using its sticky tongue. When threatened, it adopts a defensive posture, inflating its body and displaying its spines to appear larger and more threatening. While calm, it is an expert in the art of camouflage and uses its appearance to protect itself from predators.
The Kirk's Dik-dik is a small antelope, recognizable by its modest size and distinctive features, including its elongated snout and large, expressive eyes. Standing about 40 cm tall at the withers and weighing between 3 and 6 kg, it is one of the smallest members of the antelope family. Its coat is usually light brown or gray, with a paler belly and distinct facial markings. The Kirk's Dik-dik primarily inhabits savannas and wooded areas in East Africa, notably in Somalia, Kenya, Tanzania, and Ethiopia. It feeds mainly on leaves, fruits, and herbaceous plants. This small herbivore is mostly active at dusk and during the night, using its well-developed sense of smell to detect predators, emitting a characteristic call to alert other members of its group. The Kirk's Dik-dik is typically solitary or lives in small family groups. Although it is not currently threatened, it faces dangers such as habitat loss due to agricultural expansion and hunting.
The Komodo Dragon is a large carnivorous lizard, famous for its impressive size and strength. It typically measures between 2 and 3 meters in length and can weigh up to 70 kg. Its massive body is covered with scales, usually grayish-green, which helps it blend into its natural environment. The Komodo Dragon is found exclusively on a few islands in Indonesia, including Komodo, Rinca, Flores, and Gili Motang. This apex predator feeds on a variety of animals, from birds to mammals like deer, as well as carrion. It primarily hunts using its developed sense of smell, able to detect odors from several kilometers away. Due to its powerful bite and saliva filled with bacteria, the Komodo Dragon can incapacitate its prey and wait for it to succumb to infection before feeding. The species is listed as vulnerable, threatened by habitat loss, illegal hunting, and excessive tourism. Conservation efforts are in place to protect this unique creature and its habitat.
The Black-winged Stilt is an elegant wader bird, easily recognized by its long, slender legs and bright white plumage. Measuring around 35 to 40 cm in length and with a wingspan of 70 to 80 cm, this bird is distinguished by its fine, straight black beak, which is slightly upturned. The Black-winged Stilt primarily inhabits wetlands, marshes, shallow rivers, and ponds across Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It mainly feeds on aquatic insects, crustaceans, and small fish, which it catches by walking in shallow water and probing with its beak. This wader is particularly known for its graceful way of moving on its long legs, often walking slowly in the water or performing elegant hops. During the breeding season, the Black-winged Stilt builds its nest on isolated islands or sandbanks, where females lay 3 to 4 eggs. The species is listed as of least concern, although it is vulnerable to habitat loss and water pollution.
The Red Squirrel is a small tree-dwelling mammal, well-known for its reddish-brown fur and long ears, often tipped with tufts of hair. It typically measures between 20 and 25 cm in length, with a bushy tail that can reach up to 25 cm in length. This rodent is mainly found in deciduous and mixed forests across Europe and Asia, but it is also present in urban parks and gardens. The Red Squirrel is omnivorous, feeding mainly on nuts, seeds, mushrooms, and occasionally insects or bird eggs. Highly agile, it moves with ease between trees, using its tail as a stabilizer. It is a territorial animal that builds ball-shaped nests made of twigs, moss, and leaves, often placed in tree trunks or branches. While the species is still fairly widespread, it faces threats such as habitat loss, competition with the introduced Grey Squirrel, and collisions with vehicles.
The Barn Owl is a nocturnal bird of prey, easily recognizable by its heart-shaped face and large white wings. It typically measures between 33 and 40 cm in length, with a wingspan of 80 to 95 cm. Its plumage is mainly white with beige and brownish hues on its back, while its face, with its distinct shape, is a bright white, making it immediately identifiable. The Barn Owl primarily inhabits agricultural areas, open meadows, clear forests, and abandoned buildings or churches, where it finds places to nest. It primarily feeds on small mammals, such as mice and voles, but may also hunt birds or insects. Its hunting method is very silent, due to the unique structure of its feathers, which reduce flight noise. It is a solitary bird that usually hunts at night. While the Barn Owl is not currently endangered, it faces threats such as habitat loss, secondary poisoning from consuming contaminated prey, and collisions with vehicles.
The Eider Duck is a large sea duck, easily recognized by its distinctive plumage. The adult male has a white body with a black head and neck, while the female is more muted with a brown speckled plumage. The Eider measures about 55 to 70 cm in length, with a wingspan of 100 to 125 cm, and weighs between 1.5 and 2.5 kg. It is primarily found in coastal regions of the North Atlantic, notably in Northern Europe, Canada, and Alaska. This duck primarily feeds on mollusks, crustaceans, and small fish, which it finds by diving underwater. It is also known for its social behavior, often living in large colonies during the breeding season. The Eider Duck is particularly famous for its down, a soft and insulating material harvested from the female's nests after laying, used to make luxury duvets and pillows. While the species is not immediately endangered, it is threatened by marine pollution, habitat loss due to coastal urbanization, and hunting.
The Moose is a large herbivorous mammal, the largest member of the deer family, easily recognizable by its imposing silhouette and large ears. It can stand up to 2 meters tall at the withers, with a weight ranging from 300 to 700 kg, with males typically being larger than females. Its fur is thick, usually dark brown or black, and it has long legs that allow it to move easily through forested or marshy areas. The Moose is primarily found in the boreal forests of Europe, Asia, and North America, where it mainly feeds on leaves, bark, branches, and aquatic plants. It is a solitary animal, preferring quiet areas and is mainly active at dusk and night. During the breeding season, males emit powerful calls to attract females and mark their territory. While the species is not currently endangered, it faces threats such as habitat loss, vehicle collisions, and hunting.
The Common Eland is a large herbivorous ungulate, belonging to the bovidae family, and one of the largest species of antelope. It can stand up to 1.5 meters tall at the withers and weigh between 400 and 900 kg, with males generally being larger than females. Its coat is usually light brown or gray, with lighter vertical stripes on the flanks. The Common Eland has large, spiral horns that can reach up to 80 cm in males. It primarily inhabits savannas and grasslands in sub-Saharan Africa, where it feeds mainly on grasses, leaves, and bushes. It is a social animal, living in large groups, especially during the breeding season. While the Common Eland is currently listed as of least concern, it faces threats such as habitat loss, hunting, and competition with livestock for food resources.
The Giant Eland, or Tragelaphus derbianus, is a large, robust, and majestic antelope, easily recognizable by its spiral-shaped horns, present only in males. It measures between 1.4 and 1.7 meters at the shoulder and can reach a length of 2.5 to 3 meters, including its tail. Its weight ranges between 600 and 1,000 kg, making it one of the largest antelopes. Its coat is generally light brown to gray, with white markings on the belly and throat. The Giant Eland primarily inhabits open savannas, light forests, and mountainous regions in Central and West Africa, mainly in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Cameroon, Gabon, and Angola. Herbivorous, the Giant Eland primarily feeds on grasses, leaves, and fruits, and it is capable of consuming a wide variety of vegetation, allowing it to adapt to different environments. It is a social animal that lives in family groups or small herds. While the species is classified as of least concern, it is threatened by habitat loss and hunting.

The Asian Elephant is a large land mammal, known for its imposing size and large rounded ears. It typically stands between 2 and 3.5 meters at the withers and weighs between 2,000 and 5,000 kg. Its coat is generally grayish, although some individuals may have a more brownish tint. The Asian Elephant differs from the African Elephant in its smaller size, narrower ears, and its trunk, which has a single "finger" at the tip. This elephant primarily inhabits tropical forests, savannas, and wetland areas in South and Southeast Asia, including India, Thailand, Sri Lanka, and Cambodia. It is herbivorous, feeding on leaves, bark, fruits, and grasses. The Asian Elephant has often been associated with human communities due to its historical role in labor, transport, and religious ceremonies. However, the species is threatened by habitat loss due to agriculture, poaching for its valuable tusks, and conflicts with human populations. It is listed as endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
The Forest Elephant is a large land mammal, characterized by its smaller size compared to the Asian Elephant and the African Savannah Elephant, standing around 2 to 3 meters at the withers and weighing between 2,000 and 5,000 kg. Its coat is gray, but its skin is often rougher than other elephants, and its ears are smaller, adapted to its forest habitat. The Forest Elephant primarily inhabits the dense forests of Central and West Africa, where it feeds on a wide variety of vegetation, including leaves, bark, fruits, and roots. Unlike the Savannah Elephant, it is more discreet and less social, though it may form small family groups. This elephant plays a key role in its ecosystem, contributing to seed dispersal and forest regeneration. However, the species is threatened by deforestation, poaching for its valuable tusks, and conflicts with human communities. It is currently listed as vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
The African Savannah Elephant is the largest land mammal, and the largest of all terrestrial animals. It can stand up to 4 meters tall at the withers and weigh between 4,000 and 7,500 kg. Its coat is gray, with rough skin often covered in dust or mud to protect it from the sun and parasites. The African Savannah Elephant is easily recognizable by its large ears, shaped like the map of Africa, which help regulate its body temperature. This elephant is primarily herbivorous, feeding on leaves, bark, fruits, and plants. It inhabits savannas, grasslands, and open forests across sub-Saharan Africa. The African Savannah Elephant is a social animal, living in family groups led by an older female. It plays a crucial role in its ecosystem by creating openings in vegetation and dispersing seeds. However, the species is threatened by habitat loss, poaching for its valuable tusks, and conflicts with human communities. The African Savannah Elephant is currently listed as vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Emu
Dromaius novaehollandiae
The Emu is a large flightless bird, belonging to the ratite family, which also includes the ostrich and the kiwi. It typically stands between 1.5 and 1.9 meters tall and weighs between 40 and 60 kg. Its plumage is generally brown-gray, with fine feathers that give it a slightly ruffled appearance. The Emu is recognizable by its long bare neck and small wings, which prevent it from flying. It is endemic to Australia, where it inhabits a variety of environments, from open forests to savannas and semi-desert areas. This bird is primarily herbivorous, feeding on seeds, fruits, roots, and young shoots. Although it cannot fly, the Emu is a fast runner, capable of reaching speeds up to 50 km/h over short distances. It is often solitary or lives in small groups, except during the breeding season. The Emu plays an important role in seed dispersal, contributing to the regeneration of vegetation. While the species is currently listed as of least concern, it faces threats such as habitat loss, hunting, and collisions with vehicles.
The European Nightjar is a nocturnal bird, often difficult to spot due to its perfectly camouflaged plumage that helps it blend into its surroundings. It measures about 23 to 26 cm in length, with a wingspan of 50 to 55 cm. Its plumage is primarily brown, with complex patterns of spots and streaks that perfectly mimic the colors and textures of forest floors or dry meadows. The European Nightjar primarily feeds on nocturnal insects, which it captures in flight with its wide mouth open. It hunts at dusk and during the night, using its broad, rounded wings to maneuver silently through the air. This bird is often seen flying in circles or zigzags above fields, forests, or open areas. During the breeding season, the female lays its eggs directly on the ground, often in well-hidden spots. While the species is not currently endangered, it faces threats such as habitat loss, light pollution, and the decline of nocturnal insects.
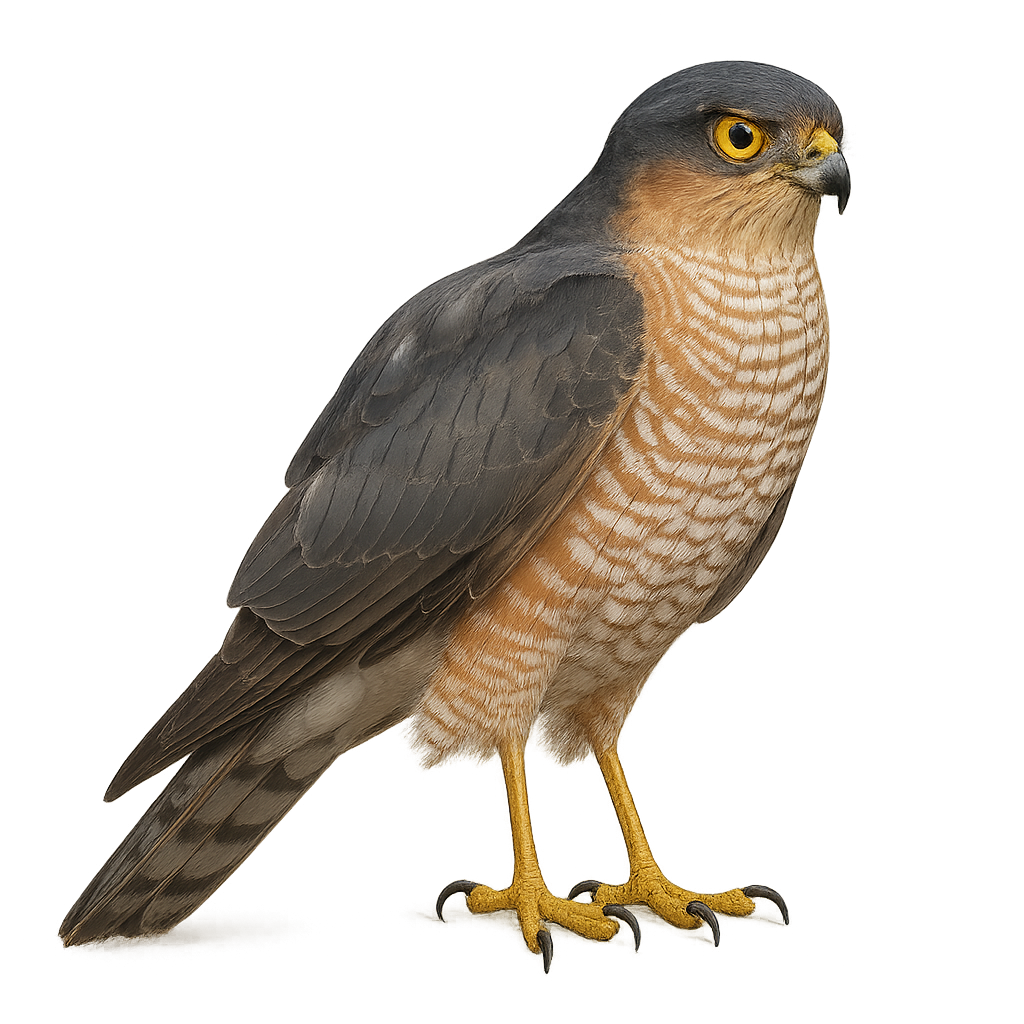

The European Sparrowhawk is a small raptor from the Accipitridae family, easily recognizable by its gray-brown plumage and narrow wings adapted for hunting in forests. It measures about 30 to 40 cm in length, with a wingspan of 60 to 90 cm, and weighs between 150 and 250 g. The male is generally smaller than the female. Its plumage varies depending on sex and age, but adults have bluish-gray feathers on the back and brownish horizontal bars on the belly. The European Sparrowhawk primarily inhabits dense forests and wooded areas in Europe, but it can also be found in urban parks and gardens. This raptor is an excellent hunter, primarily feeding on smaller birds, which it captures in flight after a rapid pursuit through trees. It often hunts using a silent, swift flight technique and is capable of capturing prey in confined spaces. Although the European Sparrowhawk is currently listed as of least concern, it faces threats such as habitat loss, disturbance of its nesting sites, and persecution by humans.
The Common Pheasant, or Colchian Pheasant, is a medium to large-sized bird, easily recognizable by its bright colors and silky plumage. The adult male is particularly spectacular, with shiny plumage in shades of green, red, gold, and blue, and a long tail adorned with fine feathers. It measures about 70 cm in length, most of which is its tail, and weighs between 0.8 and 1.5 kg. The female, more discreet, has brown spotted plumage that helps her blend into her surroundings. Native to Asia Minor and the Caucasus region, the Colchian Pheasant has been introduced to many parts of the world for hunting and decoration. It typically inhabits wooded areas, cultivated fields, and grasslands. Its diet is omnivorous, consisting of seeds, berries, insects, and sometimes small vertebrates. The species is mainly active at dawn and dusk. While the Common Pheasant is not threatened, it faces risks such as habitat loss, excessive hunting, and predation by carnivores.
The Kestrel is a small raptor from the falcon family, easily recognizable by its light brown plumage and dark spots that adorn its back. It measures about 30 to 35 cm in length, with a wingspan of 70 to 80 cm, and weighs between 150 and 200 g. The adult male has more colorful plumage, with shades of gray and black bands on the tail, while the female has a duller, brownish plumage. This falcon is common throughout Europe, Asia, and North Africa, where it primarily inhabits fields, meadows, heathlands, and even urban areas. The Kestrel feeds mainly on small mammals, insects, reptiles, and sometimes smaller birds. It is especially known for its hovering flight technique, where it remains suspended in the air by rapidly beating its wings before diving to capture prey. While the species is not currently endangered, it faces threats such as habitat loss, reduced prey populations, and disruption by human activities.
The Merlin is a small raptor, one of the fastest birds, easily recognizable by its compact plumage and vibrant colors. It measures between 28 and 34 cm in length, with a wingspan of 60 to 80 cm, and weighs between 150 and 250 g. The male has a blue-gray plumage on its back, with black wings and a head marked with black bands, while the female is generally larger and duller, with brownish hues. The Merlin is found primarily in Europe, Asia, and North America, where it inhabits a variety of habitats, from open areas such as meadows and agricultural zones to forests. This bird primarily feeds on smaller birds, small mammals, and insects. It hunts in flight, using its impressive speed to capture its prey. It is particularly known for its fast and agile aerial maneuvers. While the species is not endangered, it faces threats such as habitat loss, human disturbance, and the reduction of prey populations.
The Hobby Falcon is a small diurnal raptor, often confused with other falcons due to its similar size, but it is distinguished by its elegant plumage and unique characteristics. It measures about 30 to 40 cm in length, with a wingspan of 70 to 90 cm, and weighs between 150 and 250 g. Its plumage is primarily grayish, with a darker head and back and a lighter belly. Males have a lighter plumage than females, which are generally larger and darker. This falcon primarily inhabits open areas such as meadows, heathlands, and sparse forests, as well as mountains and agricultural zones. It hunts by flying at high speed, capturing small birds, insects, and sometimes small mammals. Its flight is fast and direct, often interrupted by sharp turns and dives to capture its prey. While the species is not endangered, it faces threats such as habitat loss and the reduction of its prey populations.
The Red-footed Falcon is a small raptor, particularly recognizable by its delicate plumage and vivid colors. It measures about 30 to 35 cm in length, with a wingspan of 70 to 80 cm, and weighs between 150 and 200 g. The adult male has a distinctive blue-gray plumage, with pointed wings and a lighter head, while the female is browner and slightly larger. The Red-footed Falcon primarily inhabits open areas such as meadows, agricultural fields, and steppes in Eastern Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It primarily preys on insects, small birds, and sometimes reptiles. This falcon is known for its ability to catch prey in flight, performing fast and precise maneuvers. It is particularly active at dusk and in the evening, hence its name "Red-footed" (referring to its late-day hunting). Although the species is not yet endangered, it is threatened by habitat loss and the decline of its prey populations.
The Peregrine Falcon is a medium-sized raptor, known for its impressive speed and exceptional hunting abilities. It measures between 40 and 50 cm in length, with a wingspan of 100 to 120 cm, and weighs between 600 and 1,000 g. Its plumage is typically blue-gray on the back, with a lighter belly and black markings on the head and wings. The Peregrine Falcon is especially famous for its stooping hunting technique, where it can reach speeds exceeding 300 km/h, making it the fastest animal in the world. It primarily feeds on birds, which it catches in flight, but can also hunt small mammals. The Peregrine Falcon lives in a variety of habitats, including cliffs, urban buildings, and coastal areas. It is a widely distributed species, found on every continent except Antarctica. Although it was once threatened by hunting and pesticides, it has now made a recovery thanks to conservation efforts, including the release of young birds and habitat protection programs.

The Fennec is a small fox, easily recognized by its large ears, which can measure up to 15 cm long, nearly a third of its body size. It measures about 24 to 41 cm in length, with a tail measuring 18 to 30 cm, and weighs between 0.8 and 1.5 kg. Its fur is light beige to sandy, allowing it to blend perfectly into its desert environment. The large ears of the Fennec are not only a distinctive feature but also play a crucial role in regulating its body temperature by dissipating excess heat. The Fennec primarily inhabits the deserts and semi-desert regions of North Africa, especially the Sahara. It is a nocturnal animal, hunting primarily at night to avoid the intense heat of the day. Its diet is omnivorous, consisting of small mammals, insects, fruits, and roots. Thanks to its digging skills, it is able to find water beneath the sand, allowing it to survive in an environment where water is scarce. While the Fennec is not currently threatened, it may face risks related to habitat destruction and illegal capture for the pet trade.

The Fer-de-lance is a venomous viper found primarily in the rainforests of Central and South America. It is a medium to large snake, typically measuring between 1.5 and 2.5 meters in length, although some individuals can reach up to 3 meters. Its body is robust, and its color ranges from brown, gray, to olive, with diamond-shaped patterns along its back, which helps it blend into its environment. Its head is triangular and distinct from the body, with characteristic scales that give it a "spearhead" appearance. This snake is primarily terrestrial and often hides under leaves or in underbrush to hunt or rest. The Fer-de-lance is an opportunistic predator, feeding mainly on small mammals, birds, and frogs. Its venom is extremely potent and can cause severe injury or death if antivenom is not administered quickly. It usually strikes by surprise, launching itself at its prey or an intruder. While it is an important predator in its ecosystem, it faces threats related to deforestation and habitat loss.
The Greater Flamingo is a large bird with distinctive plumage, easily recognizable by its vivid colors and graceful silhouette. It stands about 1.4 to 1.7 meters tall and weighs between 2.5 and 4 kg. Its plumage is primarily pale pink, with more intense shades on the wings, and its long legs and neck give it a majestic posture. The Flamingo's beak is curved downward, allowing it to filter water and feed primarily on plankton, small shrimp, and algae. This bird primarily inhabits wetlands, saline lagoons, and salt marshes, where it often gathers in large colonies. Flamingos feed by dipping their heads into the water while walking in shallow waters, using their beaks to filter food. While the species is not threatened, it faces risks related to habitat loss, pollution, and human disturbance.
The Northern Gannet is a large seabird, easily recognized by its brilliant white plumage and large black-tipped wings. It measures about 85 cm in length, with a wingspan of 170 to 180 cm, and weighs between 2.5 and 3.5 kg. Its long, pointed beak, along with its pale yellowish head, makes it a formidable predator in its marine environment. The Northern Gannet primarily inhabits the rocky coasts of the North Atlantic, where it nests in impressive colonies, often situated on steep cliffs. This bird is an excellent diver, catching its prey by plunging dramatically from heights of up to 30 meters, reaching speeds in excess of 100 km/h. Its diet mainly consists of fish, which it catches either in flight or by diving underwater. While the species is not endangered, it faces risks such as marine pollution, declining fish populations, and disturbances to its nesting sites.
The Beech Marten is a small carnivorous mammal belonging to the mustelid family. It measures between 40 and 50 cm in length, with a tail that can reach up to 30 cm, and typically weighs between 1.5 and 2 kg. Its fur is dense and smooth, typically brown in color, with a lighter belly and a distinctive white patch on the throat. The Beech Marten is agile and opportunistic, primarily hunting small mammals, birds, eggs, as well as fruits and insects. It is mainly nocturnal and solitary, but can be observed in a wide variety of habitats, including forests, orchards, and even urban areas. It is known for its ability to climb trees and enter attics and lofts of human dwellings. While the Beech Marten is relatively common in Europe, it faces threats related to habitat loss and human activities, such as road traffic and deforestation.
The Common Pochard is a medium-sized diving duck, measuring between 42 and 49 cm in length. The male has a reddish-brown head, black breast, and light grey body, while the female displays a more subdued brown-grey plumage. This species inhabits lakes, ponds, and slow-flowing rivers rich in aquatic vegetation. It feeds mainly on aquatic plants but also consumes invertebrates. The Common Pochard is migratory, breeding in Europe and Asia, and wintering further south. It is currently classified as vulnerable due to population declines, primarily caused by habitat loss and pollution.
The Tufted Duck is a medium-sized, elegant diving duck, measuring 40 to 47 cm in length. The male displays glossy black plumage with striking white flanks and a distinctive black tuft on the back of the head. The female is dark brown with paler flanks and a more modest tuft. Both sexes have a bluish-grey bill and bright yellow eyes. This species frequents lakes, ponds, reservoirs, and slow-moving rivers, often in flocks, and prefers areas rich in aquatic vegetation. It feeds mainly on mollusks, insect larvae, crustaceans, and aquatic seeds. A partial migrant, it is present year-round in temperate regions. Generally of Least Concern, though locally threatened by water pollution and wetland loss.
The Ferruginous Duck is a small diving duck measuring between 38 and 42 cm in length with a wingspan of 63 to 67 cm. The male has a dark chestnut plumage with white undertail coverts and distinctive white eyes. The female is duller brown with dark brown eyes. This species inhabits shallow lakes, marshes, and ponds rich in aquatic vegetation, preferring calm areas with dense reed beds. It feeds mainly on seeds and aquatic plants, supplemented by mollusks, aquatic insects, and small fish. The Ferruginous Duck is migratory, breeding in Eastern Europe and Asia, and wintering in North Africa, South Asia, and around the Mediterranean. Listed as Near Threatened by the IUCN, it faces habitat loss, pollution, and illegal hunting.
The Senegal bush baby, also known as Galago moholi, is a small nocturnal primate native to the forests and savannas of West Africa, particularly Senegal and Gambia. This primate is easily recognized by its large eyes, pointed ears, and silky fur. It primarily feeds on insects, fruits, and nectar. The Senegal bush baby is an excellent climber and moves quickly from tree to tree using its long legs and prehensile tail. It is a social animal, often living in small groups, and is mainly active at night, using powerful vocalizations to communicate.
The Common Goldeneye is a medium-sized diving duck, measuring about 42 to 50 cm in length. The breeding male has a glossy dark green head, a distinct white spot below the eye, and a bright yellow eye. The female is brown with a chocolate-colored head and a subtle white collar. It inhabits lakes, slow rivers, and coastal bays in Europe, Asia, and North America. A migratory species, it nests in tree cavities or artificial nest boxes. Its diet includes mollusks, crustaceans, aquatic insects, and small fish. Though generally of Least Concern, it may be impacted locally by the loss of natural nesting sites.
The Gaur is a large bovine, considered one of the most impressive species of wild cattle. It stands between 1.8 and 2 meters at the withers and can weigh from 500 to 1,000 kg, with males generally being larger and heavier than females. Its coat is dark, typically black or dark brown, with light markings on the legs and a distinctive mane around the neck. The Gaur primarily inhabits dense forests and mountains in South and Southeast Asia, especially in India, Nepal, Indonesia, and Malaysia. Herbivorous, it primarily feeds on grasses, young shoots, leaves, and fruits. The Gaur is a social animal, living in groups, although it is often observed alone or in small groups while foraging. Due to hunting, habitat loss, and conflicts with human populations, the Gaur is listed as vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
The Ganges gavial is a distinctive crocodilian, easily recognized by its long, narrow snout that allows it to capture fish in the rivers of the Indian subcontinent. This aquatic reptile is primarily found in the rivers of the Ganges and its tributaries in India and Nepal. The Ganges gavial is an excellent swimmer and feeds almost exclusively on fish, which it captures using its long, slender snout like a pincer. Although relatively calm, it is listed as endangered due to habitat loss and river pollution. It is currently protected by conservation programs.
The Bright's Gazelle is an elegant, medium-sized antelope, recognizable for its slender proportions and long, thin legs. It stands about 75 cm at the withers and weighs between 30 and 40 kg. Its coat is generally light beige, with darker markings on the flanks and a distinctive black stripe running along its lateral line. Adult males have fine, curved horns, while females generally lack them. The Bright's Gazelle primarily inhabits the savannas and steppes of East Africa, particularly in Ethiopia and Kenya. It is herbivorous, feeding mainly on grasses, leaves, and plants. Like all gazelles, it is fast and agile, capable of running at speeds of up to 80 km/h to escape predators. Although the Bright's Gazelle is not currently endangered, it faces threats related to habitat loss, hunting, and competition with livestock for food resources.
The Grant's Gazelle is an elegant, medium-sized antelope, easily recognizable by its long legs and generally sandy-colored coat with distinctive markings. It stands about 75 cm at the withers and weighs between 40 and 60 kg. The coat of the Grant's Gazelle is primarily beige with darker vertical stripes along the flanks and a black stripe running across its back. Adult males have long, slightly curved horns in the shape of a lyre, while females generally lack them. This gazelle primarily inhabits savannas, grasslands, and wooded areas in East Africa, particularly in Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. Herbivorous, it primarily feeds on herbaceous plants, leaves, fruits, and bark. Very fast and agile, the Grant's Gazelle can reach speeds of up to 80 km/h, allowing it to escape many predators. Although the species is not endangered, it faces threats such as habitat loss, hunting, and competition with livestock for food resources.
The Thomson's Gazelle is a small, elegant gazelle known for its speed and grace. It stands about 60 cm at the withers, with a body length of 90 cm, and weighs between 20 and 30 kg. Its coat is mainly beige, with distinct white markings on its belly and a black stripe running along each side of its body. The adult male has curved lyre-shaped horns, while females generally lack them. The Thomson's Gazelle primarily inhabits the savannas and grasslands of East Africa, particularly in Tanzania and Kenya. It is herbivorous, feeding mainly on grasses, young shoots, and leaves. Very fast, the Thomson's Gazelle can reach speeds of 80 to 90 km/h, allowing it to escape many predators. Although it is currently relatively common, the Thomson's Gazelle faces threats related to habitat loss and human activities, including hunting and competition with livestock.
The Leopard gecko is a terrestrial species native to the desert and semi-desert regions of Asia, particularly Pakistan, India, and Nepal. This gecko is easily recognized by its dark spots on a pale yellow background, giving it a unique appearance. Unlike other geckos, it has movable eyelids, allowing it to blink, unlike other species that have fixed eyelids. The Leopard gecko is a nocturnal predator, primarily feeding on insects and small invertebrates. It is popular in the reptile trade due to its calm temperament and ease of care.
The Tokay gecko is a large lizard native to the tropical forests of Southeast Asia. This gecko is particularly known for its vibrant colors, with a gray or bluish body speckled with orange or red spots, making it easily recognizable. The Tokay gecko is nocturnal and arboreal, living in forested habitats, often near human dwellings. It is also famous for its distinctive call, resembling its name, tokay," which it uses to defend its territory or attract a mate. This gecko is a carnivorous predator, feeding mainly on insects and small vertebrates."
The Hazel Grouse is a small, terrestrial bird belonging to the pheasant family, easily recognizable by its subtly colored plumage and robust build. It measures about 40 to 45 cm in length and weighs between 500 and 700 g. Its plumage is primarily brown and gray, with patterns of spots and bars that allow it to blend effectively into the dense vegetation of forests. The Hazel Grouse primarily inhabits dense deciduous and mixed forests, where it feeds on seeds, berries, young shoots, and insects. Although it is rather discreet and difficult to spot, it is often heard through its soft, deep call. The Hazel Grouse is a fairly sedentary bird, but it may migrate short distances depending on weather conditions. It is also an emblematic bird of wooded areas and forest landscapes. While it is not endangered, the Hazel Grouse may be threatened by the loss of its forest habitat and the degradation of its breeding sites.
The Gemsbok is a large, sturdy antelope native to the arid regions of Southern Africa. It stands between 1.2 and 1.5 meters at the withers and weighs between 200 and 250 kg. Its coat is primarily gray or beige, with white markings on the belly, legs, and face, giving it a distinctive appearance. It has long, straight horns, which can reach up to 1 meter in length, and are characteristic of the species. The Gemsbok inhabits savannas, steppes, and deserts, where it feeds primarily on herbaceous plants, roots, and fruits. It is well adapted to extreme heat and drought conditions, thanks to its ability to reduce its body temperature and feed on sparse vegetation. While the Gemsbok is capable of surviving in desert environments, it is also able to travel long distances in search of food and water. The species is not currently endangered, but it faces threats related to habitat loss and hunting.
The Common Genet is a small, agile, and elegant carnivore, easily recognizable by its long and slender body, as well as its characteristic spots. It measures between 45 and 60 cm in length, with a tail measuring 40 to 50 cm, and typically weighs between 1.5 and 2.5 kg. Its coat is usually light gray or brown, speckled with dark spots that form a distinctive pattern on its back and flanks. The Common Genet has a bushy tail and a body shape that allows it to easily climb trees and slip into narrow spaces. It primarily inhabits forests, woodlands, and wooded areas in North and South Africa, as well as the Iberian Peninsula. This carnivore is omnivorous, feeding mainly on small mammals, birds, insects, fruits, and berries. The Common Genet is also an excellent climber, often seen moving through trees in search of food or to escape danger. While the Genet is not currently threatened, it faces threats related to habitat loss and human persecution.

Gibbons, members of the Hylobatidae family, are primates particularly known for their agility and their ability to move through the canopy. They are the smallest of the great apes, measuring between 40 and 70 cm in height, with long, powerful arms that can reach up to 2.5 times the length of their body. Their weight typically ranges from 5 to 15 kg, depending on the species. Gibbons are primarily known for their mode of locomotion called "brachiation," where they move by swinging from branch to branch at impressive speeds, often at high altitudes. Their fur is typically dense, varying in color from black to light brown, and some species have distinct facial markings. Gibbons primarily inhabit the tropical forests of Southeast Asia, where they feed mainly on fruits, leaves, and small insects. These primates are social and typically live in small family groups. While gibbons are not all at immediate risk, several species are endangered due to habitat loss, poaching, and the illegal wildlife trade.
The Northern Giraffe is a subspecies of giraffe, characterized by its slender body and long neck. It stands about 4.5 to 5.5 meters tall, with males being larger and bulkier than females. Northern giraffes weigh between 800 and 1,200 kg. Their coat is light beige with irregular patches of brown or orange, which are smaller and more closely spaced than those of other giraffe subspecies. These patches are outlined in white, creating a distinctive pattern. The Northern Giraffe primarily inhabits the savannas and open woodlands of northern Kenya, particularly in the Samburu National Reserve and surrounding areas. Herbivorous, it feeds mainly on acacia leaves and other tall vegetation, which it reaches with its long neck and prehensile tongue. The Northern Giraffe is an endangered species, due to habitat loss and human conflicts, including poaching and encroachment on its land.
The Southern Giraffe is a subspecies of giraffe, characterized by its slender body, long neck, and robust legs. It typically stands between 4.3 and 4.8 meters tall, with males being larger and heavier than females, weighing between 800 and 1,200 kg. Its coat is light brown to beige, with irregular darker patches that are bordered by white. The patches of the Southern Giraffe are larger and more spaced out than those of other subspecies, giving it a distinctive pattern. It primarily inhabits the savannas and woodlands of southern Africa, notably in South Africa, Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe. Herbivorous, it feeds primarily on acacia leaves, berries, and fruits, which it reaches with its long neck and prehensile tongue. While the species is currently less threatened than other giraffe subspecies, the Southern Giraffe faces risks related to habitat loss and population fragmentation.
The Maasai Giraffe is a subspecies of giraffe, easily recognized by its irregular and jagged patches, which differ from those of other subspecies. It typically stands between 4.3 and 4.8 meters tall, with males being larger and heavier than females, weighing between 800 and 1,200 kg. Its coat is light beige to light brown, with irregularly shaped leaf-like patches that are bordered in white. These patches are smaller and more scattered than those of the Southern Giraffe. The Maasai Giraffe primarily inhabits the savannas and grasslands of East Africa, particularly in Kenya and Tanzania. It is herbivorous, feeding mainly on acacia leaves and other tall vegetation, which it reaches with its long neck and prehensile tongue. Although the Maasai Giraffe is currently considered less threatened than other giraffe subspecies, it faces threats such as habitat loss and poaching.
The Wolverine is a robust and solitary carnivore, often compared to a small bear due to its size and strength. It measures about 65 to 87 cm in length, with a tail measuring 30 to 40 cm, and weighs between 10 and 30 kg. Its fur is typically dark brown, with lighter markings on the legs and throat, forming a distinctive "mask" around its face. The Wolverine has powerful musculature, allowing it to capture prey much larger than itself, such as deer or reindeer, although it primarily feeds on small mammals, insects, and carcasses. It is an opportunist, capable of stealing food from other predators such as wolves or bears. The Wolverine primarily inhabits the northern forests of Asia and North America, including Scandinavia, Russia, Canada, and Alaska. It is an excellent climber and swimmer, well-adapted to cold, snowy environments. Although its population remains relatively stable in some areas, the Wolverine faces threats related to habitat loss, climate change, and human persecution.
The Blue Wildebeest is a large herbivorous antelope, easily recognizable by its massive body, imposing head, and black mane. It stands about 1.3 to 1.5 meters at the withers and typically weighs between 150 and 250 kg. Its coat is generally grayish-blue, with black markings on the head, legs, and shoulders. The Blue Wildebeest has curved horns that can reach 80 cm in length. It primarily inhabits the savannas, grasslands, and woodlands of Southern Africa, notably in South Africa, Botswana, and Namibia. Herbivorous, the Blue Wildebeest mainly feeds on grasses and low vegetation, often seen in large herds in open plains. It is commonly seen during large migrations, moving in search of food and water. While the species is not currently endangered, it faces risks related to habitat loss and hunting.
The Black Wildebeest is a large herbivorous antelope, easily recognizable by its robust build and massive head. It stands about 1.3 to 1.5 meters at the withers and weighs between 150 and 250 kg, with males generally being larger and heavier than females. Its coat is a deep black, with white markings on the throat and legs, and a black mane that distinguishes its neck. The Black Wildebeest is particularly known for its curved horns, which can reach up to 80 cm in length. It primarily inhabits the savannas and grasslands of West and Southern Africa, notably in Senegal, Namibia, and Botswana. Herbivorous, it primarily feeds on grasses and other herbaceous vegetation. The Black Wildebeest often lives in large groups, which helps protect it from predators. While the species is not endangered, it is threatened by habitat loss and climate change, which alters its living conditions.
The Glaucous Gull is a large seabird, easily recognizable by its imposing size and distinctive plumage. It measures between 60 and 70 cm in length, with a wingspan of 140 to 150 cm, and weighs between 1.2 and 2.5 kg. Its plumage is primarily white, with light gray wings and black markings on the tips of the feathers. The head and beak are generally yellow, with a red band on the beak. This gull is an excellent swimmer and an opportunistic hunter, feeding mainly on fish, crustaceans, and human waste when near urban areas or ports. The Glaucous Gull primarily inhabits coastal regions of the Arctic and North Atlantic and is well adapted to cold, marine environments. Although it is not endangered, it faces risks related to pollution, habitat loss, and human disturbances.
The Bluethroat is a small songbird, easily recognizable by its bright blue throat, bordered by a black band, forming a distinctive "mirror" pattern. It measures about 13 to 14 cm in length, with a wingspan of 22 to 25 cm, and weighs around 15 to 20 g. Its plumage is generally brownish on the back and light on the belly, with white and orange markings on the sides of its chest. The Bluethroat is primarily found in marshy areas, shrublands, and riverbanks in Europe and Central Asia, although some populations migrate to North Africa during the winter. It is especially known for its melodious song, which is often heard during the breeding season. The species primarily feeds on insects, worms, and small berries. While the Bluethroat is not endangered, it faces risks related to the loss of its natural habitat and changes in wetland areas.
The Mountain Gorilla is a subspecies of gorilla, primarily found in the volcanic mountains of Central Africa, notably in the forests of the Virunga region, between Rwanda, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. This gorilla is smaller than its cousin, the lowland gorilla, with an average height of 1.4 to 1.8 meters and a weight ranging from 140 to 220 kg for males, and 90 to 120 kg for females. Its fur is dense, typically black, with silver-gray hair on the backs of adult males, hence the name "silverback." Mountain Gorillas live in family groups led by a dominant male, the silverback, who is responsible for the protection and well-being of the group. They primarily feed on plants, fruits, leaves, and stems. Although they are peaceful and shy animals, Mountain Gorillas are critically endangered due to habitat loss, illegal hunting, and diseases transmitted by humans.
The Western Gorilla is a large primate species, closely related to its cousin the mountain gorilla. It is slightly smaller, with an average size of 1.6 to 1.8 meters for males and 1.4 to 1.6 meters for females, weighing between 140 and 200 kg for males and 70 to 120 kg for females. Its fur is generally black, with lighter hair on the back of adult males, who are referred to as "silverbacks" due to the silver color of their back fur. Western Gorillas primarily inhabit the tropical forests of West and Central Africa, notably in Cameroon, the Republic of Congo, the Central African Republic, and Guinea. They feed mainly on plants, fruits, leaves, and stems, and they are predominantly herbivores. Western Gorillas live in social groups led by a dominant male, and they are known for their calm and peaceful behavior. While they are not as endangered as mountain gorillas, Western Gorillas are still at risk due to habitat loss, poaching, and disease.
The Great Green Macaw is a large, colorful, and majestic parrot known for its vibrant green plumage, with touches of blue, yellow, and red on the wings and face. It measures about 85 to 95 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.2 to 1.4 meters, and weighs between 900 and 1,200 g. Its dominant green plumage is complemented by blue feathers on the wings and red around the face and chest. The Great Green Macaw primarily inhabits the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, notably in Colombia, Venezuela, Panama, Costa Rica, and Nicaragua. It feeds mainly on fruits, nuts, seeds, and flowers. This parrot is highly social and typically lives in family or small groups, but can also be seen in large flocks in its natural habitat. Although the Great Green Macaw is not yet immediately endangered, it faces threats such as habitat loss, illegal wildlife trade, and deforestation.
The Eurasian Eagle-Owl is a large nocturnal raptor, one of the most imposing owls in the world. It measures between 60 and 70 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.6 to 1.8 meters, and weighs between 1.5 and 4.5 kg. Its plumage is primarily brown, with white and black mottled patterns, and its eyes are bright orange, giving the bird a piercing gaze. It also has tufts of feathers on its head that resemble ears, which give it a distinctive appearance. The Eurasian Eagle-Owl primarily inhabits forests, mountains, and rocky areas in Europe, Western Asia, and the Middle East. It is an opportunistic hunter, feeding mainly on small mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles or amphibians. The Eurasian Eagle-Owl is a solitary and territorial bird, known for its powerful and deep calls, often heard at night. While the species is not endangered, it may be affected by the destruction of its natural habitat and human disturbances.
The Ringed Plover is a small coastal bird, easily recognizable by its compact size and distinctive plumage. It measures about 20 to 23 cm in length, with a wingspan of 40 to 45 cm, and weighs between 40 and 60 g. Its plumage is mainly beige and white, with black markings on its head and chest, and a distinctive black band around its eyes. The Ringed Plover is a migratory bird, primarily found on beaches, shorelines, and mudflats, where it feeds on small invertebrates, such as worms, crustaceans, and insects. It is often seen running quickly on the sand, searching for food, then stopping abruptly to catch it. The Ringed Plover lives in colonies during the breeding season, but generally prefers to remain alone or in small groups. Although it is not currently endangered, the Ringed Plover is vulnerable to human disturbances, such as the loss of its coastal habitat and the impact of pollution.
The Greater Kudu is an elegant, large antelope, easily recognized by its long, slender legs, streamlined body, and impressive spiral-shaped horns. It stands between 1.3 and 1.6 meters at the withers, with males weighing between 190 and 270 kg, and females weighing between 120 and 180 kg. Its coat is light gray to brown, with vertical white stripes on the body, which help it blend into forests and savannas. Males have long, spiral-shaped horns that can reach up to 1.5 meters in length, while females lack horns. The Greater Kudu primarily inhabits open forests, wooded areas, and savannas of sub-Saharan Africa, notably in East and Southern Africa. Herbivorous, it feeds mainly on leaves, bark, and fruits. This antelope is rather discreet and shy, typically living alone or in small family groups. While it is not currently in immediate danger, the Greater Kudu is threatened by habitat loss and hunting.
The Great Skua is a large, powerful seabird, belonging to the Stercorariidae family. It measures about 50 to 60 cm in length, with a wingspan of 120 to 130 cm, and weighs between 500 and 1,000 g. Its plumage is primarily brown and gray, with white markings on the wings and a generally dark head. The Great Skua is a migratory bird, found mainly in the coastal regions of the North Atlantic, particularly in Northern Europe, Iceland, Greenland, and parts of Canada. It is especially known for its piratical behavior, stealing food from other seabirds, such as gulls or fishing birds, by chasing them and forcing them to abandon their catch. While territorial, it is also an excellent swimmer and diver, feeding mainly on fish and crustaceans. The Great Skua is vulnerable to the loss of its coastal habitat and human disturbances, including pollution and disruptions caused by tourism.

The Capercaillie is a large bird of the pheasant family, easily recognizable by its imposing size and distinctive plumage. It measures about 80 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.2 meters and a weight ranging from 3 to 6 kg for males and 2 to 3 kg for females. The male's plumage is dark, with a reddish chest, a crest of feathers on the head, and a large V-shaped tail. The female, on the other hand, is more discreet, with a brown mottled plumage that allows her to better blend into the environment. The Capercaillie primarily inhabits coniferous and deciduous forests, particularly in the mountains and wooded areas of Europe, notably in France, Switzerland, Germany, and other mountainous regions. It feeds mainly on young shoots, seeds, fruits, and insects. This bird is also known for its spectacular mating displays, during which the male puffs up his chest, spreads his tail, and makes powerful calls to attract females. Although the species is not immediately endangered, the Capercaillie faces threats from deforestation, human disturbance, and habitat loss.
The Great Horned Owl is a large nocturnal raptor, one of the most imposing owls on the American continent. It measures between 50 and 70 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.2 to 1.5 meters, and weighs between 1.5 and 2.5 kg. Its plumage is mainly brown, speckled with black, with lighter markings on its belly and wings. It has large tufts of feathers on its head that resemble ears, and piercing yellow eyes. This owl inhabits a variety of habitats, including forests, wooded areas, and open landscapes across North America, notably in the United States, Canada, and Central America. It is primarily nocturnal and carnivorous, feeding on small mammals, birds, and occasionally reptiles. It is also known for its impressive hunting abilities, flying silently to surprise its prey. Although the Great Horned Owl is not currently threatened, it may be affected by habitat loss and human disturbance.
The Great Egret is a large wading bird, easily recognizable by its entirely white plumage, long legs, and long, sinuous neck. It stands about 85 to 105 cm tall, with a wingspan of 1.3 to 1.7 meters, and weighs between 800 and 1,500 g. The Great Egret has a long, slender yellow beak and bright green eyes. It primarily inhabits wetlands, marshes, estuaries, and lake shores in Europe, Africa, Asia, and the Americas. This bird is an excellent fisherman, feeding mainly on fish, crustaceans, and aquatic insects, which it captures by diving or slowly probing the water with its beak. During the breeding season, the Great Egret is known for its elegant courtship dances and its plumage adorned with long, delicate feathers, giving it a majestic appearance. While the species is not endangered, it is sometimes threatened by habitat loss and water pollution.
The Eared Grebe is a small grebe measuring between 28 and 35 cm in length with a wingspan of 57 to 59 cm. In breeding plumage, it has a black head adorned with golden feathers forming a crest, a black neck, a black chest, and chestnut flanks. In non-breeding plumage, it is more subdued, with a black back, black cap, white cheeks, and a white belly. It frequents shallow lakes and ponds, rich in aquatic vegetation, where it primarily feeds on small fish and aquatic invertebrates. Reproduction occurs in summer, with a clutch of 3 to 6 eggs laid in a floating nest. The young are capable of swimming shortly after hatching and can be carried on the parents' backs. A migratory species, it winters in the Mediterranean and warmer regions. Listed as Least Concern by the IUCN.
The Little Grebe is the smallest European grebe, measuring about 29 cm in length with a wingspan of 40 to 45 cm. In breeding plumage, it has a bright chestnut throat and nape, giving it its name, and a yellow spot at the base of the bill. In non-breeding plumage, it is more subdued, with a dark brown back and a light belly. It inhabits wetlands such as lakes, ponds, marshes, and reed beds, where it can easily hide. It feeds primarily on aquatic insects, small crustaceans, tadpoles, and small fish. Reproduction occurs from March to July, with one or two clutches of 4 to 7 eggs each. The young are precocial and can swim and dive immediately after hatching. A partial migrant, it winters in the milder regions of Europe. Listed as Least Concern by the IUCN.
The Great Crested Grebe is the largest of the European grebes, measuring between 46 and 51 cm in length with a wingspan of 85 to 90 cm. In breeding plumage, it has a black crest, a reddish collar, and a long, pointed bill. In non-breeding plumage, it is more subdued, with a dark back and a light belly. It inhabits shallow lakes, ponds, and marshes, often surrounded by aquatic vegetation. It primarily feeds on fish, aquatic insects, and small crustaceans. Reproduction occurs in spring and summer, with a clutch of 3 to 6 eggs laid in a floating nest. The young, with black and white striped plumage, are often carried on the parents' backs. A partial migrant, it winters in the Mediterranean and warmer regions. Listed as Least Concern by the IUCN.
The Azureus Poison Dart Frog is a brightly colored and striking species, known for its vivid blue color that varies in intensity. Native to the humid tropical forests of Guyana, Suriname, and Brazil, it is famous for its camouflage abilities and skin glands that secrete potent toxins, used for defense against predators. This frog is primarily terrestrial and lives in areas near streams and swamps, where it feeds on insects and other small prey. Due to its coloration, it serves as a warning signal to predators. It is primarily diurnal.
The Helmeted Tree Frog is a fascinating amphibian species, known for the distinctive helmet-like protuberance on its head. This protuberance, resembling a helmet, helps it camouflage among the leaves and branches of trees in the humid tropical forests. It is mainly found in the forests of Costa Rica, Panama, and Nicaragua. It is nocturnal and terrestrial, spending much of its time in the canopy near streams where it lays its eggs. This frog is rather discreet and often hides in dense vegetation to avoid predators.
Baudin's Tree Frog is a fascinating amphibian species, often found in the humid tropical forests of Central America, primarily in Mexico, Costa Rica, and Guatemala. It is easily recognized by its bright coloration, which ranges from light green to yellow, with distinct patterns on the legs and back. This frog is semi-arboreal, meaning it spends part of its time on trees and bushes, near stagnant waters or streams. It is nocturnal and uses its coloration to blend into its environment when resting. It is also capable of making long leaps to escape predators.
The Cochranella Frog is a fascinating amphibian species, known for its translucent skin that allows its internal organs to be visible. Unlike other glass frogs, its skin is slightly granular, which helps it camouflage better in the dense vegetation of its habitat. This frog lives in the humid tropical forests of Central America, mainly in Costa Rica and Panama, where it is found on leaves hanging above streams. Its small size, combined with its discreet behavior, makes it hard to spot. The eggs are laid on leaves above the water, and the tadpoles fall into the stream as they hatch. These frogs are primarily nocturnal and prefer to avoid human interaction.
Fitzinger's Rain Frog is a terrestrial amphibian species found in the humid tropical forests of Central America, mainly in Costa Rica and Panama. It is known for its rough skin and typically gray-brown coloration, which helps it blend seamlessly into its environment. This frog is nocturnal and prefers to live in damp understory areas, where it hides under dead leaves or rocks. Its small size, combined with its discreet behavior, makes it hard to spot. Unlike other tree frogs, it is primarily terrestrial and spends most of its time on the ground, near temporary water sources where it lays its eggs.
The Glass Frog is a fascinating species of amphibian, known for its translucent skin that allows its internal organs to be visible. It typically measures between 2 and 3 cm long and is commonly found on leaves hanging above streams in the tropical rainforests of Central and South America. Its transparent skin serves as an excellent camouflage, helping it blend seamlessly into its environment. This frog’s ability to blend with the vegetation, combined with its small size, makes it hard to spot. Its eggs are laid on leaves above water, and the tadpoles fall into the water once they hatch. This species is nocturnal and somewhat shy, preferring to avoid human interaction.
The Vietnamese Mossy Frog is a unique amphibian species, easily recognized by its rough skin and green coloration that resembles moss, providing it with perfect camouflage in its natural habitat. This frog lives in the humid forests of Vietnam, particularly in rocky areas and trees. It is primarily nocturnal, spending the day motionless, camouflaged among leaves or moss. When it moves at night, it is capable of climbing vertical surfaces thanks to its sharp claws, making it an excellent climber. Its coloration and skin texture help it blend into its environment and avoid predators.
The Common Frog is a widespread species of frog in Europe, easily recognized by its brown or green skin, often spotted with dark markings. It primarily lives in wetland areas such as marshes, ponds, and riverbanks. This frog is an opportunist, feeding mainly on insects, worms, and small invertebrates that it captures with its quick tongue. The Common Frog is often seen during its movements toward water for breeding, a characteristic behavior in spring. It is active during the day and evening, although its habits are more pronounced during the breeding season.
The Tomato Frog is a striking amphibian species native to Madagascar, easily recognizable by its bright red color and large skin glands that secrete a toxic mucus when threatened. These frogs grow to about 10 cm and are primarily terrestrial, living in the dry tropical forests and savannas of Madagascar. Their bright coloration serves as a warning signal to predators. They are nocturnal and spend the day hiding under leaves or in burrows to avoid heat and predators. During the breeding season, they gather near water sources where they lay their eggs.
Boulenger's Poison Frog is an amphibian species native to the tropical forests of Brazil. It is primarily recognizable by its bright color and distinctive skin patterns, which range from bright yellow to green. These frogs produce a potent venom that protects them from predators. It is primarily terrestrial and lives in humid, wooded areas, often near streams. The Boulenger’s Poison Frog is nocturnal, hiding under leaves or in ditches during the day to avoid the heat of the sun. Its bright color also serves as a warning signal to predators.
Wallace's Flying Frog is a remarkable amphibian species, famous for its ability to glide from tree to tree. This frog, with long and flexible limbs, has wide feet with membranes that allow it to stabilize itself in flight. It primarily lives in the humid tropical forests of Malaysia, Indonesia, and Borneo. It feeds on insects while suspended in the branches of trees. During the breeding season, it moves to ponds or streams to lay its eggs. Wallace's Flying Frog is also nocturnal and uses its flight to escape predators.
The Grizzly Bear is a subspecies of the brown bear, imposing and robust, often considered one of the most powerful land predators in North America. It measures between 2 and 3 meters in length, with a shoulder height ranging from 1 to 1.5 meters, and weighs between 200 and 680 kg, with males generally being larger than females. Its fur is dense and can range from light to dark brown, sometimes with silver hues that give it a grizzled appearance. The Grizzly primarily inhabits forests, mountains, and prairie areas in North America, notably in Alaska, Canada, the Rocky Mountains, and U.S. national parks like Yellowstone. Omnivorous, it primarily feeds on berries, roots, fish, but also small mammals and sometimes animal carcasses. While feared due to its size and strength, the Grizzly is a shy animal and prefers to avoid human contact. The species is protected in many regions, although its population is still threatened by habitat loss, illegal hunting, and conflicts with humans.
The Hawfinch is a small passerine bird with a very powerful beak, designed to crack hard seeds and kernels. It measures about 22 cm in length and weighs between 50 and 70 g. Its plumage is mainly brown and gray, with white markings and a black patch on the head, while its wings are black with distinct white spots. The beak is wide, conical, and very robust, and it is the most remarkable feature of the bird. The Hawfinch primarily inhabits forests and wooded gardens in Europe and Western Asia, notably in France, Germany, Russia, and Turkey. It primarily feeds on seeds, particularly fruit pits and tree seeds. Its behavior is rather discreet and solitary, although it can be seen in small groups during the winter months. While the species is not endangered, habitat loss and deforestation may pose potential threats.
The Common Crane is a large migratory bird, easily recognizable by its slender silhouette, long neck, and extended wings. It stands about 1.2 meters tall, with a wingspan of 2 to 2.5 meters, and weighs between 4 and 6 kg. Its plumage is mainly gray, with white markings on the head, neck, and wings. It has a red head and a small tuft of feathers on top, giving it a distinctive appearance. The Common Crane primarily inhabits wetlands, marshes, and lakes across Europe and Asia, with large populations in Scandinavia, Germany, Poland, and the Mediterranean Basin. It is a migratory bird that travels to southern Europe and Africa for the winter. It feeds mainly on plants, roots, seeds, and occasionally insects. The Common Crane is also known for its impressive group migrations, with thousands of individuals flying in a "V" formation. While the species is not endangered, it is vulnerable to the loss of its natural habitat and disruption of its breeding sites.
The Japanese Crane is a large migratory bird, recognized for its elegant silhouette and spectacular courtship dances. It stands about 140 cm tall, with a wingspan of 2.4 to 2.8 meters, and weighs between 6 and 10 kg. Its plumage is mainly white, with black feathers on its back and wings, and a distinct red head, which is often featherless. It also has black patches around its eyes. The Japanese Crane primarily inhabits marshes, rice fields, and wetlands in Japan, but it is also found in China and Russia. It mainly feeds on aquatic plants, seeds, small insects, and occasionally small fish. This species is famous for its ritual courtship dances, during which the partners engage in graceful jumps and movements. The Japanese Crane is an endangered species due to habitat loss, pollution, and poaching. Conservation efforts have been made to protect its breeding habitats and resting areas.
The Crowned Crane is a large crane species, easily recognizable by its majestic golden plume crown on its head. It stands about 1 meter tall, with a wingspan of 1.8 to 2.2 meters, and weighs between 3 and 5 kg. Its plumage is mainly light gray, with white feathers on its belly and wings, and a head adorned with a golden crest, giving it a royal appearance. This species is primarily found in East Africa, notably in Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania, where it inhabits wetlands, marshes, and grasslands. The Crowned Crane primarily feeds on seeds, roots, insects, and occasionally small vertebrates. It is a social bird, living in groups and often performing spectacular courtship displays, during which it engages in dances and calls. Although the Crowned Crane is considered "vulnerable," conservation efforts have been implemented to protect the species, as it faces threats from habitat loss, hunting, and human disturbance.

The Cheetah is a large feline known for its exceptional speed, making it the fastest land mammal. It measures about 1.1 to 1.5 meters in length, with a shoulder height of around 75 cm, and weighs between 40 and 65 kg. Its coat is short, golden to light brown with distinct black spots, allowing it to blend effectively in the savannas. It has a round head with large nostrils, sharp eyes, and distinctive black tear marks on its cheeks, which help it focus its vision while hunting. The Cheetah primarily inhabits sub-Saharan Africa, with small populations in Iran, in open habitats such as savannas, grasslands, and deserts. Carnivorous, it mainly feeds on gazelles, springboks, and other small animals. Unlike other large cats, the Cheetah hunts using speed rather than brute strength. It can reach speeds of 100 to 110 km/h in a few seconds, but this speed can only be maintained for short distances. Although the Cheetah is not critically endangered, it faces threats like habitat loss, poaching, and reduced natural prey.
The European Bee-eater is a small, colorful bird, easily recognizable by its vibrant plumage, which features a combination of bright colors, mainly blue, green, yellow, and orange. It measures about 28 to 30 cm in length, with a wingspan of 40 to 45 cm, and weighs between 30 and 40 g. Its beak is long and pointed, perfectly adapted to catching insects in flight, primarily wasps, bees, and other flying insects. The European Bee-eater primarily inhabits open areas, grasslands, forest edges, and steppes in Europe, as well as North Africa and Western Asia. It is migratory and mostly travels to sub-Saharan Africa for the winter. This small bird lives in colonies, and its nests are often dug into cliffs or riverbanks. The European Bee-eater is known for its swift flights and acrobatic behavior while capturing its prey. Although the species is not endangered, it may be threatened by habitat loss and human disturbances, such as the degradation of natural habitats.
The Hartebeest is a medium-sized antelope, easily recognizable by its large lyre-shaped horns and distinctive coat. It stands about 1.1 to 1.3 meters tall at the shoulder, with a weight ranging from 90 to 150 kg. Its coat is generally reddish-brown, with characteristic white markings on the belly, legs, and around the eyes, and a darker coat on the back. The Hartebeest primarily inhabits savannas, grasslands, and grassy areas in East and Southern Africa, notably in Kenya, Tanzania, South Africa, and Namibia. Herbivorous, it primarily feeds on grasses, leaves, and young shoots. It lives in social groups, usually composed of females and young, while adult males often live alone or in small groups. While the Hartebeest is not currently endangered, it faces threats such as habitat loss, hunting, and disease.
The Black Guillemot is a medium-sized seabird, measuring between 32 and 38 cm in length with a wingspan of 49 to 58 cm. In breeding plumage, it has a black body with a large white wing patch, bright red feet, and a red interior to its bill. In winter, its plumage becomes paler, with a light grey back and head and white underparts. It inhabits rocky coasts of the North Atlantic and Arctic, nesting in crevices of cliffs or under rocks. Its diet mainly consists of fish, crustaceans, and mollusks, which it captures by diving up to 50 meters deep. Although listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, it is sensitive to marine pollution and predation by introduced species.
The Common Guillemot is a seabird characterized by its black and white plumage, and its streamlined body which allows it to swim with agility. It measures about 40 to 45 cm in length and weighs between 500 and 700 g. Its head is black with sharp white eyes, and its wings are short and pointed, suited for diving. The Common Guillemot primarily lives on coastal cliffs, where it nests in very dense colonies, often on inaccessible sites. It is found mainly in Northern Europe, particularly in Scandinavia, the United Kingdom, and Iceland, but also along the coasts of the North Atlantic. The Common Guillemot is an excellent diver, primarily feeding on fish, particularly small herring and capelin, which it catches by diving underwater in search of prey. While the species is not endangered, it is vulnerable to marine pollution, climate change, and disruption of its breeding sites.

The Bearded Vulture is a large vulture, easily recognizable by its distinctive head, large wings, and brown and white plumage. It measures about 1.1 to 1.3 meters in length, with a wingspan of 2.6 to 2.8 meters, and weighs between 4.5 and 7.5 kg. Its head is covered with dark feathers, while its wings and back are mainly brown, with lighter feathers on its belly. The Bearded Vulture is unique among vultures for its feeding behavior, as it primarily feeds on bones. It is capable of breaking the hardest bones by dropping them from great heights to shatter them, allowing it to access the bone marrow. It primarily inhabits mountains, notably the Alps, the Pyrenees, and the Himalayas, where it also feeds on carcasses of dead animals, such as chamois or mouflons. Although the species was once endangered, conservation efforts have helped restore its population in certain areas. However, the Bearded Vulture remains vulnerable to human disturbance, habitat loss, and the decline of its natural prey.
The Common Eider is a medium-sized seabird, easily recognizable by its distinctive plumage and diving behavior. It measures about 40 cm in length, with a wingspan of 65 to 75 cm, and weighs between 500 and 900 g. Its plumage is primarily black and white, with a black head, a wide white band around the neck, and white spots on the wings. The male, during the breeding season, has a bright orange beak and a distinctive white line running from the beak to the back of the head. The Common Eider primarily inhabits the cold waters of the North Atlantic, notably around the coasts of Iceland, Greenland, Canada, and Northern Europe. It is an excellent diver, feeding mainly on small fish, crustaceans, and marine invertebrates, which it captures underwater. The Common Eider migrates southward during the winter. Although the species is not currently endangered, it is vulnerable to marine pollution, climate change, and disturbance of its breeding sites.
The Snowy Owl is a large nocturnal raptor, easily recognizable by its pure white plumage, speckled with dark spots on its back and wings. It measures about 55 to 65 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.3 to 1.5 meters, and weighs between 1.5 and 2.5 kg. Its head is round, with large, piercing yellow eyes and a short, hooked beak. The Snowy Owl primarily inhabits the Arctic regions, notably in Canada, Alaska, Scandinavia, and Russia, where it frequents tundras and snowy landscapes. It primarily feeds on small mammals, such as lemmings, but also hunts birds and occasionally fish. This raptor is an excellent hunter, capable of spotting its prey with its keen vision, even in low light conditions. Although the Snowy Owl is not currently endangered, it is sensitive to climate change and the loss of its natural habitat.
The Common Merganser is a large diving duck measuring between 58 and 71 cm in length, with a wingspan of 82 to 97 cm. The male features a dark green iridescent head, white body, and black back, while the female has a reddish-brown crested head and light gray body. This duck is characterized by its long, slender red bill with serrated edges, ideal for catching slippery fish. It inhabits clear-water rivers and lakes in forested regions of Europe, Asia, and North America. Nesting in tree cavities or cliff crevices, it lays between 6 and 17 eggs per season. Its diet mainly consists of fish, but also includes amphibians, crustaceans, and aquatic insects. Although listed as Least Concern, habitat loss can locally impact its populations.
The Hooded Merganser is a medium-sized duck, easily recognizable by its distinctive crest and vibrant colors. It measures about 40 to 50 cm in length, with a wingspan of 60 to 70 cm, and weighs between 400 and 700 g. The male, during the breeding season, has a black and white head with an impressive crest of white feathers on top. Its plumage is mainly black and white, with shades of brown and green, and it has a short, wide beak adapted for feeding on fish, crustaceans, and aquatic invertebrates. The female, on the other hand, is more subtle, with light brown plumage and a less prominent crest. The Hooded Merganser primarily inhabits North America, particularly in the northeastern United States, where it frequents lakes, rivers, and wetland areas. It is an excellent diver, capable of diving underwater to capture its prey. Although the species is not in immediate danger, it is vulnerable to habitat loss and water pollution.
The Red-breasted Merganser is a slender diving duck, measuring about 52 to 58 cm in length with a wingspan of 67 to 82 cm. The male features a dark green head with a shaggy crest, a white collar, a rusty speckled chest, and a thin red bill. The female has a reddish-brown head with a more subdued crest, a grayish body, and a duller red bill. This duck inhabits coastal waters, estuaries, bays, and large lakes, favoring saline or brackish areas. It primarily feeds on small fish, but also consumes crustaceans, aquatic insects, and amphibians, captured using its serrated bill adapted for fishing. A migratory species, it nests on the ground near water, often concealed under vegetation or in rocky crevices. Although listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, the Red-breasted Merganser is sensitive to water pollution, coastal habitat destruction, and human disturbances.
The Harpy Eagle is one of the most powerful and impressive raptors in the world, easily recognizable by its large size and distinctive crest of feathers on its head. It measures between 86 and 107 cm in length, with a wingspan of 2 to 2.3 meters, and weighs between 6 and 10 kg. Its plumage is primarily dark gray and black, with white spots on the wings and belly, and a head adorned with a crest of feathers, giving it an imposing appearance. The Harpy Eagle primarily inhabits the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, notably in Mexico, Panama, Colombia, and Brazil. Carnivorous, it primarily feeds on mammals such as monkeys, sloths, and coatis, which it captures in flight or on trees with its powerful talons. Although the Harpy Eagle is not yet critically endangered, its population is threatened by deforestation, habitat loss, and illegal hunting.
The Ermine is a small carnivorous mammal of the weasel family, easily recognizable by its immaculate white winter coat, which contrasts with its black-tipped tail. It measures about 25 to 35 cm in length, with a tail that can reach up to 10 cm, and weighs between 100 and 350 g. During the summer, its coat is typically brown with a lighter belly, but it turns completely white in winter, except for the black tip of its tail. The Ermine primarily inhabits forests, grasslands, and mountainous areas across Eurasia and North America. It is an excellent hunter, feeding mainly on small mammals such as mice, voles, but also on birds and eggs. The Ermine uses its hunting skills to capture prey with great agility and speed. While it is not endangered, the Ermine can be affected by habitat loss and climate change, particularly affecting the color of its fur.
The Grey Heron is a large wading bird, easily recognizable by its slender silhouette, long neck, and large legs. It stands about 90 cm tall, with a wingspan of 1.5 to 1.9 meters, and weighs between 1.5 and 2 kg. Its plumage is primarily gray, with white markings on the belly and underside of the wings, and a white head adorned with distinctive black feathers. It has a long, pointed yellow beak, adapted for capturing its prey, primarily fish, amphibians, insects, and occasionally small mammals. The Grey Heron inhabits wetlands, marshes, rivers, and lakes across Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It is an excellent hunter, patiently waiting by the water's edge to capture its prey with its beak. Although the species is not endangered, it can be vulnerable to water pollution, habitat loss, and human disturbance.
The Cattle Egret is a small heron with primarily white plumage, featuring touches of yellow on the neck and head during the breeding season. It measures about 55 to 60 cm in length, with a wingspan of 90 to 100 cm, and weighs between 300 and 500 g. This heron is notable for its social behavior, often seen in the company of large herds of cattle or near farm animals, hence its name "cattle egret." It takes advantage of the presence of these animals to hunt insects, worms, and other small animals disturbed by the movement of livestock. The Cattle Egret primarily inhabits Africa, Asia, and parts of Europe, such as the Mediterranean. It feeds mainly on small invertebrates, insects, and occasionally small fish, and is particularly efficient in agricultural and wetland areas. Although the species is widely spread, it may be vulnerable to habitat loss and changes in farming practices.
The Purple Heron is a large wading bird, easily recognizable by its colorful plumage, ranging from purple to reddish, with shades of brown and blue. It measures about 80 to 100 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.3 to 1.5 meters, and weighs between 600 and 1,200 g. Its beak is long, thin, and pointed, with a yellowish-green color, while its legs are long and gray. During the breeding season, the Purple Heron sports decorative plumes on its head and neck. It primarily inhabits wetlands, marshes, rivers, and lakes across Europe, Africa, and Asia, where it feeds on fish, crustaceans, small mammals, and occasionally insects. It primarily hunts at night or during twilight, using its great agility to capture prey in the water. Although the species is not immediately endangered, it is vulnerable to habitat loss, water pollution, and human disturbance.
The Short-eared Owl is a small nocturnal raptor, easily recognizable by its pale yellowish plumage and large, piercing yellow eyes. It measures about 34 to 40 cm in length, with a wingspan of 80 to 95 cm, and weighs between 180 and 400 g. Its face is disc-shaped, like that of other owls, and its plumage, which is cream or brown, is speckled with dark spots that provide excellent camouflage in the grasslands and marshes where it resides. The Short-eared Owl primarily inhabits open areas, such as marshes, grasslands, and farmland, across Europe, Asia, and North America. It mainly hunts small mammals, such as voles and mice, as well as birds and insects. This raptor is an excellent nocturnal hunter, using its very sensitive ears and sharp vision to locate prey in the dark. Although the species is not immediately endangered, it is vulnerable to habitat loss, water pollution, and human disturbance.
The Long-eared Owl is a medium-sized nocturnal raptor, easily recognizable by its large tufts of feathers shaped like "ears" on its head. It measures about 35 to 40 cm in length, with a wingspan of 85 to 100 cm, and weighs between 250 and 400 g. Its plumage is generally gray or brown with dark banded patterns, allowing it to blend perfectly in wooded and open forest areas. It has large yellow eyes and a disc-shaped face, like other owls, which helps it capture sound in the dark. The Long-eared Owl primarily inhabits forests, woodlands, and heathlands across Europe, Asia, and North Africa, where it primarily feeds on small mammals, such as voles, mice, and occasionally birds. It generally hunts at dusk, using its sharp vision and keen hearing to detect its prey. While the species is not endangered, it is vulnerable to deforestation and habitat loss.
The Common Hippopotamus is a large semi-aquatic mammal, easily recognizable by its massive body and thick skin. It measures between 3.3 and 4.5 meters in length, with a weight reaching 1,500 to 1,800 kg, or more. Its body is primarily gray, with pink skin underneath the belly and ears and eyes positioned high on its head, allowing it to see and hear while submerged in water. Hippos are primarily herbivores, feeding on grass and aquatic vegetation in large quantities, mostly at night. They spend most of their time in the water to regulate their body temperature and prevent dehydration, while still being able to move quickly on land. The Common Hippopotamus primarily inhabits sub-Saharan Africa, in rivers, lakes, and swamps. Although it is a powerful and territorial animal, it is threatened by habitat loss, hunting, and conflicts with human populations.
The Pygmy Hippopotamus is a smaller species of hippopotamus, much smaller than its cousin the Common Hippopotamus, with an adult size measuring about 1.5 to 1.75 meters in length and weighing between 180 and 275 kg. Its coat is gray-olive or dark brown, with smooth and thick skin. Unlike the Common Hippopotamus, the Pygmy Hippopotamus primarily inhabits the forests of West Africa, particularly in Liberia, Sierra Leone, Guinea, and Côte d'Ivoire, and prefers shallow rivers and swamps rather than vast expanses of water. It is primarily herbivorous, feeding on aquatic vegetation and foliage, but unlike its cousin, it does not spend all its time in the water and can be more active on land. The Pygmy Hippopotamus is a nocturnal and solitary species, often elusive and difficult to observe. Although it is less exposed to threats than the Common Hippopotamus, it is still endangered due to habitat loss, hunting, and human disturbance.
The Red-shouldered Hawk is a large bird of the Cracidae family, easily recognizable by its imposing plumage and its crest on the head. It measures about 75 to 90 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.2 to 1.4 meters, and weighs between 2 and 3 kg. Its plumage is primarily brown, with lighter feathers on the belly and distinctive markings on the wings and back. Its head is adorned with a reddish crest, giving it a distinctive appearance. The Red-shouldered Hawk lives primarily in the tropical and subtropical forests of Venezuela, Colombia, and Panama. It is often found in mountainous regions, where it frequents wooded areas and rocky slopes. The Red-shouldered Hawk is primarily herbivorous, feeding on fruits, seeds, and leaves. It is a terrestrial bird, preferring to move by walking rather than flying. Although the species is not critically endangered, it is vulnerable to deforestation and loss of its natural habitat.
The Southern Hornbill, also known as the Yellow-billed Hornbill, is a large tropical bird easily recognized by its large beak and distinctive casque. It measures about 55 cm in length and weighs between 130 and 150 g. Its plumage is primarily black and white, with characteristic yellow and orange hues on the beak and casque, giving it a striking appearance. The Southern Hornbill primarily inhabits forests and savannas in Southern Africa, notably in Namibia, South Africa, and Botswana. This bird is omnivorous, feeding on fruits, insects, small reptiles, and occasionally small mammals. It is known for its social behavior, often living in small groups or families. Although the species is not currently endangered, it can be vulnerable to habitat loss due to agriculture and deforestation.
The Eurasian Oystercatcher is a coastal bird easily recognizable by its black and white plumage and long orange beak. It measures about 40 to 45 cm in length, with a wingspan of 75 to 85 cm, and weighs between 300 and 400 g. Its beak is long and straight, ideal for digging up shellfish and other mollusks, which it primarily consumes, though it also feeds on worms and marine insects. The Eurasian Oystercatcher primarily inhabits the coasts of Europe, north-west Africa, and parts of Asia. It prefers beaches, estuaries, and mudflats where it can forage at low tide. This bird is very territorial and can be seen in small colonies during the breeding season, but typically lives alone or in small groups outside of that period. Although the species is not immediately endangered, it is sensitive to habitat loss, beach pollution, and human disturbance.
The Eurasian Hoopoe is a bird with a spectacular plumage, easily recognizable by its colorful crest of feathers that it raises in the shape of a tuft on its head. It measures about 25 to 29 cm in length, with a wingspan of 44 to 48 cm, and weighs between 40 and 70 g. Its plumage is primarily light beige, with black and white stripes on the back and wings, and its beak is long, thin, and slightly curved, ideal for probing the ground in search of insects and other small prey. The Eurasian Hoopoe primarily inhabits open areas, such as grasslands, orchards, forest edges, and cultivated areas across Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It mainly feeds on insects, such as ants, termites, and larvae, which it catches by probing the ground. This bird is an excellent flier, capable of flying long distances with powerful wingbeats. Although the species is not endangered, it is vulnerable to habitat loss and the intensification of agriculture.
The Striped Hyena is a medium-sized carnivore, easily recognizable by its striped coat and unique behavior among hyenas. It measures about 90 cm in length, with a shoulder height of 60 cm, and weighs between 40 and 60 kg. Its coat is mainly gray or beige, with black stripes on the flanks, helping it blend into its environment. The Striped Hyena has a wide head, large ears, and an elongated muzzle, along with a short tail. Unlike the spotted hyena, the Striped Hyena is more solitary and prefers to hunt alone or in small groups. It primarily feeds on small mammals, reptiles, and insects, but is also opportunistic and a scavenger, feeding on the carcasses of dead animals. It is found mainly in North Africa, in arid and semi-arid areas such as deserts and savannas. While the Striped Hyena is not endangered, it is threatened by habitat loss and human conflict.
The Spotted Hyena is a robust carnivore, known for its complex social behavior and distinctive call. It measures between 90 and 150 cm in length, with a shoulder height of about 70 cm, and weighs between 40 and 80 kg. Its coat is characterized by black and brown spots on a yellow-gray background, giving it a unique appearance. The Spotted Hyena primarily inhabits savannas, open grasslands, and wooded areas in sub-Saharan Africa, where it forms large clans organized around a strict hierarchy. It is primarily carnivorous, feeding on large prey such as gazelles and zebras, but it is also an opportunistic scavenger, feeding on carcasses of animals killed by other predators. It is an effective hunter, using group strategies to capture prey. Although the species is relatively abundant, it is sometimes viewed negatively due to its reputation as a scavenger, but it plays an important role in ecosystems by eliminating carcasses and regulating animal populations.

The Bald Ibis is a large migratory bird, easily recognizable by its dark plumage and bare head, adorned with a light down. It measures about 65 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.3 to 1.4 meters, and weighs between 1.5 and 2.5 kg. Its plumage is brownish-red, with metallic green and purple hues that appear in the light. The head of the Bald Ibis is almost completely devoid of feathers, except for a small tuft of feathers on the top. It has a long curved beak, adapted for probing the ground in search of small invertebrates, worms, and seeds. The Bald Ibis primarily inhabits wetlands, marshes, and river valleys in the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Europe. It is primarily herbivorous and insectivorous, feeding on aquatic plants and small animals found in marshy areas. The Bald Ibis is a migratory species, moving in groups during the breeding season and winter. While the species has been severely reduced in its range, conservation efforts have helped maintain small populations in certain areas. However, it remains vulnerable to habitat loss and human disturbance.
The Glossy Ibis is an elegant bird, easily recognizable by its iridescent brown-green plumage and its long, curved bill shaped like a sickle. It measures about 60 to 70 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.1 to 1.2 meters, and weighs between 350 and 500 g. Its plumage is generally dark, with metallic shades of green and bronze that shine in the light. The Glossy Ibis is also distinguished by its long, slender legs and graceful neck. This bird primarily inhabits wetlands, such as marshes, rivers, and shallow lakes, where it feeds on small aquatic invertebrates, mollusks, insects, and fish. It uses its long, curved bill to probe in the water and mud in search of food. The Glossy Ibis is a migratory species, living in colonies during the breeding season. It is primarily found in Europe, North Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia. While the species is not immediately endangered, it is sensitive to habitat loss and water pollution.
The Sacred Ibis is a large bird with primarily white plumage, with black feathers on its wings and a bare head. It measures about 65 to 75 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.2 to 1.3 meters, and weighs between 1.5 and 2.5 kg. Its beak is long and curved, adapted for probing the ground in search of small invertebrates, fish, crustaceans, and mollusks. The Sacred Ibis primarily inhabits wetlands, such as marshes, rivers, and lakes, in sub-Saharan Africa, as well as Southeast Asia and Egypt. This bird holds particular significance in ancient Egyptian culture, where it was associated with the deity Thoth, the god of wisdom and writing. The Sacred Ibis is often seen in large colonies and prefers to feed in groups, probing water and mud for food. Although the species is not immediately endangered, it is vulnerable to habitat loss, pollution, and hunting.
The Marine Iguana is a unique species found exclusively on the Galápagos Islands. This iguana is the only reptile to have adapted to aquatic life, feeding on marine algae that it collects underwater while diving. It has a distinct morphology with a robust body and a long tail, allowing it to swim efficiently. Marine iguanas are often seen basking on rocks in the sun to regulate their body temperature after their dives into cold water. This thermal hibernation behavior is essential for their survival in the Galápagos environment.

The Black Iguana, also known as Ctenosaura similis, is a medium-sized terrestrial reptile, easily recognizable by its bright colors and distinctive scales. It measures between 40 and 60 cm in length, with a tail that can measure up to twice its body length, and weighs between 300 and 600 g. Its body is typically dark gray to black, with light spots and stripes that help it blend into its natural environment. The Black Iguana primarily inhabits dry and arid areas and dry forests in Central America, notably in Costa Rica, Nicaragua, and Honduras. It primarily feeds on fruits, leaves, and flowers but can also consume insects and small animals. Although it is an excellent climber, it prefers to spend most of its time on the ground or in shrubs. The Black Iguana is known for its ability to move quickly to escape predators and can also swim and dive into water for protection. While the species is generally considered not threatened, it is vulnerable to habitat destruction and illegal collection for the wildlife trade.
The Green Iguana is a large herbivorous reptile, easily recognizable by its long and sturdy body, as well as its bright green coloration. It measures between 1.5 and 2 meters in length, including its tail, and can weigh between 4 and 5 kg. Its body is covered with large scales and plates, and it has a crest running down its back. Its vibrant green color, especially in young individuals, becomes duller with age. The Green Iguana primarily inhabits tropical forests, mangroves, and wooded areas in Central and South America, as well as parts of the Caribbean. This reptile is primarily herbivorous, feeding on leaves, fruits, flowers, and sometimes young shoots. The Green Iguana is an excellent climber and spends much of its time in trees or resting on branches. While it is a widespread species, it is threatened by deforestation, illegal collection for the wildlife trade, and habitat loss.
The Impala is a medium-sized, slender, and graceful antelope, easily recognizable by its elegant, curved horns and its light brown to reddish coat, with a white belly and tail. It stands about 70 to 90 cm at the shoulder, with a total length of 1.2 to 2 meters, and weighs between 40 and 75 kg. Males have long, fine, lyre-shaped horns that can reach up to 90 cm in length, while females, which lack horns, are generally smaller. The Impala primarily inhabits savannas and woodland grasslands in East and Southern Africa, where it forms complex social groups. It primarily feeds on grass, but may also eat leaves and fruits when grass is less abundant. The Impala is an excellent runner, capable of making long leaps to escape its predators. Although the Impala is quite widespread, it is vulnerable to habitat loss and excessive hunting.

The Pyrenean Chamois, or Rupicapra pyrenaica, is a medium-sized ungulate, easily recognizable by its reddish-brown coat and curved horns. It measures about 70 to 80 cm at the shoulder, with a length of 1 to 1.2 meters, and weighs between 25 and 50 kg. Its body is compact and robust, adapted for mountainous terrain, with long and powerful legs, perfect for moving on steep slopes. The Pyrenean Chamois primarily inhabits the mountains of the Pyrenees, the northern region of Spain, and southern France. It prefers rocky slopes and wooded areas, where it feeds mainly on grasses, plants, berries, and young shoots. The Pyrenean Chamois is a shy and elusive animal, living in family groups during the winter, but often separating into small groups or remaining solitary during the summer. Although the species nearly disappeared in the early 20th century, conservation efforts have led to its recovery. The Pyrenean Chamois is currently classified as a species of least concern, but it remains vulnerable to hunting and habitat loss.
The Jaguar is a large, robust, and powerful feline, easily recognizable by its spotted coat, characterized by dark rosettes on a golden or yellow background. It measures between 1.2 and 1.8 meters in length, with a tail of 60 to 80 cm, and weighs between 45 and 100 kg, with males generally being larger than females. Its body is massive and muscular, adapted for hunting in a variety of environments, from tropical forests to savannas. The Jaguar possesses one of the most powerful jaws in the animal kingdom, capable of piercing the thick skin of its prey, such as capybaras, deer, and even reptiles like caimans. It is also capable of swimming and often hunts aquatic animals. This feline primarily inhabits Central and South America, from southern Mexico to Argentina, preferring tropical forests, swamps, and riparian zones. While the species is still relatively widespread, it is threatened by deforestation, illegal hunting, and habitat loss.
The Bohemian Waxwing is a small colorful bird, easily recognizable by its characteristic crest and the black edges of its feathers. It measures about 20 cm in length, with a wingspan of 30 to 35 cm, and weighs between 50 and 70 g. Its plumage is primarily light gray with bright yellow and red hues on its wings and tail, and it has red and yellow feathers decorating the tips of its plumage. The Bohemian Waxwing primarily inhabits the dense coniferous and deciduous forests of northern Europe and Asia, as well as North America. It is often found in groups, feeding primarily on berries, especially those from juniper and sea buckthorn trees, but it can also eat insects and seeds. This small passerine is also known for its soft call and social behavior, particularly during migration in groups. Although the species is not endangered, it is sensitive to climate change and the availability of its preferred food, berries.
The Kakapo is a nocturnal and terrestrial parrot, easily recognizable by its moss-green plumage and large wings, although this bird cannot fly. It measures about 60 cm in length and weighs between 2 and 4 kg, making it the heaviest parrot. Its plumage is mainly green, with yellow and brown hues that help it blend into its natural environment. The Kakapo is found exclusively in New Zealand, where it prefers dense forests and mountainous areas. It is herbivorous and feeds on plants, fruits, seeds, and roots. Due to its inability to fly, it has developed excellent climbing skills and primarily moves by walking. The species has been severely threatened over the centuries by predation from introduced mammals and habitat loss. Today, the Kakapo is an extremely rare and critically endangered bird, with intense conservation efforts focused on protecting the remaining individuals.
The Kangaroo is an iconic marsupial, famous for its large size, powerful hind legs, and long tail. It typically measures between 1 and 1.8 meters in length, with a tail length of 80 to 100 cm, and can weigh between 18 and 90 kg, depending on the species. Its coat varies depending on the species but is generally gray or red, with dense fur that protects it from the extreme temperatures of Australia. The Kangaroo is an excellent jumper, capable of covering large distances with its powerful hind legs and its tail, which serves as a counterbalance when it moves. Herbivorous, it primarily feeds on grass, leaves, and young shoots. Kangaroos primarily inhabit open plains, forests, and savannahs in Australia. They are social animals, often living in groups called "mobs," although they can also be solitary. While the species is not endangered, it is sometimes threatened by habitat loss, bushfires, and competition with livestock.
The Red Kangaroo is one of the most iconic and largest species of kangaroos in Australia. It is easily recognizable by its red-brown fur and large size, with adult males reaching over 2 meters in length, including their tail. The Red Kangaroo lives in the dry and semi-arid regions of the Australian Outback, where it primarily feeds on grasses and plants. This animal is an excellent jumper and uses its powerful hind legs to travel at high speeds, often performing impressive leaps. While it is mainly active at dusk and dawn, it can also adapt to the extreme temperatures of its environment.
The Kea is a large parrot endemic to New Zealand, easily recognizable by its bright green plumage and reddish-edged feathers on its neck and under its wings. It measures about 48 cm in length and weighs between 800 and 1,200 g. This parrot is one of the most intelligent of its kind, capable of using tools to solve complex problems and adapt to a variety of environments. The Kea is omnivorous and opportunistic, feeding on fruits, roots, seeds, small animals, as well as carcasses of dead animals. It is particularly known for its curious and sometimes destructive behavior, earning it a reputation as a "thief" in some areas. The Kea primarily inhabits the alpine mountains of the South Island of New Zealand, where it resides at high altitudes. While the species is protected, it remains vulnerable to habitat loss and human threats such as trapping and vehicle collisions. The Kea population has declined over the years, but conservation efforts are underway to ensure its survival.
The Kiang is a large wild equid, closely related to the horse, primarily found in the high plateaus and mountains of the Himalayas and Tibet. It stands about 1.3 to 1.5 meters at the shoulder and weighs between 300 and 400 kg. Its coat is typically brownish-red or gray-brown with lighter shades on the belly and around the legs, and it has a short and sparse mane. The Kiang has a broad head and a bushy tail, similar to that of a horse. It primarily inhabits arid regions and high-altitude grasslands, feeding on grasses and woody plants. Highly social, the Kiang lives in large groups that move together in search of food. Unlike other wild equids, it is more tolerant of cold conditions and can survive at extremely high altitudes, up to 5,000 meters. While the species is relatively abundant in its range, it can be threatened by habitat loss due to climate change and human pressure, particularly from grazing and hunting.
The Kiwi is a bird endemic to New Zealand, famous for its brown, fluffy plumage, small size, and long straight bill. It measures about 40 to 50 cm in height, with a wingspan of 60 to 80 cm, and weighs between 1 and 4 kg depending on the species. The Kiwi is one of the most distinctive birds in the world due to its unique appearance: it has small wings that do not allow it to fly, a long delicate nose, and short legs adapted for its terrestrial life. It primarily inhabits the forests, woods, and grasslands of New Zealand, where it feeds on earthworms, insects, fruits, and roots. The Kiwi is a nocturnal bird, feeding primarily at night and being particularly vulnerable to introduced predators such as rats, mustelids, and dogs. It is also threatened by the loss of its natural habitat, and several species of Kiwi are critically endangered. Active conservation, such as nest protection and predator elimination, is essential to ensure the survival of these iconic birds.
Koala
Phascolarctos cinereus
The Koala is an iconic tree-dwelling marsupial from Australia, easily recognizable by its grey-silver fur, large round ears, and heart-shaped black nose. It measures about 60 to 85 cm in length and weighs between 4 and 15 kg, with males generally being larger than females. The Koala has powerful claws adapted for its tree-dwelling lifestyle, spending almost its entire life in trees and feeding primarily on eucalyptus leaves. Its diet is very specific, and while eucalyptus is an abundant food source, it is also toxic to most other animals, providing the Koala with some degree of protection from predators. The Koala is a nocturnal and solitary animal, spending the majority of the day sleeping in trees, seeking refuge in Australia's forested areas. It is a symbol of Australian wildlife, but its habitat is threatened by deforestation, bushfires, and disease, which has led to a decline in its population. Conservation efforts are underway to protect this marsupial and its natural habitat.
The Parasitic Jaeger, or Stercorarius parasiticus, is a medium-sized seabird, easily recognizable by its pointed wings and dark plumage. It measures about 45 to 50 cm in length, with a wingspan of 110 to 125 cm, and weighs between 300 and 450 g. Its plumage is typically dark brown or gray on the back, with a lighter belly. Adults have a distinctive feature: a forked tail with extended feathers, especially in males. The Parasitic Jaeger is a migratory bird that primarily inhabits the Arctic and subarctic regions but moves to more temperate zones during the winter. This bird is particularly known for its parasitic behavior, in which it chases other seabirds to force them to drop their catch, allowing the Jaeger to steal their food. The Parasitic Jaeger is also an excellent flyer, capable of traveling long distances. While the species is not endangered, it is sensitive to human disturbances and climate changes that affect its coastal habitat.
The Rock Ptarmigan is a mountain bird adapted to the harsh conditions of high peaks. It measures about 35 to 40 cm in length and weighs between 350 and 650 g. In winter, its plumage is entirely white, allowing it to blend into the snow, while in summer, it has a brown-red plumage with dark spots to better blend into the rocks and grasses of the mountains. The Rock Ptarmigan primarily inhabits mountainous regions of Europe, Asia, and North America at high altitudes, where it feeds on plants, seeds, berries, and young shoots. Due to its thick plumage and feather-covered legs, it is well adapted to cold conditions but is also vulnerable to climate change, particularly to the loss of its mountainous habitat. The species is protected in some areas but remains sensitive to human disturbances, such as mountain tourism and temperature changes.
The Willow Ptarmigan is a mountain bird, smaller than its cousin the Rock Ptarmigan, found in cold regions and forested areas of northern Europe and Asia. It measures about 30 to 35 cm in length and weighs between 250 and 400 g. Its plumage changes with the seasons: in winter, it is entirely white, allowing it to blend into the snow, while in summer, it has a brown-red spotted plumage, perfect for blending into the moors and shrubs. The Willow Ptarmigan primarily inhabits taiga and tundra regions, where it feeds on leaves, berries, and young shoots. It is often seen on the ground or in bushes, searching for food. While the species is not immediately threatened, it is vulnerable to disturbances from deforestation and climate change, which affect mountain ecosystems.
The Scottish Ptarmigan, or Lagopus lagopus scotica, is a subspecies of the Willow Ptarmigan, specifically found in the mountains of Scotland. It measures about 30 to 35 cm in length and weighs between 300 and 450 g. Its plumage changes with the seasons: in winter, it is entirely white, allowing it to blend perfectly into the snow, while in summer, it has a brown-red spotted plumage that makes it blend into the Scottish moorlands. The Scottish Ptarmigan inhabits the highlands, particularly in the northern mountains of Scotland, where it primarily feeds on plants, berries, seeds, and young shoots. Although it is a bird difficult to spot due to its excellent camouflage, it remains vulnerable to climate change and the loss of its natural habitat. The Scottish Ptarmigan is also threatened by predation from foxes and mustelids and by human activities, including tourism and land management.
The West Indian manatee is a large marine mammal, often called the 'sea cow.' It primarily lives in shallow coastal waters, estuaries, and rivers of the Caribbean, Gulf of Mexico, and Florida. This herbivorous mammal feeds mostly on aquatic plants and can consume up to 100 kg of vegetation per day. The West Indian manatee is a calm and slow-moving animal, with thick skin and sensitive whiskers that help it detect food in the water. While not aggressive, it is endangered due to habitat loss, boat collisions, and water pollution.
The Langur is a type of monkey primarily found in the forests of South and Southeast Asia. There are several species of langurs, all characterized by dense and typically colorful fur, ranging from black to gray, sometimes with golden or white tints depending on the species. These primates typically measure between 40 and 70 cm in length, with a long, prehensile tail that can exceed the length of their body. They weigh between 10 and 20 kg, with males generally being larger than females. Langurs are herbivores, primarily feeding on leaves, fruits, seeds, and flowers, and they often live in organized social groups. They are known for their ability to move quickly through trees thanks to their long and agile limbs. While some langurs are threatened by deforestation and habitat loss, many species are still relatively widespread within their range. Langurs play a crucial role in the ecosystem by helping to disperse seeds and maintaining the balance of forest vegetation.

The European Rabbit is a small herbivorous mammal, widely distributed across Europe and in certain parts of the world where it has been introduced. It measures about 40 to 50 cm in length, with a short tail and soft fur that varies from light gray to brown, with a white belly. The European Rabbit is known for its long ears, bright eyes, and powerful hind legs that allow it to leap quickly. It typically lives in groups in burrows called "warrens," which it digs in soft soils or dense vegetation. This rabbit is primarily herbivorous, feeding on grasses, roots, leaves, and fruits. While it is an excellent breeder, with several litters a year, it is vulnerable to predators such as foxes, birds of prey, and carnivores. Despite its large population, the European Rabbit is threatened in some areas by excessive hunting, habitat loss, and the spread of diseases. It plays an important role in ecosystems as prey for many carnivores and as an ecological engineer, digging burrows that alter soil structure.
The Pallas's Cat, or Otocolobus manul, is a small wild cat primarily found in the steppes and mountains of Central Asia. It measures about 50 cm in length, with a tail of about 20 to 30 cm, and weighs between 2 and 5 kg. It has a thick, dense coat that is light gray to beige, with dark stripes on the back and lighter spots on the belly, allowing it to blend perfectly into its environment. The cat is also known for its large, rounded ears and piercing eyes. The Pallas's Cat is a solitary, primarily nocturnal hunter that feeds on small mammals, birds, and insects. While it is an excellent predator, it is often difficult to spot due to its elusive nature and lifestyle in harsh terrain. The species is threatened by habitat loss, hunting, and competition with humans for natural resources. Conservation efforts are underway to protect the Pallas's Cat and its habitats.
The Cavendish Dik-dik is a small antelope found mainly in the semi-arid zones and savannas of East Africa. It stands about 40 cm tall at the shoulder, with a body length of 60 to 70 cm, and weighs between 3 and 6 kg. This small herbivore is easily recognized by its compact size, sharp muzzle, and bright eyes. Its coat is typically gray-brown, with lighter shades on the belly and distinct markings around the eyes, giving it an alert expression. The Cavendish Dik-dik is a discreet animal, often seen alone or in small family groups, preferring to avoid large human concentrations. It primarily feeds on herbaceous plants, fruits, seeds, and leaves. Its small size allows it to slip easily through bushes and tall grasses to escape predators. While the species is not currently endangered, it is vulnerable to habitat loss and pressures from human activities.
The White-fronted lemur is a species of lemur endemic to Madagascar, where it primarily lives in the humid tropical forests of the island's northwest. It is easily recognized by its gray-brown fur and the large white patch on its forehead, from which it derives its name. This lemur is primarily frugivorous, feeding on fruits, flowers, and nectar. It lives in complex social groups and exhibits strong territorial behaviors, including loud vocalizations to define its territory. Although often active during the day, it is also known to be particularly active at dusk.
The Leopard is a powerful and agile big cat, easily recognizable by its spotted coat, formed by black rosettes on a golden or yellow background. It typically measures between 1.2 and 1.9 meters in length, with a tail of 60 to 100 cm, and weighs between 30 and 90 kg, with males generally being larger than females. The Leopard is a solitary, nocturnal hunter, known for its ability to climb trees, often to hide its prey and avoid other carnivores. It is an opportunist, feeding on various types of prey, ranging from small mammals to medium-sized ungulates, and sometimes even reptiles and birds. This big cat is found across much of sub-Saharan Africa and in certain regions of Asia, including India, China, and parts of the Middle East. While the Leopard is a relatively widespread species, it is threatened by habitat loss, illegal hunting, and the depletion of its natural prey. It remains one of the most formidable and adaptable predators in the savanna, forests, and mountains.
The Garden Dormouse is a small nocturnal rodent, often compared to a miniature squirrel, found primarily in Europe and Asia. It measures about 20 cm in length, with a tail of around 12 cm, and weighs between 100 and 150 g. Its coat is typically light gray or brown, with a dark line running from its eyes to its back and a lighter area on its belly. The Garden Dormouse is primarily nocturnal and arboreal, feeding on fruits, nuts, seeds, as well as small insects and larvae. It is an excellent climber and takes refuge in trees or crevices to sleep during the day. This rodent is a hibernator, retreating into its nest in the fall to survive the winter, which is essential for its survival in the cold. Although the Garden Dormouse is protected in some areas, it is threatened by deforestation and the reduction of its natural habitat.
The Frill-necked lizard, or Frill-necked dragon, is a fascinating lizard native to the dry and wooded regions of northern Australia. This reptile is famous for its distinctive frill, a fold of skin around its neck that it can extend to impress predators or compete with other males. When threatened, it extends its frill and adopts an aggressive posture, opening its mouth wide to appear larger. The Frill-necked lizard is insectivorous, primarily feeding on insects and small invertebrates, which it captures using its quick tongue. It is also an excellent climber and can move quickly between trees.
The European Hare is a large herbivorous mammal, easily recognizable by its long ears and powerful hind legs. It measures about 50 to 70 cm in length, with a short tail and a wingspan of 70 to 90 cm, and weighs between 3 and 5 kg. Its coat varies with the seasons: in winter, it becomes lighter, while in summer, it takes on a brown or gray hue, allowing it to blend effectively into fields and meadows. The European Hare is a solitary and territorial animal, primarily found in open areas such as fields, meadows, and sparse woodlands. It is particularly fast and agile, capable of running at speeds of over 60 km/h when pursued. This hare primarily feeds on grasses, leaves, fruits, and roots. Although the species is widespread in Europe, it faces threats from hunting, habitat loss, and human disturbances.
The Cape Hare is a large herbivorous mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa, particularly found in open areas, savannas, and semi-arid regions. It measures between 50 and 70 cm in length, with a tail of 10 to 12 cm, and weighs between 2 and 4 kg. Its coat is generally light brown or gray with a lighter belly, allowing it to blend effectively into its environment. The Cape Hare is a nocturnal and crepuscular animal, primarily feeding on plants, grasses, fruits, and roots. While it is a fast runner, reaching speeds of 50 to 60 km/h, it prefers discretion and often remains hidden during the day in bushes or tall grasses. This hare is also known for its ability to remain motionless and quickly adapt to its surroundings, making it difficult for predators to spot. While the species is relatively common, it can be threatened by habitat loss and hunting.
The Iberian Hare is a rodent endemic to the Iberian Peninsula, primarily found in Spain and Portugal. It measures between 50 and 60 cm in length, with a tail of 6 to 9 cm, and weighs between 2 and 3 kg. This hare is smaller than its European cousin, with a lighter coat, often gray-brown or light brown, with darker markings on the back and a paler hue on the belly. The Iberian Hare primarily inhabits open plains, oak forests, and meadows, where it feeds on vegetation, mainly grasses, roots, leaves, and sometimes young shrub shoots. It is a crepuscular and nocturnal animal, most active at dusk and during the night. While the species is not immediately endangered, it is threatened by habitat loss, hunting, and the introduction of predators such as foxes and dogs.
The Mountain Hare is a small mammal, easily recognizable for its ability to change color according to the seasons. In winter, its coat becomes completely white, allowing it to blend perfectly into the snow, while in summer, it has a brown or gray coat, with darker shades on its back and lighter hues on its belly. It measures about 50 to 70 cm in length, with a tail of 6 to 8 cm, and weighs between 2 and 4 kg. The Mountain Hare is primarily found in the cold, mountainous regions of Northern Europe, Northern Asia, and certain mountainous areas of North America. It is a herbivorous animal that feeds on a variety of vegetation, primarily grasses, roots, fruits, and young shoots. It is mainly active at dusk and during the night, hiding in bushes or under grasses during the day. Although it is quite resilient to cold temperatures, the species is threatened by habitat loss and climate changes affecting its natural environment.
The Lion is one of the largest land predators, often called the "king of the animals." It measures between 1.2 and 2.5 meters in length, with a tail of about 80 to 100 cm, and weighs between 120 and 250 kg, with males generally being larger and more massive than females. Male lions are easily recognizable by their majestic mane, which varies in color from light blonde to dark brown. Their coat is generally golden to light brown, with lighter patches on the belly and under the legs. Lions primarily live in Africa, with a small population in Asia (particularly in Gir National Park, India). They prefer open savannas, grasslands, and light forests. The lion is a social predator that typically hunts in groups, with females doing most of the hunting. Their diet consists mainly of large herbivores such as zebras, gazelles, and buffaloes. While the lion is an iconic species, it is threatened by habitat loss, human conflicts, and the depletion of its natural prey.
The Dormouse with a Bushy Tail is a small nocturnal rodent, easily recognizable by its large bushy tail, which is one of its distinctive features. It measures about 20 to 25 cm in length, with a tail of around 10 to 15 cm, and weighs between 50 and 150 g. Its coat is generally gray or brown, with a lighter shade on the belly, and it has large round ears and bright eyes. The Dormouse with a Bushy Tail primarily lives in forests, hedgerows, and gardens, where it feeds on fruits, seeds, nuts, as well as small creatures like insects. It is mainly active at night, taking refuge in tree holes or burrows during the day. This rodent hibernates during the winter, entering a state of torpor for several months, which allows it to survive the cold temperatures. While the species is not currently endangered, it faces threats from deforestation and the reduction of its natural habitat.
The Common Dormouse is a small nocturnal rodent, often compared to a miniature squirrel, found mainly in forests, hedgerows, and gardens across Europe. It measures about 7 to 9 cm in length, with a tail of 5 to 7 cm, and weighs between 15 and 30 g. Its coat is typically brown or gray with a light belly, and it has large black eyes and round ears. The Common Dormouse is an arboreal and nocturnal animal that primarily feeds on fruits, seeds, nuts, and sometimes insects. It is an excellent climber, often living in trees or natural cavities. This small rodent is known for its hibernation behavior: it enters torpor during the winter months, retreating into its nest to survive the cold temperatures. Although it is widespread, it is threatened by habitat loss and human disturbances.
The Gray Dormouse is a small nocturnal rodent, closely related to the Common Dormouse, found mainly in Europe in forests, hedgerows, and gardens. It measures between 10 and 15 cm in length, with a tail of about 8 to 12 cm, and weighs between 40 and 100 g. Its coat is generally light gray or brown-gray, with lighter shades on the belly and dark eyes that give it a lively expression. The Gray Dormouse is an excellent climber and is primarily arboreal. It feeds on fruits, seeds, nuts, and sometimes insects and small worms. This rodent is known for its ability to hibernate during the winter, retreating into natural cavities or nests made of leaves and moss to survive the cold temperatures. While it is relatively common, it is threatened by habitat loss, deforestation, and disturbances caused by human activity.
The European Golden Oriole is a brightly colored bird, easily recognizable by its striking plumage. The male is particularly vivid yellow with black wings, while the female has a more subdued plumage, mainly olive green and yellow. It measures about 25 cm in length and weighs between 40 and 60 g. This migratory passerine bird primarily inhabits open forests, orchards, and hedgerows, mostly in Europe, and migrates to North Africa for the winter. The European Golden Oriole is known for its melodious and powerful song, consisting of clear and repetitive notes. Its diet is primarily insectivorous, feeding on caterpillars, wasps, and other insects, but it also consumes fruits such as berries. This bird is discreet and hard to observe as it spends most of its time high up in trees. While its population is stable in some regions, it is threatened by deforestation, the loss of its natural habitat, and the reduction of its food sources due to pesticide use.
The Maned Wolf is a large carnivore native to South America, particularly known for its distinctive mane that surrounds its neck, giving the animal a majestic and unique appearance. It measures about 1 meter in body length, with a tail of about 30 to 40 cm, and weighs between 20 and 30 kg. Its coat is generally orange or golden in color, with darker shades on the head and legs, and a dark mane extending along its neck and throat. The Maned Wolf primarily inhabits the prairies and open savannas of Brazil, especially in the Pantanal region. It is an opportunistic predator, mainly feeding on small mammals, birds, and reptiles, but it can also consume fruits and plants. This wolf is an excellent runner and uses its speed to capture prey. Although the Maned Wolf is little known, it is an endangered species due to habitat loss, cattle trampling of land, and diseases. Conservation efforts are in place to protect this unique species.
The Arctic Wolf is a subspecies of the gray wolf, primarily found in the cold and snowy regions of the Arctic, particularly in northern Canada, Alaska, and Greenland. It measures about 1.5 to 2 meters in length, including its tail, and weighs between 30 and 50 kg, with males generally being larger than females. Its coat is thick and pure white, allowing it to blend perfectly into the snowy landscapes. This wolf has evolved to adapt to the extreme conditions of its environment, with wide paws that allow it to walk in deep snow, and dense fur that protects it from the cold. The Arctic Wolf lives in family groups, typically consisting of 5 to 10 individuals, who hunt together for prey such as caribou, birds, and other mammals. Although this subspecies is adapted to its environment, it is vulnerable to climate change, which affects the distribution of its prey and natural habitat. The Arctic Wolf is also threatened by hunting and habitat loss due to human activity.
The Coastal Wolf is a subspecies of the gray wolf primarily found along the coasts of Alaska and the North Pacific, as well as on certain islands. This wolf is adapted to its coastal environment, where it primarily hunts marine prey such as seals, fish, and seabirds. It measures about 1.3 to 1.5 meters in length, with a tail of about 30 to 40 cm, and weighs between 30 and 50 kg. Its coat is typically gray, brown, or black, with lighter shades on the belly and a thick mane around the neck. The Coastal Wolf is a social predator that lives in family groups and hunts in packs, often in areas close to water or on beaches. In addition to marine prey, it may also feed on deer, bears, and small mammals. While this subspecies is less widespread than others, it is well adapted to its environment and plays an important role in maintaining the balance of coastal ecosystems. However, it is threatened by habitat loss, human disturbances, and hunting.
The Eastern Wolf is a subspecies of the gray wolf, primarily found in the regions of Eastern Europe, notably in Poland, Romania, Bulgaria, and Ukraine. It measures about 1.2 to 1.5 meters in length, with a tail of 35 to 45 cm, and weighs between 25 and 45 kg, with males generally being larger and more massive than females. Its coat is thick and generally light gray to dark gray, with brown and white shades on the belly and legs. The Eastern Wolf primarily inhabits forests, mountains, and protected areas, where it hunts prey such as deer, wild boars, roe deer, and sometimes small mammals. It is a social predator, living in packs, and cooperates with other members of its group to capture prey. Although this subspecies has been the subject of conservation programs, it remains vulnerable to hunting, habitat loss, and conflicts with humans.
The Golden Wolf is a medium-sized canid native to the Middle East and certain regions of East Africa. It measures about 1.2 to 1.5 meters in length, including its tail, and weighs between 11 and 20 kg. Its coat is generally golden yellow or light brown, with black markings on its back and legs, and lighter shades on its belly. It has long, pointed ears and a narrow, elongated head. The Golden Wolf is primarily carnivorous, feeding on small mammals, birds, reptiles, and sometimes fruits. It lives in family groups or small packs and often hunts cooperatively with other members of the group. The Golden Wolf prefers open areas such as savannas, steppes, and mountains and is particularly adapted to semi-arid environments. Although the species is not immediately endangered, it is threatened by habitat loss, human conflict, and competition with larger carnivores such as jackals and lions.
The Gray Wolf is a large carnivore, often considered the ancestor of all modern subspecies of wolves. It measures between 1.2 and 1.8 meters in length, with a tail of 30 to 50 cm, and weighs between 25 and 40 kg, though some individuals can reach 70 kg. Its coat is typically gray, but it can also include shades of white, brown, and black depending on the region and season. The Gray Wolf lives in a variety of habitats, from deep forests to tundra regions, and from mountains to plains. It is a social predator that lives in packs, cooperating with other members of its group to hunt prey such as deer, elk, bison, and other large mammals. The Gray Wolf plays an essential role in ecosystem balance by regulating herbivore populations. Although it is protected in many areas, it remains threatened by habitat loss, hunting, and conflicts with humans.
The Eurasian Otter is a semi-terrestrial aquatic mammal found primarily in rivers, lakes, and coastal areas of Eurasia. It measures between 60 and 90 cm in length, with a tail of about 30 to 40 cm, and weighs between 5 and 12 kg. Its coat is thick and waterproof, dark brown on the back and lighter on the belly, allowing it to stay warm and move easily in the water. The Eurasian Otter is an excellent swimmer, using its hind limbs to propel itself and its tail to stabilize. It primarily feeds on fish but can also hunt amphibians, crustaceans, and small mammals. It is a solitary animal or lives in small family groups, marking its territory with traces and droppings. Although the species is protected in many areas, it is threatened by water pollution, habitat loss, and poaching.
The Sea Otter is a marine aquatic mammal primarily found along the coasts of the Pacific Ocean, particularly in North America and Northeast Asia. It measures between 1 and 1.5 meters in length, with a short tail of about 30 cm, and weighs between 14 and 45 kg, with females generally being smaller than males. Its coat is extremely dense and waterproof, with fine hairs that help it stay warm in the cold ocean waters. Unlike many other marine mammals, the Sea Otter does not have a layer of fat beneath its skin, making its fur all the more crucial for survival. This carnivore primarily feeds on shellfish, crustaceans, mollusks, fish, and sea urchins, often using rocks as tools to open them. The Sea Otter often lives in family groups called "rafts," floating together on the water's surface. Although it is protected in many areas, the Sea Otter is still threatened by pollution, habitat loss, and hunting.
The Canada Lynx is a medium-sized cat characterized by its thick paws and large pointed ears adorned with black tufts of fur. It measures about 80 to 105 cm in length, with a short tail of about 10 to 15 cm, and weighs between 8 and 14 kg. Its coat is generally light gray to reddish-brown, with darker spots on the flanks and a lighter underside. The Canada Lynx primarily inhabits the boreal forests of North America, particularly in Canada and northern parts of the United States. It primarily feeds on hares, particularly the Snowshoe Hare, but may also hunt small mammals, birds, and fish. This solitary predator is known for its great stealth and ability to blend into its snowy environment. While the species remains relatively stable, it faces threats such as habitat loss, competition with other predators, and the impacts of climate change.
The Iberian Lynx is a medium-sized cat endemic to the Iberian Peninsula, primarily found in southern Spain and Portugal. It measures about 80 to 100 cm in length, with a tail of about 10 to 15 cm, and weighs between 8 and 14 kg, with males generally being larger than females. Its coat is pale beige to light brown, with darker spots on the back and flanks, and a lighter underside. It has pointed ears, adorned with tufts of black fur, and a small beard on its chin. The Iberian Lynx primarily inhabits wooded and semi-desert areas, where it hunts prey such as hares, birds, and especially ungulates like deer and rabbits, which are its main food source. This solitary predator is highly territorial and uses calls and claw marks to demarcate its territory. Although it is one of the most endangered cats in the world, conservation efforts have helped increase its population, but it remains vulnerable to habitat loss and the decline of its natural prey.
The Bobcat is a medium-sized cat native to North America, where it is widespread, particularly in the United States, Canada, and Mexico. It measures about 80 to 110 cm in length, with a short tail of 10 to 15 cm, and weighs between 8 and 14 kg, although some males can reach 20 kg. Its coat is typically tawny or grayish with dark spots, and it has black tufts of fur on its ears, a characteristic feature of this species. The Bobcat is an excellent solitary hunter, primarily feeding on hares, rabbits, as well as birds and small mammals. It is particularly known for its ability to hunt in a variety of environments, ranging from dense forests to more open regions. This predator uses its great stealth to approach its prey before launching a quick attack. While the Bobcat remains relatively stable in terms of population, it is threatened by habitat loss and illegal hunting in some areas.
The Atlantic Puffin is a seabird characteristic of the coasts of the North Atlantic, particularly around the British Isles, Greenland, Iceland, and parts of Canada. It measures about 30 cm in length, with a wingspan of 50 to 60 cm, and weighs between 300 and 500 g. It is distinguished by its black and white plumage and its colorful beak, which is bright orange with red and blue bands during the breeding season. Outside of the breeding period, the Atlantic Puffin loses its bright colors and its beak becomes paler. This bird is an excellent diver, primarily feeding on fish and crustaceans, which it catches by diving underwater with great agility. The Atlantic Puffin is also known for its social behavior, gathering in large colonies during breeding on cliffs or remote islands. Although it is widely distributed, the Atlantic Puffin is sensitive to human disturbances, such as disruptions caused by tourism, and ocean pollution, particularly oil spills.
The Little Blue Penguin, also known as the Fairy Penguin, is the smallest of the penguin species, measuring about 30 to 40 cm in height and weighing between 1 and 1.5 kg. It has a distinctive blue-gray plumage on its back and wings, with a white belly. Its beak is short and dark, and its feet are pink or gray. The Little Blue Penguin primarily lives along the coasts of New Zealand and Australia, inhabiting colonies on beaches, islands, and cliffs. Unlike other penguins, the Little Blue Penguin is capable of swimming at impressive speeds, allowing it to hunt fish, crustaceans, and squid underwater. Although it is an excellent swimmer, it also spends time on land, where it digs burrows or hides in shrubs to protect itself from predators. While its population remains relatively stable, it faces threats such as climate change, predation by introduced animals, and habitat disruption.
The King penguin is the second largest species of penguin, after the emperor penguin. It primarily lives on subantarctic islands and the coasts of Antarctica. This penguin is easily recognizable by its distinctive black and white plumage and its bright orange coloring on the sides of the head and neck. It primarily feeds on fish, krill, and squid, which it captures by diving into the water. The King penguin is a social species, living in dense colonies, and is known for its spectacular courtship displays.

The Markhor is a wild goat species native to the mountains of Central Asia, primarily found in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Tajikistan, and India. It stands about 1.2 to 1.5 meters tall at the shoulder, with a body length of 1.5 to 2 meters, and weighs between 30 and 115 kg, with males generally being larger and more massive than females. The Markhor is famous for its impressive spiral horns, which can grow up to 1.5 meters long in adult males. Its coat is thick, typically brown or gray, with lighter fur on the belly and legs. It lives in mountainous and rocky areas, often at altitudes between 1,000 and 3,000 meters. The Markhor is an herbivore, feeding on mountain vegetation, including shrubs, leaves, and grasses. Although it is an agile climber and skilled at navigating steep terrain, it is also preyed upon by large predators such as snow leopards. The Markhor is classified as vulnerable due to overhunting, habitat loss, and human disturbances, but conservation efforts have helped stabilize its population in some areas.
The Alpine Marmot is a large rodent primarily found in the mountainous regions of Europe, especially in the Alps, the Pyrenees, and the mountains of Italy. It measures about 40 to 60 cm in length, with a tail of 10 to 15 cm, and weighs between 3 and 7 kg, with females generally being a little smaller than males. Its coat is thick and typically brown-gray, with a lighter belly, allowing it to blend into its rocky and grassy environment. The Alpine Marmot lives in burrows dug into the ground, where it takes refuge to sleep, escape predators, and hibernate during the winter, a period when it enters a state of torpor for several months. During the summer season, it primarily feeds on grasses, roots, flowers, and berries. The Alpine Marmot is a social animal, typically living in family groups or colonies. While its population remains relatively stable, it is threatened by climate change and human development of its natural habitat.
The Common Porpoise is a small cetacean from the Phocoenidae family, found primarily in the temperate and cold waters of the North Atlantic and the North Sea, although its range also extends to certain parts of the Baltic Sea. It typically measures between 1.3 and 2 meters in length and weighs between 40 and 65 kg. Its coat is dark on the back and light on the belly, and it has a small dorsal fin located near the back. The Common Porpoise has a rounded snout and is easily recognizable by its small, rounded pectoral fins. It primarily feeds on fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods, hunting using echolocation to locate prey in the water. Although it is often seen in small groups, it generally prefers to swim alone or in small family units. While the species is classified as of least concern, it faces threats such as pollution, accidental bycatch in fishing nets, and disturbances caused by maritime traffic.
The Grey-headed Kingfisher is a medium-sized bird, easily recognized by its grey head and colorful plumage. It measures about 25 cm in length and weighs between 50 and 70 g. Its back is typically metallic blue, with a contrasting white belly, and its wings are bright blue with touches of green and orange. This kingfisher is distinguished by its wide, straight bill, suited for hunting. It primarily lives in wooded areas and along the shores of rivers and lakes, where it feeds mainly on fish, aquatic insects, and small amphibians. The Grey-headed Kingfisher hunts by diving from a perch or electrical wire, capturing its prey with great precision. These birds are solitary, although some form pairs during the breeding season. It is widely distributed in Southeast Asia, particularly in India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar. While its population remains relatively stable, the Grey-headed Kingfisher can be threatened by habitat destruction, water pollution, and poaching.
The Smyrna Kingfisher is a colorful, medium-sized bird found primarily in Southeast Asia and surrounding regions. It measures about 25 to 30 cm in length and weighs between 40 and 70 g. This kingfisher is distinguished by its brilliant plumage and vibrant colors: a metallic blue back, an orange-red head, and a white belly. Its bill is long, straight, and pointed, perfect for catching prey such as fish, aquatic insects, and small reptiles. The Smyrna Kingfisher typically lives near bodies of water like rivers, lakes, and marshes, where it can dive to catch its food. It is often observed alone or in pairs during the breeding season when it builds a nest in tree cavities or rocks. Although its population remains relatively stable in some areas, it faces threats such as habitat destruction and water pollution.
The European Kingfisher is a small aquatic bird, easily recognized by its vivid plumage and bright colors. It measures about 17 to 19 cm in length and weighs between 30 and 40 g. Its back is a brilliant metallic blue, while its belly is a bright orange. Its bill is long, straight, and pointed, perfectly suited for catching fish and aquatic insects. This kingfisher primarily lives along rivers, lakes, and canals in Europe, where it perches on branches or rocks near the water. When hunting, it dives quickly in a headfirst plunge to capture its prey, often using its excellent vision to locate fish underwater. The European Kingfisher is a solitary bird, defending its territory by emitting a sharp call. While it is relatively common in many parts of Europe, it can be threatened by water pollution and habitat destruction.
The Belted Kingfisher is a medium-sized aquatic bird, easily recognized by its bright plumage and vivid colors. It measures about 28 cm in length and weighs between 100 and 150 g. Its back is a brilliant metallic blue, while its belly is white with orange patches on the chest. It has a long, straight, pointed bill, suited for catching fish and other aquatic prey. The Belted Kingfisher is an excellent diver, often perching on branches or electrical wires above the water before diving at high speed to catch its prey. It primarily lives in rivers, lakes, marshes, and coastal areas of North America, from southern Canada to Mexico. These birds are solitary and defend their territory by emitting sharp calls. While its population remains relatively stable, it is threatened by habitat loss due to water pollution and wetland destruction.
The Giant Kingfisher is the largest of the kingfisher species, measuring between 40 and 45 cm in length and weighing between 200 and 300 g. It has a distinctive plumage, with a metallic blue back, a gray head, and a white belly. Its bill is particularly long and powerful, suited for capturing large aquatic prey, such as fish, reptiles, and even crustaceans. This kingfisher primarily inhabits the banks of rivers and lakes in sub-Saharan Africa, India, Sri Lanka, and southern China, where it often hunts from branches or rocks above the water. Although it is primarily solitary in its hunting activities, it can sometimes be seen in pairs or families during the breeding season. The Giant Kingfisher is an excellent diver but is also known for its ability to catch prey while flying over the water and striking with its bill at great speed. While the species is widely distributed, it faces threats related to habitat loss and water pollution.
The Collared Kingfisher is a small colorful bird, measuring about 15 to 18 cm in length, and weighing between 20 and 30 g. It is distinguished by its head adorned with a characteristic crest made of bright blue feathers, and its brilliant plumage which combines shades of metallic blue and bright orange. Its back is cobalt blue and its belly is orange, with a striking contrast between the two. This kingfisher primarily inhabits wetlands in sub-Saharan Africa, often near rivers, marshes, and lakes, where it primarily hunts fish and aquatic insects. It is often seen diving from a perch to catch its prey, using its pointed and powerful bill to grab it with great precision. While it is generally a solitary bird, it can sometimes be seen in pairs during the breeding season. Although the population of the Collared Kingfisher is relatively stable, it faces threats such as habitat loss and water pollution.
The Pied Kingfisher is a medium-sized aquatic bird, measuring about 25 cm in length and weighing between 80 and 120 g. It is easily recognized by its distinctive black and white plumage, with a black head, white back, and wings that are also black and white. Its belly is generally white, and it has a long, straight, pointed bill, perfectly suited for catching fish and aquatic insects. This kingfisher primarily inhabits coastal areas, rivers, lakes, and marshes in sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, and southern Asia. It primarily feeds on small fish, but can also catch insects, crustaceans, and small frogs. The Pied Kingfisher is an excellent diver, often seen diving into the water at high speed from a perch to catch its prey. While often observed alone or in small groups, it can sometimes be seen in pairs during the breeding season. While it is widely distributed, it can be threatened by water pollution and habitat loss.
The Purple Kingfisher is a small aquatic bird distinguished by its vibrant plumage and bright colors. It measures about 16 to 17 cm in length and weighs between 30 and 40 g. Its plumage is an intense blue with purple hues and bright orange tones on the belly. This kingfisher has a long, straight, pointed bill, perfectly suited for catching fish and aquatic insects. It primarily inhabits the humid regions and tropical forests of Southeast Asia, especially in areas along rivers and marshes. The Purple Kingfisher often hunts by perching on branches or rocks near the water, diving quickly to catch its prey. While generally solitary, it sometimes forms pairs during the breeding season. Although the species is relatively widespread, it faces threats such as deforestation and pollution of waterways.
The Green Kingfisher is a small, vibrant aquatic bird, measuring about 25 cm in length and weighing between 50 and 100 g. It is distinguished by its bright green plumage on its back, with a white chest and belly, sometimes tinged with orange. Its bill is long, pointed, and straight, ideal for catching fish and aquatic insects. This kingfisher primarily inhabits North and Central America, especially along rivers, lakes, and marshes. It hunts by diving directly into the water from an elevated perch, such as a tree or electrical wire, to capture its prey. The Green Kingfisher is a territorial bird, often observed alone or in small groups during the breeding season. While it is widely distributed, it faces threats such as water pollution, habitat loss, and human disturbance.
The Alpine Swift is a large swift measuring between 20 and 23 cm in length, with a wingspan of 51 to 58 cm. It has a white belly and throat, separated by a brown pectoral band, and a brown-gray back. It is often confused with the Common Swift, but it is larger and more robust. A migratory species, it winters in tropical Africa and returns to Europe between March and April. It primarily nests in inaccessible rock cavities but can also occupy urban sites. It feeds exclusively on insects captured in flight, often at high altitudes. It is monogamous, and pair bonds can last over ten years. In Switzerland, it is present from late March to late October. A protected species, it is considered potentially threatened due to the loss of its natural nesting sites.
The Pale Swift is a migratory bird species that is mainly found in southern Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa. This small bird is easily recognizable by its grayish color and sleek body, perfectly adapted for speed and maneuverability in flight. It spends most of its life in flight, only landing to breed. It feeds primarily on insects that it catches while flying, often at high speed. The Pale Swift is an open-sky bird, frequently seen at high altitudes near mountains or soaring over urban areas in search of food.
The European Marten is a small carnivorous mammal, measuring between 45 and 55 cm in length, with a tail of 25 to 30 cm. It typically weighs between 1.5 and 2 kg, with males being slightly larger than females. Its fur is reddish-brown on the back, with a lighter belly, sometimes pale yellow, and a distinctive white patch on the throat. The European Marten primarily inhabits forests, woodlands, and mountains across Europe, although it can also be found in agricultural areas and urban parks. It is an excellent climber and spends a lot of time in trees, where it primarily hunts birds, small mammals, insects, and fruits. The European Marten is a solitary, territorial animal, with nocturnal and crepuscular behavior. While its population remains relatively stable, it is threatened by habitat loss, hunting, and road collisions.
The Little Auk is the smallest of the Atlantic alcids, measuring about 19 to 21 cm in length with a wingspan of 34 to 38 cm. Its plumage is black on the back and head, with a white face and belly. It has a short, stout bill adapted for catching small marine prey. A gregarious species, it forms massive breeding colonies on Arctic rocky coasts, nesting in crevices or under boulders. Outside the breeding season, it lives in the open sea, often near pack ice. It feeds mainly on copepods, krill, and small fish, which it captures by diving. Although currently listed as Least Concern, climate change and ocean pollution pose potential threats to its habitats.
The Sagittarius Hornbill, or Tockus alboterminatus, is a medium-sized bird primarily found in the savannas and open forests of Central and East Africa, notably in Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. It measures about 45 to 50 cm in length and weighs between 100 and 150 g. This bird is distinguished by its predominantly light gray and white plumage, with touches of black on the wings and tail, as well as a long, curved beak, characteristic of hornbills and messengers. Its name "sagittarius" comes from its beak, which resembles an arrow. The Sagittarius Hornbill primarily feeds on fruits, seeds, small insects, and small vertebrates. It is also known for its social behaviors and can be observed in small groups or pairs, and while less noisy than other hornbills, it emits distinct communication calls. The species is not currently endangered but may be affected by deforestation and loss of its natural habitat.
The Black Kite is a large bird of prey, measuring about 55 to 60 cm in length, with a wingspan of 150 to 160 cm and weighing between 800 g and 1.5 kg. It is distinguished by its predominantly black plumage with gray and brown shades, and a lighter head, often silvery-gray. This raptor has long, pointed wings, ideal for soaring and maneuvering in the air. The Black Kite is primarily found in Europe, but its range also extends to North Africa and the Middle East. It primarily inhabits open areas such as countryside, sparse forests, and riverbanks, where it feeds on small mammals, birds, reptiles, and also carrion. The Black Kite is an excellent glider, using thermal currents to stay aloft with minimal effort. This bird is also known for its social behavior and can be seen in groups, especially during migration. Although it is not in immediate danger, it faces threats such as habitat loss, poisoning, and collisions with power lines.
The Red Kite is a large bird of prey, measuring about 60 to 70 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.5 to 1.8 meters. It typically weighs between 1.2 and 1.5 kg. This raptor is distinguished by its reddish-brown plumage on the back and wings, with a lighter head and a deeply forked tail, giving it a characteristic silhouette in flight. The Red Kite primarily inhabits open forests, agricultural areas, and meadows, where it hunts small mammals, birds, insects, and carrion. It is an excellent glider and uses thermal currents to stay aloft effortlessly, allowing it to spot prey from a distance. The Red Kite is also a social bird, often seen in groups during the migration period, although it is generally solitary outside this time. While its population remains relatively stable, it faces threats such as habitat loss, pollution, and collisions with power lines.
The Walrus is a large marine mammal from the Odobenidae family, measuring between 3 and 4 meters in length and weighing between 800 and 1,500 kg. Males are generally much larger than females. This cetacean is distinguished by its long tusks, which can reach up to 1 meter in length in adult individuals, and its large, sensitive whiskers that help detect food on the ocean floor. The Walrus has short fur, typically brown or gray, but its skin is covered by a thick layer of blubber that helps it stay warm in the icy waters of the Arctic and North Atlantic. Walruses primarily inhabit coastal regions, where they feed mostly on mollusks, crustaceans, and fish. They spend a large part of their time on the ice, where they rest and socialize in large groups. While their population remains relatively stable, walruses face threats such as hunting, habitat loss, and the effects of climate change on their environment.
The Houtouc Motmot is a colorful and fascinating bird, primarily found in the tropical forests of Central and South America, notably in Costa Rica, Panama, and Colombia. It measures about 40 cm in length and is easily recognized by its vibrant plumage, often dominated by shades of blue, green, and orange. What particularly distinguishes this bird are its tail feathers, which are long and feature a characteristic fan at the tips. The Houtouc Motmot is a small predator, feeding primarily on insects, small reptiles, and sometimes fruits. It is often seen perched on low branches, where it watches its surroundings in search of prey before diving quickly to catch it. Although often solitary or in small families, it emits a piercing call to signal its presence. The species is not currently endangered, but it is sometimes threatened by deforestation and the loss of its natural habitat.
The Rufous Motmot is a medium-sized tropical bird, measuring between 38 and 43 cm in length. It is identifiable by its bright blue crown bordered by a black band, green back, and rufous chest. Its long tail ends with two racket-shaped feathers, characteristic of the genus. Found in the humid forests of Central and South America, it frequents forest edges and open woodlands. Omnivorous, it feeds on insects, small vertebrates, and fruits. It nests in tunnels dug into banks or slopes, where the female typically lays 3 to 4 white eggs. Although currently listed as Least Concern, deforestation poses a threat to its natural habitats.
The Black-legged Kittiwake is a medium-sized gull, measuring about 40 to 45 cm in length, with a wingspan of 90 to 110 cm. It is easily recognizable by its white plumage with light gray wings and a black head during the breeding season. What particularly distinguishes this gull is the shape of its tail, which is deeply forked, hence its name "tridactyla." It primarily inhabits coastal regions of the North Atlantic, notably in rocky areas, cliffs, and subarctic islands. The Black-legged Kittiwake feeds mainly on fish, crustaceans, and marine insects. It is often seen flying over the water in search of food or resting on rocks. Although the population of this species is stable, it may be threatened by human disturbances, particularly the disruption of breeding colonies and marine pollution.
The Mouflon is a small wild sheep found primarily in the mountains of Europe, the Middle East, and Central Asia. It measures between 70 and 80 cm in height at the withers and weighs between 40 and 80 kg, with males generally being larger and more imposing than females. What distinguishes the Mouflon is the presence of large, curved horns in males, while females have smaller and less pronounced horns. Their coat is generally reddish-brown in the summer, with a white belly and a darker mane along the back, which becomes thicker and fuller in the winter. The Mouflon primarily inhabits mountainous areas, forests, and meadows, where it feeds on grasses, leaves, shrubs, and roots. It is an excellent climber and moves easily across rocky and steep terrain. While its population remains stable, the Mouflon may be threatened by habitat loss, hunting, and competition with domesticated livestock.
The Corsican Mouflon is a subspecies of the Mouflon, native to the island of Corsica, where it primarily inhabits mountains and rocky areas. It measures about 70 cm in height at the withers and weighs between 40 and 70 kg. What distinguishes the Corsican Mouflon are its horns, which are particularly large and spirally curved in males, while females have smaller horns. Its coat is generally reddish-brown with lighter shades on the belly and a darker mane along the back. The Corsican Mouflon is an agile animal and an excellent climber, capable of moving easily through the steep and rocky terrain of its natural habitat. It feeds primarily on grasses, shrubs, leaves, and roots. While its population remains relatively stable on the island, it faces threats related to habitat loss and hunting. These animals are solitary or live in small groups, primarily during the breeding season.
The Narwhal is a unique cetacean, often referred to as the "unicorn of the seas" due to the long twisted tusk it possesses, typically in males. It measures between 4 and 5 meters in length and can weigh up to 1,600 kg. The narwhal's tusk can reach up to 3 meters in length and is actually a tooth that grows asymmetrically, often spiraling. Its body is gray to white with black and white patches that vary from one individual to another. The Narwhal primarily inhabits the cold waters of the Arctic, where it feeds on fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods. It is an excellent diver, capable of descending to great depths in search of food. While its population remains relatively stable, it is threatened by climate change, water pollution, and human disturbances. Due to its beauty and rarity, it is also highly sought after for illegal horn trade.
The Proboscis Monkey is a large primate native to the tropical forests of Borneo and Sumatra. It measures about 60 to 75 cm in length and weighs between 15 and 25 kg. It is easily recognizable by its prominent, elongated nose, which can measure up to 10 cm in adult males. This nose is particularly developed in males and plays a role in vocalizations and attracting females. Its coat is generally brown or reddish, with a lighter belly. The Proboscis Monkey primarily inhabits mangroves, lowland forests, and mountain forests, where it feeds mainly on leaves, fruits, seeds, and roots. It is an excellent climber and spends much of its time in the trees, typically living in social groups consisting of several females and their young. While its population remains relatively stable, it faces threats such as deforestation, hunting, and habitat loss.
The Red-crested Pochard is a medium-sized diving duck, measuring between 53 and 58 cm in length with a wingspan of 84 to 88 cm. The male is notable for its rounded, bright reddish-orange head, vivid red bill, black chest, and white flanks. The female is more subdued, with brown plumage, pale cheeks, and a dark bill. This species inhabits eutrophic lakes and ponds rich in aquatic vegetation, often bordered by reed beds. It primarily feeds on aquatic plants like pondweeds and charophytes, but also consumes aquatic invertebrates, including mollusks and insects. Migratory, the Red-crested Pochard winters around the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. Although listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, it is sensitive to the degradation of wetlands.
The Ocelot is a medium-sized wild cat, measuring between 55 and 100 cm in length (excluding the tail) and weighing between 8 and 16 kg. It is distinguished by its spotted and striped coat, which helps it blend effectively into dense forests and wooded areas where it lives. Its fur is generally golden or grayish, with black marks in the form of spots or rosettes across the body. The Ocelot is a nocturnal and solitary hunter, primarily feeding on small mammals, birds, reptiles, and fish. It is agile and fast, capable of climbing trees to hunt or escape predators. This cat is primarily found in Central and South America, in tropical forests, savannas, and mountainous areas. While its population remains stable in some regions, the Ocelot is threatened by deforestation, illegal hunting, and habitat loss.
The Stone-curlew is a large, ground-dwelling bird primarily found in open and arid regions of Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa. It measures about 40 to 45 cm in height and weighs between 350 and 500 g. What distinguishes the Stone-curlew is its cryptic plumage, generally brown-gray in color, allowing it to blend effectively among vegetation or rocks. It has large yellow eyes and a distinctive call, which is often heard during the night, hence its name. This bird primarily feeds on insects, worms, and small invertebrates found on the ground. The Stone-curlew is mostly active at dusk and at night, feeding slowly while scanning its surroundings. While not in immediate danger, it faces threats from habitat loss, intensive agriculture, and human disturbance.
The Okapi is a herbivorous mammal native to the rainforests of the Democratic Republic of Congo in Central Africa. It measures between 1.5 and 2 meters in length and weighs between 200 and 350 kg, resembling a combination of a giraffe and a horse. Its coat is generally dark brown with characteristic white bands on its legs, similar to those of a zebra, hence its nickname "zebra-headed giraffe." The Okapi is a solitary and secretive animal, primarily feeding on leaves, fruits, and plant shoots. It inhabits dense forests, where it uses its sense of smell and great discretion to escape predators. While its population remains relatively stable, the Okapi is threatened by deforestation, poaching, and human conflict.
The Bornean orangutan is a large primate, measuring about 1.2 to 1.5 meters in height and weighing between 40 and 90 kg. It is easily recognized by its reddish fur and long arms, which allow it to move effortlessly through the trees. This species is native to the island of Borneo, where it primarily inhabits tropical forests. The Bornean orangutan is an herbivore, feeding mainly on fruits, leaves, bark, and small insects. It is a solitary animal, with very discreet behaviors and a great ability to adapt to its environment. Due to deforestation, illegal hunting, and the loss of its natural habitat, this species is classified as endangered.
The Sumatran orangutan is a majestic primate, measuring between 1.2 and 1.4 meters in height and weighing between 30 and 70 kg. It has a shiny reddish fur, with long arms adapted to its arboreal lifestyle. Native to the island of Sumatra in Indonesia, this orangutan primarily inhabits tropical lowland forests and swampy areas. Its diet mainly consists of fruits, leaves, bark, and small insects. It is primarily solitary and has a great ability to camouflage among the trees. Unfortunately, this species is critically endangered due to massive deforestation, forest fires, and illegal hunting.
The Tapanuli orangutan is a recently discovered primate species, considered one of the rarest and most endangered in the world. It measures about 1.2 meters in height and weighs between 30 and 60 kg. This ape has a shiny reddish coat, with long arms adapted to its life in the trees. Native to the mountains of the Tapanuli region in northern Sumatra, Indonesia, this orangutan primarily inhabits montane tropical forests. It feeds mainly on fruits, leaves, and bark. The Tapanuli orangutan is a solitary and secretive animal and is considered critically endangered due to deforestation, mining, human conflict, and forest fires.
The Moose is a large deer found primarily in North America, particularly in coniferous forests and wetlands. It can reach up to 2 meters in height at the withers and weigh between 350 and 600 kg. Males are distinguished by their large antler racks, which can reach a span of 1.8 meters. Their coat is typically dark brown to black, with a lighter belly and a small mane of hair under the neck. The Moose is a herbivore, feeding mainly on leaves, branches, bark, fruits, and aquatic plants. It is an excellent swimmer and spends a great deal of its time feeding in lakes and rivers. While its population remains stable, it is threatened by habitat loss and hunting.
The Platypus is a unique aquatic mammal native to Australia and Tasmania. It measures between 40 and 60 cm in length and weighs around 1 to 2.5 kg. This animal is particularly remarkable due to its appearance, which combines characteristics of different animals: it has a flat bill similar to a duck's, webbed feet adapted for swimming, and a flat tail. The Platypus is a carnivore, primarily feeding on small aquatic invertebrates, worms, and crustaceans. It lives in rivers and lakes, spending much of its time diving underwater in search of food. Although it is an excellent swimmer, the Platypus is also capable of moving quickly on land. This species is listed as "near threatened" due to habitat loss and water pollution.
The Orca, also known as the "killer whale," is a large cetacean from the dolphin family, measuring between 6 and 8 meters in length and weighing up to 6 tons. It is distinguished by its striking black and white coloration, with white patches around the eyes and on the flanks. The Orca is a top predator in the food chain, primarily feeding on fish, marine mammals, sharks, and sometimes even whales. It lives in social groups called "pods," led by the dominant female, where cooperation and hunting strategies are essential. The Orca is found in all oceans around the world, but it prefers cold and temperate waters. While its population remains relatively stable, the Orca is threatened by pollution, a decline in prey, and human-caused disturbances.
The Beisa Oryx is a large antelope found primarily in the arid and semi-desert regions of East Africa, particularly in Somalia, Ethiopia, and Kenya. It stands between 1.2 and 1.5 meters at the shoulder and weighs around 100 to 150 kg. The Beisa Oryx is easily recognized by its long, straight horns, which can reach up to 1 meter in length. Its coat is sandy-colored, with black markings on the flanks, legs, and around the eyes, helping it blend into its desert environment. This herbivore feeds primarily on bushes, grasses, and succulent plants. Although the Beisa Oryx is capable of tolerating extremely high temperatures, it is also well adapted to cover large distances in search of food and water. This species is currently listed as "near threatened" due to habitat loss and hunting.
The Fur Seal, also known as the hair seal, is a marine mammal primarily found along the coasts of the Southern Hemisphere, particularly in Australia, South Africa, and subantarctic islands. It measures between 1.5 and 2.5 meters in length and weighs between 200 and 350 kg. Its dense and waterproof fur, which gives it its name, consists of short, soft hairs covering a layer of subcutaneous fat that insulates it from the cold. The Fur Seal is an excellent swimmer, capable of diving to significant depths to feed on fish, cephalopods, and crustaceans. It lives in colonies, forming strong social groups, especially during the breeding season. While the population of fur seals remains relatively stable, this species is threatened by hunting, habitat loss, and ocean pollution.
The Andean Bear, also known as the spectacled bear, is a large mammal found primarily in the tropical forests and mountains of South America, particularly in Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, and Peru. It measures about 1.5 to 2 meters in length and weighs between 100 and 200 kg. Its coat is generally black, with white or cream markings around its eyes in the shape of spectacles, hence its name. The Andean Bear is an omnivore, primarily feeding on fruits, plants, honey, and insects, but it may also eat small mammals or birds. It is an excellent climber, using its powerful claws to move through trees in search of food. Although its population remains stable in some areas, the Andean Bear is threatened by habitat loss, deforestation, and poaching.
The Brown Bear is one of the largest terrestrial carnivores, measuring between 1.5 and 2.5 meters in length and weighing between 100 and 800 kg, depending on the subspecies and habitat conditions. Its coat ranges from light brown to dark brown, and it is often denser during the winter. The Brown Bear primarily lives in forests, mountains, and Arctic regions, but can also be found in tundra and prairie areas. It is omnivorous, feeding on fruits, roots, small mammals, fish, and even carrion. The Brown Bear is also an excellent swimmer and climber. Due to hunting, habitat loss, and conflicts with humans, some subspecies of Brown Bears are threatened or endangered.
The Kermode Bear, also known as the "spirit bear" or "white-furred bear," is a rare subspecies of the American Black Bear. It measures between 1.2 and 1.8 meters in length and weighs between 70 and 250 kg. What particularly distinguishes the Kermode Bear is its coat, which can vary from black to creamy white, although the majority of these bears have black fur. This subspecies primarily lives in the humid forests of British Columbia, Canada, and feeds mainly on fruits, berries, fish, and small mammals. The Kermode Bear is typically solitary and inhabits remote areas. Although it is relatively rare, it is not considered to be in immediate danger, though it faces threats from habitat loss and other human-related activities.
The Sloth Bear, also known as the lip bear, is a large carnivorous mammal primarily found in the tropical and subtropical forests of India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, and Myanmar. It measures about 1.4 to 1.8 meters in length and weighs between 50 and 150 kg. What particularly distinguishes the Sloth Bear is its face, which has highly mobile lips and long fur around the mouth, giving it its name. Its coat is generally black with white markings on the chest and throat, forming a sort of crescent shape. The Sloth Bear is an omnivore, feeding on fruits, honey, insects, roots, and small animals. Although it is primarily terrestrial, it is also capable of climbing trees. Due to habitat loss and poaching, this species is currently listed as vulnerable.
The American Black Bear is a large carnivore primarily found in North America, in forests, mountains, and wooded areas. It measures between 1.5 and 2.5 meters in length and weighs between 45 and 250 kg, depending on the subspecies and habitat conditions. Its coat ranges from black to light brown, and it has a short muzzle and a large head. The Black Bear is an omnivore, primarily feeding on fruits, berries, nuts, roots, fish, small mammals, and sometimes carrion. It is also an excellent climber and a skilled swimmer, capable of moving through trees and crossing rivers in search of food. While its population remains relatively stable, the Black Bear is threatened by habitat loss, vehicle collisions, and hunting.
The Asiatic Black Bear, also known as the Tibetan Bear, is a medium-sized mammal found primarily in the mountains of Central Asia, the Indian subcontinent, China, and Russia. It measures between 1.2 and 1.8 meters in length and weighs between 60 and 200 kg. Its coat is typically black, with a distinctive white "V"-shaped mark on its chest. The Asiatic Black Bear is an omnivore, feeding on fruits, berries, roots, small animals, insects, and occasionally carrion. It is an excellent climber and spends much of its time in trees, where it feeds and rests. While the Asiatic Black Bear remains relatively common in some regions, it faces numerous threats such as habitat loss, illegal hunting, and poaching for its body parts.
The Polar Bear is one of the largest land carnivores, measuring between 2 and 3 meters in length and weighing between 350 and 700 kg, depending on habitat conditions and the season. It is perfectly adapted to the icy conditions of the Arctic, with dense, waterproof fur that protects it from the cold, as well as a layer of subcutaneous fat that helps it survive in extreme temperatures. Its coat is typically white or cream, allowing it to blend in with the snow and ice. The Polar Bear is an excellent swimmer and primarily feeds on seals, which it hunts by patiently waiting near breathing holes or swimming under the ice. However, the Polar Bear faces growing threats due to climate change, which is shrinking its ice habitat and affecting its ability to hunt.
The Giant Panda is a large mammal native to the mountains of China, primarily found in the regions of Sichuan, Shaanxi, and Gansu. It measures between 1.2 and 1.8 meters in length and weighs between 70 and 160 kg. What distinguishes it is its black and white coat, with black patches around its eyes, ears, and paws. The Giant Panda is a strict herbivore, feeding almost exclusively on bamboo, although it may occasionally eat fruits, roots, and small animals. It lives in bamboo forests, where it spends most of its day feeding due to the low nutritional value of its diet. The Giant Panda is a symbol of conservation due to its rarity, and although it is still considered vulnerable, conservation efforts have helped stabilize its population.
The Red Panda, also known as the Lesser Panda, is a small mammal native to the mountains of the Himalayas and southern China. It measures between 50 and 65 cm in length, with a bushy tail of 30 to 50 cm, and weighs between 3 and 6 kg. Its coat is predominantly reddish, with white patches around the eyes, ears, and muzzle. The Red Panda is primarily arboreal, living in temperate and mountainous forests, where it feeds on bamboo, fruits, berries, roots, and occasionally insects. Although it is an excellent climber, it is also active on the ground. The Red Panda is a vulnerable species, primarily threatened by habitat loss, deforestation, and illegal hunting.
The Small-scaled Pangolin is an insectivorous mammal found primarily in Central and West Africa, notably in Cameroon, Gabon, and the Republic of Congo. It measures about 50 to 80 cm in length, with a tail that can reach half its body size, and weighs between 5 and 7 kg. Its body is covered with small, hard scales made of keratin, which protect it from predators. When threatened, the Pangolin curls into a ball, exposing only its scales. It primarily feeds on ants, termites, and larvae, which it captures with its long tongue. Although the Pangolin is an excellent burrower, it is vulnerable due to intensive poaching for its scales and habitat loss. It is currently listed as "vulnerable" by the IUCN.
The Javan Pangolin, also known as the Malayan Pangolin, is a mammal species native to Southeast Asia. It is easily recognized by its body covered with large keratin scales, which protect it from predators. This nocturnal and solitary animal primarily feeds on ants and termites, which it captures with its long, sticky tongue. The Javan Pangolin is an endangered species, mainly due to habitat loss and poaching for its scales and meat. This pangolin is an excellent burrower, digging dens and hides for protection.
The Temminck's Pangolin is a small insectivorous mammal found primarily in Sub-Saharan Africa, notably in South Africa, Botswana, Namibia, and Zimbabwe. It measures about 50 to 60 cm in length, with a tail that makes up a significant portion of its size, and weighs between 3 and 7 kg. This pangolin is covered with large scales made of keratin, which protect it from predators. When threatened, it curls into a ball with its scales rolled outward. It primarily feeds on termites and other insects, which it captures with its long, sticky tongue. Although the Temminck's Pangolin is an excellent burrower, it is unfortunately threatened by poaching for its scales and by habitat loss.
The Giant Pangolin is the largest of the pangolin species, measuring between 1.2 and 1.5 meters in length, with a tail that can account for up to half of its total length. It weighs between 30 and 40 kg. This mammal, covered in large keratin scales, primarily lives in the forests of Central Africa, particularly in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo. It is an excellent burrower and primarily feeds on termites and other insects, which it captures with its long tongue. The Giant Pangolin is a nocturnal and solitary species, using its powerful claws to dig burrows or open insect nests. Although its population is not well-known, the Giant Pangolin is threatened by deforestation, illegal hunting, and poaching for its scales, making it a vulnerable species.
The Snow Leopard, also known as the ounce, is a large cat primarily found in the mountains of the Himalayas, Tibet, Central Asia, and the Pamir Mountains. It measures between 1.1 and 1.3 meters in length, with a tail of 80 to 100 cm, and weighs between 27 and 55 kg. Its thick, dense fur, which is light gray to white with dark rosettes, allows it to blend perfectly into its snowy environment. The Snow Leopard is a solitary carnivore, primarily feeding on wild goats, sheep, small deer, and sometimes small mammals. It is an excellent climber and stealthy hunter, capable of pouncing on its prey from high ground. Unfortunately, this species is threatened by illegal hunting, poaching, and habitat loss. It is currently listed as "vulnerable" by the IUCN.
The Clouded Leopard is a medium-sized cat primarily found in the tropical and subtropical forests of Southeast Asia, notably in India, Nepal, Bhutan, Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia. It measures between 50 and 75 cm in length, with a tail ranging from 60 to 90 cm, and weighs between 12 and 20 kg. Its coat is characterized by spots and rosette patterns that help it blend perfectly into the dense vegetation of its habitat. The Clouded Leopard is an excellent climber and spends much of its time in trees, hunting birds, squirrels, monkeys, and small deer. Although the Clouded Leopard's population remains relatively stable, it is threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and forest fragmentation. This species is currently listed as "vulnerable" by the IUCN.
The Bearded Tit is a small passerine bird primarily found in marshy areas and reed beds of Europe and Asia. It measures about 15 to 20 cm in length and weighs between 15 and 20 g. What particularly distinguishes the Bearded Tit is its plumage in shades of brown and cream, with long black moustaches that give it its name. It is often observed in reed beds and wetlands, where it primarily feeds on seeds, insects, and arthropods. Although it is an excellent climber and stealthy thief, the Bearded Tit is unfortunately threatened by the destruction of its natural habitat and the reduction of reedbed areas. This species is currently listed as "near threatened" by the IUCN.
The Peacock is a large bird native to the Indian subcontinent, but it is now found in many parts of the world, often raised for its magnificent feathers. It measures about 2 to 2.5 meters in length, much of which consists of its tail, which can reach up to 1.5 meters in length. The Peacock's feathers are brilliantly colorful, with blue, green, and gold patterns that are displayed during courtship rituals to attract females. Outside of the breeding season, the Peacock is a terrestrial bird, feeding on seeds, fruits, insects, and small reptiles. Although this species is not in immediate danger, it is threatened by habitat loss and hunting in some regions.
The Republican Paradise-flycatcher is a small bird native to the lowland forests of Sulawesi Island in Indonesia. It measures about 20 cm in length, with a long tail that can reach up to 15 cm, and weighs between 25 and 30 g. What distinguishes the Republican Paradise-flycatcher is its bright coloration, with vivid green, blue, and red feathers and a magnificent crest shaped like a veil. The male, in particular, displays extravagant feathers during courtship displays to attract females. This bird primarily feeds on fruits, seeds, and insects. Although the Republican Paradise-flycatcher is not in immediate danger, deforestation and hunting pose potential threats to its natural habitat.
The Two-toed Sloth is an arboreal mammal native to the tropical forests of Central and South America, notably in Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia, and Ecuador. It measures between 50 and 60 cm in length, with a reduced tail and weighs between 4 and 8 kg. Its fur is long, thick, and gray-green in color, allowing it to blend into the foliage of trees. As its name suggests, it has two toes on its front limbs, which allow it to cling to branches and move slowly from tree to tree. The Two-toed Sloth is primarily herbivorous, feeding on leaves, fruits, and flowers. Although it is an excellent climber, it moves very slowly and often only leaves its trees once a week to descend to the ground for defecation. The species is currently listed as "vulner
The Common Sloth is an arboreal mammal native to the tropical forests of Central and South America, particularly in South America, from Costa Rica to Brazil. It measures between 50 and 70 cm in length, with a tail of 4 to 6 cm, and weighs between 4 and 8 kg. Its fur is long and thick, gray-brown in color, with lighter and sometimes greenish patches due to algae growing on its hair. The Common Sloth primarily feeds on leaves, fruits, and flowers, which it eats very slowly. It is known for its extreme slowness, moving at a speed of 0.03 km/h, making it one of the slowest animals in the world. This behavior is due to its slow metabolism and a diet that is low in calories. Although the population of common sloths is not immediately threatened, they are vulnerable to habitat loss and human disturbances.
The Brown Pelican is a large seabird native to the American coasts, measuring between 100 and 137 cm in length with a wingspan of 200 to 228 cm. It is characterized by its brown-gray plumage, white head with a yellowish crown during the breeding season, and a long bill with an expandable throat pouch capable of holding up to 11 liters of water. This pelican is known for its dramatic fishing technique: diving from several meters high to catch fish, mainly sardines and anchovies. It inhabits coastal areas, estuaries, mangroves, and sandy beaches, nesting in colonies on islands or isolated areas. Although currently listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, the Brown Pelican experienced significant declines in the 20th century due to pesticide pollution, particularly DDT. Conservation efforts have led to population recoveries, but habitat degradation remains a concern.
The Dalmatian Pelican is a large aquatic bird primarily found in Eastern Europe, the Middle East, and parts of Asia. It measures about 1.5 to 1.8 meters in length, with a wingspan of 2.3 to 2.5 meters, and weighs between 7 and 15 kg. What distinguishes the Dalmatian Pelican is its white plumage, sometimes tinged with yellow or pink, as well as its distinctive crest and long curved bill. It also has a pouch under its bill that allows it to capture fish. The Dalmatian Pelican primarily feeds on fish, which it catches by diving into the water or filtering with its bill. It is typically found near lakes, rivers, and wetlands. While the population of the Dalmatian Pelican is stable in some regions, it is still threatened by habitat loss, water pollution, and human disturbance.
The Crested Guan is a large forest bird, measuring between 76 and 91 cm in length and weighing up to 2.4 kg. It has dark olive-brown plumage with white spots on the neck and chest, a rufous rump and belly, and a bushy crest on its head. Its throat features a large red wattle, and the skin around the eye is bluish-gray. Social in nature, it lives in pairs or family groups of 6 to 12 individuals, feeding on fruits and young leaves in the trees. It builds its nest in trees, where the female lays two or three white eggs. Although classified as Near Threatened by the IUCN, it is vulnerable to habitat loss and hunting.
The Barbary Partridge is a terrestrial bird native to the mountains of North Africa and Western Asia. It measures about 30 cm in height and weighs between 300 and 500 g. Its plumage is characterized by brown and gray tones, with a distinctive "V"-shaped pattern on the chest. The Barbary Partridge primarily inhabits rocky, dry mountain habitats, where it feeds on seeds, roots, berries, and small insects. It is an excellent runner and, although capable of flying, prefers to move by running through the underbrush. This species is threatened in some regions due to excessive hunting and habitat loss, and it is protected in several countries.
The Grey Partridge is a plump galliform bird, measuring 28–32 cm in length with a wingspan of about 45 cm. It is identified by its mottled brown-grey plumage and a distinctive dark horseshoe-shaped patch on the belly. Males and females are very similar, though the belly patch is usually more defined in males. Found in open farmland, grasslands, fallows, and cultivated fields across Europe and temperate Asia. It is ground-dwelling and sedentary, preferring to run rather than fly when disturbed. Its diet includes seeds, leaves, shoots, and insects, which are vital for chicks. The species is in decline in some areas due to agricultural intensification, habitat loss, and pesticide use.
The Red-legged Partridge is a medium-sized galliform bird, about 33 cm in length. It features a reddish-brown back, bluish-grey chest, and flanks striped with black and white. Its white throat is bordered by a black horseshoe-shaped collar, and it has red legs and beak. Native to southwestern Europe, it inhabits dry open areas, scrubby hills, farmlands, and fallow fields. Non-migratory and ground-dwelling, it prefers running to flying when disturbed. Its diet mainly consists of seeds, young shoots, and insects, the latter being crucial for chicks. Although listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, the Red-legged Partridge is declining in some areas due to habitat loss, overhunting, and hybridization with introduced farm-reared birds.
The Little Ringed Plover is a small migratory bird primarily found in wetlands, sandy beaches, and riverbanks in Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It measures about 18 cm in length and weighs between 30 and 50 g. Its plumage is gray-brown on the back, with white underparts and a distinctive black ring around the neck and eyes. The Little Ringed Plover primarily feeds on small invertebrates, mollusks, and insects found by foraging in sand and along water edges. This bird is an excellent runner and flies very quickly. While its population remains relatively stable, the Little Ringed Plover is threatened by habitat loss, pollution, and human disturbances during its breeding season.
The Minke Whale is a medium-sized cetacean, a member of the baleen whale family, found in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Southern Oceans. It measures between 7 and 10 meters in length and weighs between 5 and 10 tons. Its body is streamlined, and its color ranges from gray-blue to black, with a lighter belly. This whale primarily feeds on plankton, small fish, and crustaceans, which it filters by swimming with its mouth open. It is an excellent swimmer and can dive to impressive depths for several minutes. While its population remains stable, the Minke Whale is threatened by ocean pollution, ship collisions, and habitat loss due to human impact on marine ecosystems.
The Northern Pygmy Owl is a small nocturnal owl found primarily in North America, from southern Canada to Mexico. It measures about 20 to 25 cm in length, with a wingspan of 50 to 60 cm, and weighs between 70 and 100 g. Its plumage is mainly gray-brown, with spots and streaks that help it blend perfectly into foliage and tree trunks. The Northern Pygmy Owl primarily feeds on small mammals, insects, and reptiles that it hunts during the night. It is an excellent hunter, using its keen eyesight and sharp hearing to locate its prey in the darkness. While this species is not currently threatened, it can be affected by deforestation and the loss of its natural habitat.
The Scops Owl is a small owl native to Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It measures about 22 cm in length and weighs between 100 and 150 g. Its plumage is primarily gray-brown, with patterns of spots and streaks that help it blend into foliage and tree trunks. It has tufts of feathers on its head, giving it a distinctive appearance. The Scops Owl is a nocturnal bird, primarily feeding on small mammals, insects, and occasionally small birds that it hunts at night. It is often seen perched on tree branches or utility poles. While this species is not in immediate danger, it is sometimes affected by habitat loss and human disturbances.
The Common Warthog is a wild mammal native to Sub-Saharan Africa. It measures about 1.2 to 1.5 meters in length, with a shoulder height of 60 to 80 cm, and weighs between 50 and 150 kg. It is easily recognizable by its broad face and large curved tusks, which serve as both a defense mechanism and a tool for digging. Its fur is generally gray or light brown, and it has thick, rough skin. The Common Warthog primarily lives in savannas, grasslands, and open forests, where it feeds mainly on roots, fruits, insects, and small animals. It is a social animal, living in groups, and is mainly nocturnal. Although the Common Warthog is widespread and its population is stable, it is sometimes affected by hunting and habitat loss.
The Red-necked Phalarope is a small wader bird primarily found in marshes, salt lakes, and estuaries in North America, Europe, and Asia. It measures about 20 cm in length and weighs between 30 and 50 g. What distinguishes it is its brightly colored plumage, with red and gray tones, and its fine, pointed bill, which allows it to capture insects and small crustaceans from the water. The Red-necked Phalarope is an excellent swimmer and spends much of its time spinning on the water to capture its food. While its population is not currently in danger, it is vulnerable to habitat loss, pollution, and human disturbance, especially during the breeding season.
The Common Seal, also known as the Harbor Seal, is a marine mammal found primarily along the coasts of the North Atlantic, in Europe and North America. It measures between 1.5 and 2 meters in length and weighs between 60 and 150 kg. Its fur is typically light gray with dark spots, and its head is rounded with bright black eyes. The Common Seal is an excellent swimmer and primarily feeds on fish, crustaceans, and mollusks. It is often seen lounging on rocks or beaches. Although its population remains relatively stable, the Common Seal is sometimes threatened by pollution, hunting, and human disturbance of its breeding habitats.
The Gray Seal, also known as the Horsehead Seal, is a species of seal found in the coastal waters of the North Atlantic, particularly in Europe and North America. It measures between 2 and 3 meters in length and weighs between 170 and 300 kg. Its fur is typically silver-gray with black spots, and its head is characterized by a wide and elongated snout. The Gray Seal primarily feeds on fish, but also on crustaceans and cephalopods. It spends a lot of time on beaches and rocks for resting and breeding. Although it is not currently threatened, it can be affected by marine pollution, ship collisions, and human disturbance.
The Lovely Poison Frog is a small, diurnal terrestrial frog, measuring about 2.5 cm in length. Its body is black with two bright yellow to orange longitudinal stripes on the back, and blue-green marbling on the flanks and limbs. This species inhabits lowland humid forests, often near slow-moving streams, between 10 and 650 m elevation. It primarily feeds on small invertebrates such as ants and spiders. Although its skin contains toxic alkaloids, including batrachotoxins, their concentration is low and sometimes undetectable. The Lovely Poison Frog is listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, but is locally threatened by deforestation and pollution.
The Grey-headed Woodpecker is a bird belonging to the woodpecker family, primarily found in Eastern Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. It measures about 25 to 30 cm in length, with a wingspan of 40 to 45 cm, and weighs between 80 and 120 g. Its plumage is mainly gray, with a black and white head, and a red nape in males. It is distinguished by its sharp call and its ability to drill into tree trunks in search of larvae and insects, which are its primary food source. The Grey-headed Woodpecker lives in mixed forests and wooded areas, often nesting in dead or decaying trees. Although it is not considered threatened, the Grey-headed Woodpecker is vulnerable to deforestation and habitat loss.
The Great Spotted Woodpecker is an iconic bird of forests in Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It measures about 25 to 30 cm in length, with a wingspan of 40 to 45 cm, and weighs between 70 and 100 g. It is easily recognizable by its black and white plumage, with a red head in males and a red patch on the nape in females. The Great Spotted Woodpecker is an excellent climber, using its strong beak to tap on tree trunks in search of insects, primarily insect larvae and ants, which it extracts with its long, sticky tongue. It is often seen hammering wood in search of food or to mark its territory. The Great Spotted Woodpecker is found in a variety of forests, from broadleaf to mixed forests, and although its population remains stable, it is sometimes affected by habitat loss.
The Lesser Spotted Woodpecker is a small bird from the woodpecker family, primarily found in deciduous and mixed forests of Europe and Asia. It measures about 20 cm in length, with a wingspan of 30 to 35 cm, and weighs between 30 and 40 g. Its plumage is mainly black and white, with a small red patch on the nape, visible mostly in males. The Lesser Spotted Woodpecker is distinguished by its smaller size compared to the Great Spotted Woodpecker and its foraging habits. It primarily feeds on small insects found under the bark of trees, using its beak to strike quickly and its long tongue to extract the insects. It is an excellent climber and spends much of its time in trees. Although its population remains stable, this species may be affected by habitat loss due to deforestation.
The Middle Spotted Woodpecker is a medium-sized bird from the woodpecker family, primarily found in deciduous and mixed forests of Europe and Asia. It measures about 23 to 26 cm in length, with a wingspan of 40 to 45 cm, and weighs between 60 and 100 g. Its plumage is primarily black and white, with a red head in males and a red patch on the nape in females. The Middle Spotted Woodpecker is an excellent climber, using its strong beak to dig into tree bark in search of insect larvae, ants, and small arthropods. It generally lives in older, less disturbed forests, but its population can be threatened by deforestation and the loss of its natural habitat.
The Black Woodpecker is a large bird from the woodpecker family, primarily found in deciduous and mixed forests of Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It measures between 45 and 50 cm in length, with a wingspan of 60 to 70 cm, and weighs between 250 and 300 g. Its plumage is entirely black, except for its ivory-colored bill. In females, a red patch adorns the top of the head, while in males, the red patch extends from the top of the head down to the nape. The Black Woodpecker is an excellent climber and a skilled driller, primarily feeding on insect larvae, arthropods, and sometimes small mammals found under tree bark. It prefers mature, well-established forests, where it creates large holes in search of food. While its population remains relatively stable, the Black Woodpecker is sometimes threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.
The Three-toed Woodpecker is a small bird from the woodpecker family, primarily found in coniferous forests of Europe and Asia. It measures about 20 cm in length, with a wingspan of 40 to 45 cm, and weighs between 50 and 70 g. Its plumage is primarily black and white, with a distinctive yellow patch on the top of its head, and white streaks on its wings. What distinguishes the Three-toed Woodpecker is the presence of three toes on each foot, which allows it to climb with great agility. It primarily feeds on insect larvae, which it extracts from the bark of trees using its strong beak. The Three-toed Woodpecker lives in old forests and dense wooded areas, and although it is not currently threatened, it is vulnerable to habitat loss and human disturbance.
The Green Woodpecker is a large bird from the woodpecker family, primarily found in deciduous forests and parks in Europe. It measures about 30 to 35 cm in length, with a wingspan of 45 to 50 cm, and weighs between 200 and 250 g. Its plumage is primarily green, with yellow underparts and a red head in males, while females have a less prominent red patch. The Green Woodpecker is distinguished by its piercing call, which it uses to mark its territory. It primarily feeds on ants and their larvae, which it finds in soft soils and under tree bark, using its beak to pierce the ground and trunks. This bird is an excellent climber and spends much of its time on the ground searching for food. While its population remains relatively stable, the Green Woodpecker can be threatened by habitat loss due to intensive farming and deforestation.
The Red-backed Shrike is a medium-sized bird primarily found in hedgerows, scrubland, and open meadows across Europe and Asia. It measures about 20 to 23 cm in length and weighs between 40 and 50 g. Its plumage is characterized by a silvery-gray head, a brown back, and a whitish breast. It also has a distinctive black stripe running through its eyes. The Red-backed Shrike is an excellent hunter, primarily feeding on small birds, insects, rodents, and sometimes small reptiles. It is known for its "impaling" behavior, where it spikes its prey on thorns or barbed wire to store it. While its population remains stable in some regions, it can be threatened by habitat loss, the destruction of hedgerows, and the intensification of agriculture.
The Red-throated Diver is a seabird found primarily in the cold waters of the North Atlantic, particularly in Northern Europe and Canada. It measures about 50 to 60 cm in length, with a wingspan of 80 to 100 cm, and weighs between 1.5 and 2 kg. Its plumage is primarily gray and white, with a dark back and a light breast. The Red-throated Diver is an excellent diver, primarily feeding on fish and crustaceans, which it catches by diving underwater. It has well-adapted legs for swimming and spends a significant amount of time foraging for food at sea. While its population remains relatively stable, this species is vulnerable to human disturbances and marine pollution.
The Common Loon is a seabird primarily found in the cold waters of the North Atlantic, particularly in North America and Northern Europe. It measures about 60 to 70 cm in length, with a wingspan of 100 to 120 cm, and weighs between 1.5 and 2.5 kg. Its plumage is mainly black and white, with a dark back, white breast, and black head, giving it a distinctive appearance. The Common Loon is an exceptional diver, primarily feeding on fish and crustaceans, which it catches by diving deeply underwater. It is also known for its long migrations, moving to warmer areas during the winter. Although its population remains relatively stable, this species can be threatened by pollution, human disturbances, and habitat loss.
The Ringed Plover is a small coastal bird primarily found along beaches, estuaries, and sandy areas in Europe, North Africa, and Asia. It measures about 18 to 20 cm in length, with a wingspan of 40 to 45 cm, and weighs between 30 and 60 g. Its plumage is generally light beige with white underparts and an interrupted black ring around the neck and chest. This collar is more pronounced in males, while females have a less distinct collar. The Ringed Plover primarily feeds on small marine invertebrates and insects found in the sand or along the shore. It is often seen running along the waves, searching for food. While its population remains relatively stable, this species can be threatened by habitat loss, pollution, and human disturbances at its breeding sites.
The Grey Plover is a coastal bird primarily found along beaches and sandy areas in Europe, North Africa, Asia, and North America. It measures about 25 to 30 cm in length, with a wingspan of 60 to 70 cm, and weighs between 100 and 150 g. Its plumage is mainly silver-gray on the back with a white belly, and its wings are marked with black spots. During the breeding season, the Grey Plover displays brighter colors, with black plumage on the chest and head. It primarily feeds on marine worms, insects, and small crustaceans found in the sand, often near the high tide line. While its population remains relatively stable, this species can be threatened by habitat loss, pollution, and human disturbances at its breeding sites.
The Golden Plover is a migratory bird primarily found in tundra areas, open grasslands, and coastal regions in Europe and Asia, as well as in North America's coastal areas during winter. It measures about 25 to 30 cm in length, with a wingspan of 60 to 70 cm, and weighs between 150 and 250 g. Its plumage is primarily golden and black, with characteristic patterns on the chest and abdomen, and lighter coloring on the underside. During the breeding season, the male displays particularly bright plumage adorned with golden spots. The Golden Plover primarily feeds on small invertebrates, insects, and marine worms, which it finds by probing the ground or walking slowly in search of food. While its population remains stable, it can be threatened by habitat loss and human disturbances, particularly during the breeding period.
The Eurasian Dotterel is a migratory bird primarily found in tundra areas and alpine meadows of Europe, Central Asia, and northern China. It measures about 25 cm in length, with a wingspan of 55 to 60 cm, and weighs between 100 and 150 g. Its plumage is primarily brown, with lighter underparts and white spots on the wings. It has a brown head with distinctive black patterns around the eyes and on the throat. During the breeding season, males display brighter plumage. The Eurasian Dotterel primarily feeds on small insects, worms, and seeds found on bare soils or in grassy areas. While its population remains relatively stable, this species can be threatened by habitat loss, particularly due to climate change and disturbances at its breeding sites.
The Crestless Porcupine is a large nocturnal mammal primarily found in sub-Saharan Africa, in tropical forests and savannas. It measures between 60 and 80 cm in length, with a tail of 20 to 30 cm, and weighs between 15 and 30 kg. Its fur is primarily made up of rigid, long, sharp quills covering its back, sides, and tail. At the tip of its tail, it has modified quills that produce a distinctive sound when shaken, warning predators of its presence. The Crestless Porcupine is herbivorous and primarily feeds on roots, bark, fruits, and leaves. While its population remains relatively stable, it can be threatened by habitat destruction and hunting.
The Indian Porcupine is a large nocturnal mammal primarily found in South Asia, particularly in India, Nepal, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka. It measures about 60 to 90 cm in length, with a tail of 25 to 30 cm, and weighs between 10 and 20 kg. Its body is covered with long, rigid quills that range from black to white, forming distinct bands along its back. The Indian Porcupine uses its quills as a defense against predators and can easily detach them to throw when threatened. This porcupine is herbivorous, primarily feeding on fruits, roots, bark, and young shoots. While its population remains generally stable, it can be threatened by deforestation, habitat loss, and hunting.
The Puma is a large feline found primarily in the Americas, from Canada to the southern tip of South America. It measures between 1.1 and 1.8 meters in length, with a tail measuring 60 to 80 cm, and weighs between 40 and 100 kg, depending on the sex and subspecies. Its coat is typically sandy, gray, or brown, with a lighter underside. The Puma is a solitary predator, primarily hunting deer, small mammals, and birds. It is also capable of traveling great distances and adapting to different types of habitats, ranging from mountainous forests to desert areas. While its population remains relatively stable in certain regions, it can be threatened by habitat loss, fragmentation of its territories, and hunting.
The European Polecat is a small carnivore found primarily in Europe, inhabiting a variety of environments such as forests, meadows, and agricultural areas. It measures about 45 to 60 cm in length, with a tail of 20 to 30 cm, and weighs between 0.8 and 1.5 kg. Its fur is generally light brown or gray, with lighter underparts and a distinctive black mark on its face, surrounding its eyes. The European Polecat is a nocturnal and opportunistic predator, primarily feeding on small mammals, birds, eggs, as well as fruits and insects. While it is often perceived as a pest by farmers, it plays an important role in regulating populations of small animals. Its population is generally stable, but it can be threatened by habitat loss and road collisions.
The Bald Eagle is a large raptor primarily found in North America, near bodies of water such as lakes, rivers, and coastal areas. It measures about 70 to 90 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.8 to 2.3 meters, and weighs between 3 and 6 kg. Its plumage is primarily dark brown with characteristic white head and tail. The Bald Eagle is an excellent hunter, primarily feeding on fish, small mammals, and birds, which it captures by diving or snatching its prey with powerful talons. Although its population once faced a significant decline and was threatened, particularly due to pollution and hunting, the Bald Eagle is now a protected species, and its population has greatly recovered.
The Steller's Sea Eagle is a large raptor primarily found along the coasts of Northeast Asia, particularly in Russia and Japan. It measures about 85 to 105 cm in length, with a wingspan of 2.2 to 2.5 meters, and weighs between 4 and 9 kg, making it one of the largest eagles in the world. Its plumage is primarily dark brown with a white head and pale yellow beak. The Steller's Sea Eagle is an excellent fisherman, primarily feeding on fish, but it also hunts seabirds and marine mammals. It prefers coastal areas and islands where it can find its food and is often seen flying over the seas or resting on rocks or trees. While its population remains relatively stable, this species is vulnerable to habitat loss due to human activity, climate change, and ocean pollution.
The White-tailed Eagle is a large raptor primarily found in Eastern Europe, Northern Asia, and some regions of Central Asia. It measures about 70 to 90 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.8 to 2.3 meters, and weighs between 3 and 6 kg. Its plumage is primarily brown with a distinctive white head and tail. The White-tailed Eagle is an excellent fisherman, primarily feeding on fish, but it also hunts birds, small mammals, and scavenges carrion. It primarily inhabits areas near bodies of water such as lakes, rivers, and estuaries. While its population has been growing in some areas due to conservation efforts, this species remains vulnerable to habitat loss, water pollution, and human disturbances.
The Indian Python is a large snake primarily found in the Indian subcontinent, including Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bangladesh, and Pakistan. It typically measures between 3 and 4 meters in length, although some specimens can reach up to 6 meters, and weighs between 30 and 90 kg. Its coloration is generally beige or light brown with dark spot-like patterns along its back. The Indian Python is a constrictor, meaning it kills its prey by suffocating it before swallowing it whole. It primarily feeds on mammals, birds, and reptiles, which it captures using its strength and ability to camouflage in its environment. While its population remains relatively stable, this snake can be threatened by habitat loss and hunting for its skin.
The Reticulated Python is one of the most impressive and longest snakes in the world, growing over 7 meters in length. It is easily recognized by its complex mesh pattern on its skin, which gives it its name. Native to the tropical forests of Southeast Asia, this python is primarily terrestrial, although it is also capable of climbing trees. It typically hunts mammals and birds, using its constriction power to capture and suffocate its prey. Although generally discreet, it can be dangerous when threatened.
The Resplendent Quetzal is a colorful bird primarily found in the cloud forests of Guatemala and Mexico. It measures about 35 to 40 cm in length, with a wingspan of 50 to 60 cm, and weighs between 200 and 300 g. Its plumage is bright green with a vivid red throat and a long tail composed of elongated feathers. The male is particularly spectacular, with more colorful plumage and a distinctive crest. The Resplendent Quetzal is frugivorous, primarily feeding on fruits, berries, and small insects. It is also an important symbol in Mayan culture, representing freedom and the beauty of nature. Although its population is declining, primarily due to deforestation and poaching, this species remains protected in certain regions.
The Resplendent Quetzal is a magnificent bird primarily found in the tropical and subtropical forests of the southwestern United States, Mexico, and Central America. It measures about 30 to 40 cm in length, with a wingspan of 50 to 60 cm, and weighs between 100 and 150 g. Its plumage is a vibrant green, with a vivid red throat and a long tail composed of elongated and brilliant feathers. The male is particularly spectacular, with even more colorful plumage and a distinctive crest. The Resplendent Quetzal is primarily frugivorous, feeding on fruits, berries, and small insects. This bird is also an important symbol in the indigenous cultures of the region, representing beauty and freedom. While its population remains relatively stable, this species is still vulnerable due to deforestation and habitat loss.
The Red-eyed Tree Frog is a small arboreal frog primarily found in the humid tropical forests of Central and South America, particularly in Costa Rica and Panama. It measures about 5 to 7 cm in length and weighs between 10 and 20 g. Its body is generally green, with yellow or blue spots on the sides, and its eyes are bright red, making it a particularly recognizable species. The Red-eyed Tree Frog is insectivorous, primarily feeding on flying insects like mosquitoes and flies. It is nocturnal and spends the day hidden in foliage or tree crevices. While its population remains stable in certain protected areas, it is still threatened by deforestation and pollution of its natural habitat.
The Gliding Tree Frog is a medium-sized nocturnal arboreal frog, measuring between 5 and 8 cm. It has bright green dorsal coloration during the day, turning darker at night, with orange or bluish hues on its flanks and limbs. Its large red eyes and webbed feet enable it to "fly" from tree to tree by gliding. This species inhabits humid tropical forests in Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia, and Ecuador, between 15 and 750 m elevation. It resides in the canopy and descends to the ground to breed in temporary pools formed by rains. Breeding is explosive, with thousands of individuals gathering in a single night to lay eggs on leaves overhanging water. Tadpoles fall into the water upon hatching. Although listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, this species is locally threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.
The Raccoon is a small omnivorous mammal native to North America, but it has now spread widely to other regions of the world, including Europe and Asia. It measures about 40 to 70 cm in length, with a tail of 20 to 40 cm, and weighs between 4 and 10 kg. Its fur is primarily gray, with a distinctive black mask around the eyes, giving it a unique appearance. The Raccoon is an excellent climber and feeds on fruits, nuts, small animals, insects, as well as food scraps when it lives near human settlements. It is known for its curious behavior and its habit of "washing" its food, although this gesture is actually a reaction to the sensation of moisture in its paws. While its population is widespread, this species can sometimes be seen as a pest, especially due to its tendency to rummage through trash and cause damage to homes.
The Bat-eared Fox is a small carnivore primarily found in the savannas and semi-arid areas of Southern Africa. It measures about 40 to 50 cm in length, with a tail of 25 to 30 cm, and weighs between 1 and 2 kg. Its fur is primarily light gray or beige, with dark markings on the legs and face. What distinguishes it most are its large ears, which resemble those of a bat, and which are highly sensitive, allowing it to locate its prey, primarily insects, small mammals, and birds, through its acute hearing. The Bat-eared Fox is a nocturnal and highly social animal, often living in small groups. While its population remains relatively stable, it can be threatened by habitat destruction and hunting.
The Magellanic Fox is a small carnivore primarily found in the cold and coastal regions of Argentina and Chile, particularly in the Patagonian region. It measures about 60 to 70 cm in length, with a tail of 30 to 35 cm, and weighs between 3 and 5 kg. Its fur is generally gray, with lighter underparts and brown or reddish patches on its back and legs. This fox is omnivorous, feeding on small mammals, birds, insects, but also fruits and plants. It is mainly active during dusk and night, and usually lives alone or in small family groups. While its population remains relatively stable, this species can be threatened by habitat loss and hunting.
The Arctic Fox is a small carnivore found in the Arctic regions, primarily in Alaska, Canada, Scandinavia, and Russia. It measures about 45 to 50 cm in length, with a tail of 30 to 35 cm, and weighs between 3 and 9 kg, depending on the seasons. Its fur is typically white in winter, allowing it to camouflage in the snow, while it takes on a more brown or grayish hue in summer to blend in with the rocky and grassy landscapes. The Arctic Fox is an opportunistic omnivore, feeding on small mammals, birds, eggs, fruits, and berries. Although well adapted to the extreme living conditions of the Arctic, it is threatened by climate change, which is altering its natural habitat and the availability of its prey.
The Red Fox is a small carnivore primarily found in forests, meadows, and agricultural areas of Europe, Asia, and North America. It measures about 45 to 90 cm in length, with a tail of 30 to 50 cm, and weighs between 3 and 10 kg. Its fur is typically reddish with white underparts and on the legs, and its tail is bushy with a white tip. The Red Fox is an opportunistic and omnivorous animal, feeding on small mammals, birds, insects, fruits, and berries. It is primarily active at dusk and night. While its population remains relatively stable in many regions, it can be threatened by habitat loss, vehicle collisions, and diseases.
The Tibetan Fox is a small carnivore endemic to the mountainous regions of Tibet, Nepal, and northern India. It measures about 45 to 60 cm in length, with a tail of 30 to 40 cm, and weighs between 2 and 3 kg. Its fur is typically light gray to brown, with darker shades on the back and lighter underparts. It has large pointed ears and a long bushy tail. The Tibetan Fox is an opportunist, feeding on small mammals, birds, fruits, and berries. It primarily lives in dry and mountainous regions, where it digs burrows to protect itself from the cold. Although its population remains relatively stable, the Tibetan Fox is vulnerable to habitat loss and hunting.
The Southern White Rhinoceros is a large herbivorous mammal primarily found in the savannas and grasslands of Southern Africa, notably in South Africa, Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Namibia. It is one of the largest species of rhinoceros, measuring up to 4 meters in length and weighing between 1,500 and 2,400 kg. It is distinguished by its large square-shaped mouth, adapted for grazing, and its light gray to grayish skin. The Southern White Rhinoceros is a strict herbivore, primarily feeding on grass, though it may occasionally consume leaves and fruits. While its population has long been threatened by poaching and habitat loss, thanks to conservation efforts, its population has made a remarkable recovery and remains relatively stable.
The Javan Rhinoceros is a rare and critically endangered species of rhinoceros found primarily on the island of Java in Indonesia. It measures about 3 to 3.5 meters in length, with a tail of 60 to 80 cm, and weighs between 900 and 1,400 kg. Its fur is dark gray, with thick, wrinkled skin, and it has a single horn located on its nose. The Javan Rhinoceros is primarily herbivorous, feeding on fruits, leaves, shoots, and grass. It typically lives in tropical forests and swampy areas, where it hides in dense vegetation to avoid predators. It is threatened by habitat loss, illegal hunting, and habitat fragmentation, with only a very small remaining population, estimated at fewer than 75 individuals.
The Sumatran Rhinoceros is a critically endangered species of rhinoceros found primarily on the island of Sumatra in Indonesia. It measures about 2 to 3 meters in length, with a tail of 60 to 70 cm, and weighs between 500 and 800 kg. Its fur is generally light brown or reddish, with thick, wrinkled skin. This rhinoceros is one of the smallest members of the rhinoceros family and has two horns. The Sumatran Rhinoceros is herbivorous, feeding on leaves, fruits, roots, and shoots. It primarily lives in tropical lowland forests and swampy areas. While conservation efforts have been made to protect this species, it remains threatened by deforestation, poaching, and habitat loss, with a population estimated to be fewer than 80 individuals in the wild.
The Indian Rhinoceros, also known as the one-horned rhinoceros, is a large species of rhinoceros found primarily in the Indian subcontinent, particularly in India, Nepal, Bangladesh, and Bhutan. It measures about 3.5 to 4 meters in length, with a tail of 60 to 70 cm, and weighs between 2,200 and 3,000 kg. This rhinoceros is easily recognized by its thick, wrinkled skin, with a single horn located on its nose. It primarily feeds on grasses, leaves, and fruits, and lives in a variety of habitats, including grasslands, wetlands, and riverine forests. While its population has long been threatened by poaching and habitat loss, thanks to conservation efforts, the Indian Rhinoceros has experienced some recovery, but it remains vulnerable.
The Black Rhinoceros is a large species of rhinoceros primarily found in East and Southern Africa, notably in Kenya, Tanzania, Namibia, and South Africa. It measures about 3.5 to 4 meters in length, with a tail of 50 to 70 cm, and weighs between 800 and 1,400 kg. This rhinoceros is distinguished by its black skin (although some specimens may be gray) and its two horns located on its nose. Unlike the White Rhinoceros, it has a more pointed mouth, adapted for eating bushes and trees. The Black Rhinoceros is primarily herbivorous, feeding on leaves, fruits, twigs, and tree bark. While its population has long been threatened by poaching and habitat loss, conservation efforts have helped stabilize its population, although it remains critically endangered.
The European Roller is a colorful bird primarily found in open forests, meadows, and agricultural lands across Europe, particularly in Spain, France, Italy, and Turkey. It measures about 30 to 32 cm in length, with a wingspan of 50 to 60 cm, and weighs between 100 and 150 g. Its plumage is especially vibrant, with colors ranging from bright blue to green and brown, and it has a strong, slightly curved beak. The European Roller primarily feeds on flying insects, such as dragonflies, flies, and grasshoppers, which it catches in flight. It is known for its stunning acrobatic flights and its habit of perching on elevated spots, such as tree branches or utility poles. While its
The African straw-coloured fruit bat is a fruit-eating bat species native to sub-Saharan Africa. This bat is easily recognizable by its golden or straw-colored fur, which helps it blend into the foliage during the day. The African straw-coloured fruit bats primarily feed on fruits, nectar, and pollen, playing a crucial role in pollinating plants. They form large colonies and are often seen in flight at dusk as they head out to search for food. These bats can also travel long distances, making them adaptable to a wide range of habitats.
The saiga is an antelope from the Central Asian steppes, recognizable by its prominent, trunk-like nose that filters dust and warms inhaled air. Adapted to arid environments, it migrates in large herds in search of pastures. Its population, once declining, shows signs of recovery due to conservation efforts.
The Japanese giant salamander is one of the largest salamanders in the world, reaching lengths of up to 1.5 meters. It lives in cold rivers and mountain streams in Japan, primarily in the regions of Honshu and Shikoku. This nocturnal predator feeds mainly on fish, crustaceans, and aquatic insects. Due to its imposing appearance and secretive behavior, this salamander is often difficult to spot. It is protected due to habitat loss and river pollution.
The Spotted Salamander is an amphibian primarily found in forests and wetlands across Europe, particularly in France, Spain, and Germany. It typically measures between 15 and 25 cm in length, although some specimens can reach up to 30 cm. Its body is black with bright yellow spots, making it easily identifiable. The Spotted Salamander is a nocturnal and terrestrial animal, hiding during the day under rocks or in holes in the ground to protect itself from the heat. It is carnivorous and feeds primarily on insects, worms, small crustaceans, and other invertebrates. While it remains relatively abundant in certain regions, this species is threatened by water pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change.
The Wild Boar is a large omnivorous mammal found primarily in forests, wooded areas, and mountains of Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It measures between 1.2 and 1.8 meters in length, with a tail of 15 to 25 cm, and weighs between 50 and 100 kg, though some specimens can reach up to 200 kg. Its fur is typically brown, with darker hair on the back and lighter on the sides. The Wild Boar is a nocturnal animal, primarily feeding on roots, fruits, seeds, insects, and small animals. While it is considered game, it can sometimes pose a threat to agricultural crops due to its tendency to root through the soil. This species is widely distributed, and its population remains relatively stable, although it is sometimes threatened by excessive hunting and habitat loss.
Anas crecca is the smallest dabbling duck in Eurasia, measuring between 33 and 38 cm in length with a wingspan of 53 to 58 cm. The male in breeding plumage is distinguished by a chestnut head with an iridescent green band from the eye to the nape, a white collar, and a body finely vermiculated grey. The female is brown speckled, with a light line at the eye and a light spot on the rump. It frequents shallow wetlands such as marshes, ponds, rice fields, and mudflats, often with dense aquatic vegetation. It primarily feeds on seeds of aquatic plants, algae, small invertebrates, and insect larvae. Reproduction occurs between May and July, with the female building a well-hidden nest in vegetation, where she lays 8 to 11 eggs. Incubation lasts about 21 to 23 days. A migratory species, it winters in Europe, Asia, and North Africa.
The Garganey is a small dabbling duck measuring between 37 and 41 cm in length with a wingspan of 59 to 67 cm. The breeding male is characterized by a broad white crescent over a reddish-brown head, finely vermiculated gray flanks, and gray-blue scapulars. The female has a cryptic brown-beige plumage with three longitudinal facial stripes. This species inhabits marshes, ponds, and floodplain meadows rich in aquatic vegetation, generally avoiding brackish waters. It feeds mainly on seeds, aquatic plants, mollusks, insects, and small crustaceans. Strictly migratory, it breeds in Europe and western Asia, wintering in sub-Saharan Africa, India, and Southeast Asia. Although listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, it is locally vulnerable due to the loss of wetland habitats.
The Coral Snake is a venomous species found primarily in Central and South America, notably in Mexico, Costa Rica, Panama, and Colombia. It typically measures between 50 and 80 cm in length, although some specimens can reach up to 1 meter. It is distinguished by its red, black, and yellow rings, giving it a vibrant and easily recognizable appearance. Although coral snakes are venomous, their bite is rarely fatal due to their small size and the difficulty of delivering the bite, but it can cause severe symptoms due to their neurotoxin. These snakes typically live in tropical forests, where they hide under dead leaves or in shrubs. They primarily feed on small reptiles, amphibians, and young snakes.
The Serval is a medium-sized feline primarily found in the savannas and grasslands of sub-Saharan Africa, notably in East and Central Africa. It typically measures between 60 and 100 cm in length, with a tail of 30 to 40 cm, and weighs between 9 and 18 kg. Its coat is golden yellow, speckled with irregular black spots, which helps it camouflage effectively in its natural environment. The Serval has long legs, a small head, and large ears, which allow it to easily detect its prey, including small mammals, birds, and reptiles. It is also capable of impressive leaps to catch its prey, particularly birds in flight. While its population remains stable in some areas, the Serval is threatened by habitat loss and illegal hunting.
The Snow Monkey, also known as the Japanese macaque, is a species of primate primarily found in the mountains and snowy regions of Japan. It measures about 50 to 60 cm in length, with a tail of 20 to 25 cm, and weighs between 10 and 14 kg. Its fur is dense and thick, typically brown or gray, with a reddish face that becomes more pronounced in males, especially during the breeding season. The Snow Monkey lives in complex social groups and is especially known for its social behaviors, notably bathing in hot springs during the winter, which has become one of the most iconic images of Japan. It primarily feeds on fruits, roots, seeds, and sometimes small animals. While its population remains relatively stable, this species sometimes faces habitat loss and conflicts with human populations.
The Golden Monkey, also known as the Roxellana Rhinopithecus, is a medium-sized primate found primarily in the mountains of China, particularly in the provinces of Sichuan and Gansu. It measures about 55 to 70 cm in length, with a tail of 50 to 60 cm, and weighs between 10 and 15 kg. Its fur is a bright golden color, with reddish hues and long hair around the face that forms a kind of mane. The Golden Monkey is primarily herbivorous, feeding on leaves, fruits, seeds, and occasionally small insects. It lives in organized social groups and is often observed in mountainous forests at high altitudes. While it is protected in certain regions, this species is threatened by habitat loss, deforestation, and poaching, which has led to a decline in its population.
The Howler Monkey is a medium-sized primate found primarily in the tropical forests of Central and South America, notably in Mexico, Central America, and parts of the Amazon rainforest. It typically measures about 40 to 70 cm in length, with a prehensile tail of 50 to 75 cm, and weighs between 7 and 10 kg. Its fur varies from black to brown, and it has a large throat and powerful jaw, which allow it to produce extremely loud sounds, used to demarcate territory and communicate with other members of its group. The Howler Monkey is primarily herbivorous, feeding on leaves, fruits, and flowers. It lives in social groups and is primarily active during the day, moving slowly from tree to tree. While its population remains relatively stable, this species is threatened by deforestation and hunting.
The Geoffroy's Spider Monkey is a medium-sized primate primarily found in the tropical forests of Mexico and Central America. It typically measures about 50 to 60 cm in length, with a prehensile tail of around 70 to 80 cm, and weighs between 10 and 20 kg. Its fur is generally brown or black, with lighter spots on the belly and legs. The Geoffroy's Spider Monkey has a highly flexible and prehensile tail, which it uses to grasp tree branches and move easily through the forest canopy. It is primarily herbivorous, feeding on fruits, leaves, flowers, and sometimes small insects. These monkeys live in organized social groups and are primarily active during the day. While they are relatively numerous, they are threatened by deforestation and loss of their natural habitat.
The Eurasian Spoonbill is a medium-sized bird primarily found in wetlands across Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It measures about 80 to 95 cm in length, with a wingspan of 120 to 130 cm, and weighs between 1.5 and 2.5 kg. Its plumage is predominantly white, with a long spoon-shaped bill that allows it to forage in shallow waters, primarily feeding on aquatic invertebrates, small fish, and crustaceans. The Eurasian Spoonbill is often seen in groups, feeding in marshes, rice fields, or estuaries. It is migratory, moving to warmer regions during the winter. While its population remains stable in certain areas, the Eurasian Spoonbill faces threats related to habitat loss, water pollution, and urbanization.
The Roseate Spoonbill is a large wading bird with striking pink plumage, measuring between 71 and 86 cm in length and a wingspan of 120 to 135 cm. Its long, spatula-shaped bill is used to sweep shallow waters side to side in search of prey. Adults have a greenish bare head, white neck and back, and vivid pink wings with carmine highlights. Juveniles are paler, with a feathered head and lighter pink plumage. This species feeds primarily on small fish, crustaceans, and aquatic insects, captured by filtering mud in wetlands. It inhabits coastal marshes, mangroves, lagoons, and estuaries from the southern United States to South America. Although listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, the Roseate Spoonbill remains vulnerable to habitat degradation, particularly due to pollution and loss of wetlands.
The Springbok is a small antelope found primarily in the savannas and grasslands of South Africa, Namibia, and Botswana. It typically stands about 75 cm at the shoulder, with a body length of 1.10 to 1.30 meters, and weighs between 30 and 40 kg. Its coat is primarily white and brown, with a dark line running along its back and a large white patch on its sides. What sets the Springbok apart is its ability to perform characteristic jumps, known as "pronking," where the animal leaps into the air with its legs extended, often to signal danger or to impress another individual. The Springbok is herbivorous, feeding primarily on grass and leaves. While it remains relatively abundant in its habitat, it is sometimes threatened by hunting and habitat loss.
The Steenbok is a small antelope found primarily in dry regions and open savannas of sub-Saharan Africa, particularly in countries such as South Africa, Botswana, and Namibia. It typically stands about 45 to 60 cm at the shoulder, with a body length of 80 to 100 cm, and weighs between 8 and 15 kg. Its coat is generally fawn to light brown, with white markings on its legs and around its eyes. The Steenbok has small horns in males, but they are generally more discreet than those of other antelope species. This small herbivore feeds primarily on grasses, fruits, and leaves. It is known for its ability to hide in dense vegetation and escape quickly from predators. While its population remains relatively stable, the Steenbok is sometimes threatened by habitat loss and hunting.
The Arctic Tern is a migratory bird species primarily found in coastal regions of the Arctic during the summer, and in tropical and subtropical areas during the winter. It measures about 35 to 40 cm in length, with a wingspan of 80 to 100 cm, and weighs between 90 and 130 g. Its plumage is mostly white with gray tones on the back and wings, and its head is black with a distinctive black band around the eyes. The Arctic Tern is famous for its impressive migrations, traveling thousands of kilometers between its breeding sites in the Arctic and its wintering grounds in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Australia. It primarily feeds on fish and marine invertebrates, which it catches by diving into the water. While its population remains stable, the Arctic Tern is threatened by habitat loss, human disturbances, and climate change.
The Meerkat is a small carnivorous mammal primarily found in the dry and desert regions of southern Africa, notably in South Africa, Botswana, and Namibia. It typically measures about 25 to 35 cm in length, with a tail of 20 to 25 cm, and weighs between 0.6 and 1 kg. Its fur is gray-brown, with lighter spots on the belly, and it has a small head and large black eyes. The Meerkat is especially known for its characteristic posture, standing on its hind legs to survey its surroundings. It lives in organized social groups, called "clans," and primarily feeds on insects, small reptiles, and fruits. While its population remains relatively stable, the Meerkat is threatened by habitat loss and human disturbances.
The Common Shelduck is a large duck with a distinctive plumage, measuring between 58 and 67 cm in length. It is identified by its glossy greenish-black head, white body with a broad chestnut band, and bright red bill. Males have a prominent knob at the base of the bill, which females lack. This species inhabits estuaries, lagoons, salt marshes, tidal mudflats, and shallow lake shores, often in flocks. It nests in burrows or cavities, sometimes dug into dunes or embankments. The shelduck primarily feeds on aquatic invertebrates such as mollusks, worms, and crustaceans, filtered from the mud. While generally secure, it is vulnerable to coastal wetland destruction.
The Takin is a large herbivore found primarily in the mountainous regions of the Himalayas and China. It typically stands between 1.2 and 1.5 meters at the shoulder, with a body length of 1.5 to 2 meters, and weighs between 250 and 350 kg. Its fur is dense and ranges from golden to light brown, with longer hair around the throat and shoulders, giving it a robust appearance. The Takin is an excellent climber and primarily feeds on woody vegetation, leaves, young shoots, and fruits. It lives in social groups and is mainly active at dawn and dusk. While its population remains relatively stable in certain areas, this species is threatened by deforestation and human activities, including hunting and encroachment on its natural habitat.
The Giant Anteater, also known as the Myrmecophaga tridactyla, is a large insectivorous mammal primarily found in the tropical forests and savannas of South America, notably in Brazil, Guyana, Argentina, and Venezuela. It measures between 1.7 and 2.2 meters in length, with a tail of 60 to 90 cm, and weighs between 25 and 40 kg. Its fur is generally light gray or brown, and it has a long cylindrical snout, as well as an extremely long tongue that can reach up to 60 cm in length, which it uses to catch ants and termites. The Giant Anteater is a nocturnal animal, primarily feeding on ants, termites, and other insects found in nests. While it is an excellent digger and climber, it is threatened by habitat loss and illegal hunting.
The Mexican Tamandua, or Tamandua mexicana, is an insectivorous mammal primarily found in the tropical and subtropical forests of Mexico, Guatemala, and Honduras. It typically measures between 50 and 70 cm in length, with a tail of 40 to 50 cm, and weighs between 4 and 7 kg. Its fur is generally yellow-brown, with a black mask around the eyes and a wide black band on its back. This tamandua has a long tongue, which can reach up to 40 cm, used to catch termites and ants, its main food source. The Mexican Tamandua is also an excellent climber, spending much of its time in trees. It is generally nocturnal and primarily feeds on insects and occasionally fruits. While its population remains relatively stable, it is sometimes threatened by deforestation and the loss of its natural habitat.
The Golden Lion Tamarin is a small primate found primarily in the tropical forests of southeastern Brazil. It typically measures about 20 to 30 cm in length, with a tail of 35 to 45 cm, and weighs between 500 and 700 g. Its fur is a bright golden orange, giving it a distinctive and striking appearance. The Golden Lion Tamarin is known for its small size, great agility, and complex social behaviors. It lives in family groups and primarily feeds on fruits, insects, nectar, and small vertebrates. Although it is an excellent climber and spends most of its time in trees, this species is threatened by deforestation, habitat loss, and illegal wildlife trade.
The Bishop Tanager is a small, colorful bird found primarily in the tropical forests and wooded areas of Central and South America, notably in Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia, and Venezuela. It typically measures about 18 cm in length and weighs between 20 and 30 g. Its plumage is especially vibrant, with shades of green, yellow, and red, giving it a striking appearance, which is why it is named as such. The Bishop Tanager is frugivorous, primarily feeding on fruits, berries, and seeds, but it can also eat insects. This bird is known for its social behaviors, living in small groups or pairs, and is often observed moving through trees in search of food. While its population remains stable, it is sometimes threatened by deforestation and the loss of its natural habitat.
The Baird's Tapir is a species of tapir found primarily in the tropical forests of Central America, notably in Guatemala, Honduras, Costa Rica, and Nicaragua. It typically measures about 2 to 2.5 meters in length, with a short tail of 20 to 30 cm, and weighs between 200 and 300 kg. Its fur is predominantly black or dark brown, with lighter areas on its legs and ears. The Baird's Tapir has a long, flexible snout that allows it to grasp leaves, fruits, branches, and grasses. While it is an excellent swimmer and often spends time in water, it primarily lives in dense, humid forests. This species is threatened by deforestation, illegal hunting, and habitat loss, which has led to a decline in its population.
The Brazilian tapir, also known as the Amazonian tapir, is a large herbivorous mammal that lives in the humid tropical forests and wetland areas of the Amazon basin. It is easily recognized by its massive body, short legs, and elongated trunk-like nose, which it uses to grasp branches and leaves. The Brazilian tapir is primarily nocturnal and solitary, feeding mainly on fruits, leaves, and roots. While rather calm, it is an excellent swimmer and often spends time in water to cool off or move around. This tapir is currently listed as vulnerable due to habitat loss and hunting.
The Tarsier is a small nocturnal primate found primarily in the tropical forests of Southeast Asia, notably in the Philippines, Indonesia, and Borneo. It typically measures about 10 to 15 cm in length, with a tail of 20 to 25 cm, and weighs between 100 and 150 g. The Tarsier is known for its remarkably large eyes, which account for about one-third of its head size, allowing it to see in low-light conditions. It also has long legs and large hands, which enable it to move agilely through the trees, where it primarily hunts insects, spiders, and occasionally small vertebrates. While its population remains relatively stable in some areas, the Tarsier is threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.
The Giant Armadillo is the largest of the armadillos, found primarily in the tropical forests of South America, notably in Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay, and Argentina. It typically measures between 1.5 and 2 meters in length, including its tail, and can weigh up to 60 kg. Its fur is rough and brown, and it has a hard shell, typical of armadillos, which serves as protection against predators. The Giant Armadillo is primarily nocturnal and terrestrial, feeding mainly on insects, worms, fruits, and roots. While it is an excellent burrower, it is threatened by illegal hunting and habitat destruction, leading to a decline in its population.
The Western Capercaillie, or Lyre Grouse, is a large bird primarily found in the coniferous forests and wooded areas of Eastern and Northern Europe, notably in Scandinavia, Russia, and Poland. It typically measures about 40 to 50 cm in length and weighs between 500 and 800 g. Its plumage is mainly brown and black, with white markings and red hues on the chest. The Lyre Grouse is particularly famous for the spectacular courtship dance of the male, who spreads his feathers in a lyre shape to attract a female. It primarily inhabits dense forest habitats and feeds on berries, seeds, young shoots, and insects. While its population remains relatively stable in some areas, the Lyre Grouse is threatened by habitat loss, deforestation, and human disturbances.
The Wallcreeper is a small bird found primarily in rocky cliffs and mountains of Europe, notably in the Alps, the Pyrenees, and the Carpathians. It typically measures about 14 to 16 cm in length and weighs between 12 and 20 g. Its plumage is characterized by distinct patterns of white, gray, and black, with very prominent white markings on its wings. The Wallcreeper is an excellent climber, capable of moving on almost vertical rock faces thanks to its strong claws. It primarily feeds on insects, small arachnids, and larvae that it finds in rock crevices. Although it is a relatively rare bird, the Wallcreeper is threatened by the disturbance of its rocky habitats, particularly due to urbanization and the exploitation of natural resources.
The Tiger is a large cat primarily found in the forests, savannas, and grasslands of Asia, notably in India, China, Indonesia, and Russia. It typically measures between 2.5 and 3.5 meters in length, including the tail, and can weigh between 100 and 300 kg, depending on the subspecies. The Tiger is easily recognizable by its striped coat, which varies from yellow-orange to white, with distinctive black bands. It is a solitary and territorial predator, primarily feeding on large herbivores such as deer, wild boars, and buffalo. While it is at the top of the food chain, the Tiger is threatened by habitat loss, poaching for its fur and bones, and conflicts with human populations. Some subspecies, such as the Sumatran Tiger and the Siberian Tiger, are particularly endangered.
The Bengal Tiger is a subspecies of tiger found primarily in the forests of India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and Myanmar. It typically measures between 2.7 and 3.1 meters in length, with a tail of 1 to 1.2 meters, and weighs between 200 and 260 kg. Its fur is yellow-orange with distinct black stripes, and its impressive size makes it one of the largest and most powerful tiger subspecies. The Bengal Tiger is a solitary and territorial predator, primarily feeding on large herbivores such as deer, wild boars, and buffalo. Although its population is declining, the Bengal Tiger is one of the best-protected tiger subspecies, with active conservation efforts in wildlife reserves and national parks. It is still threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflicts.
The Eurasian Wryneck is a small bird of the woodpecker family, primarily found in open forests and clearings across Europe, especially in France, Spain, Italy, and Russia. It typically measures about 22 cm in length and weighs between 50 and 60 g. Its plumage is mainly brown, with dark spot-like patterns on the back and wings, and a light-colored throat. The Eurasian Wryneck feeds primarily on ants and other insects that it finds on tree trunks or branches. It is often observed pecking at tree bark in search of food. While its population is generally stable, the Eurasian Wryneck is sometimes threatened by habitat loss due to deforestation and changes in agriculture.
The Greek tortoise is a terrestrial species of tortoise native to the Mediterranean regions, particularly Greece, Turkey, and neighboring countries. It is easily recognized by its light brown to yellow shell, often marked with black patterns. The Greek tortoise is herbivorous, feeding primarily on plants, flowers, and vegetables. It lives in dry habitats such as rocky hills and meadows, and is well adapted to a hot and dry climate. This reptile is slow and discreet, spending much of its life hidden under bushes or rocks.
The Hawksbill sea turtle is a widely recognized species of sea turtle, known for its shell's overlapping, tile-like scales, from which it gets its name. It is primarily found in the warm tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans. This marine reptile is primarily carnivorous, feeding on jellyfish, fish, and crustaceans. The Hawksbill is particularly vulnerable due to habitat loss from pollution and illegal collection of its shell. It is also threatened by illegal fishing and loss of nesting beaches.
The Leatherback Turtle is the largest of all sea turtles and one of the largest reptiles in the world. It typically measures between 2 and 2.5 meters in length, with a weight ranging from 250 to 700 kg, although some individuals can reach up to 900 kg. Its shell is usually dark in color, sometimes tinged with gray or brown, and is covered with small, tile-like plates. The Leatherback Turtle is an excellent swimmer, capable of covering long distances across oceans. It primarily feeds on jellyfish, which it catches while swimming in deep waters. Despite its impressive size, the Leatherback Turtle is critically endangered due to plastic pollution, the loss of its nesting habitats, and poaching. Its population is declining, and it is protected in many countries.
The Olive Ridley Turtle is a species of sea turtle found primarily in the warm waters of the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans, particularly along the coasts of Central America, Mexico, India, and Southeast Asia. It typically measures between 60 and 70 cm in length and weighs between 35 and 50 kg. Its shell is olive in color, which gives it its name, and it has flippers adapted for swimming. The Olive Ridley Turtle is primarily carnivorous, feeding on jellyfish, fish, and crustaceans. It is also known for its mass nesting sites, particularly on the Pacific beaches of Costa Rica. Unfortunately, the Olive Ridley Turtle is critically endangered due to habitat loss, poaching, ocean pollution, and accidental capture in fishing nets.
The Green Sea Turtle is a large marine turtle found primarily in the warm and tropical waters worldwide, notably in the Caribbean, Pacific, Indian Ocean, and along the coasts of many tropical islands. It can reach a length of 1 to 1.5 meters and weigh between 150 and 200 kg, although some individuals can be even heavier. Its name comes from the green color of its body fat. The Green Sea Turtle primarily feeds on seagrasses and aquatic plants, which distinguishes it from other carnivorous sea turtles. It is also an excellent swimmer and can travel long distances between its breeding sites and feeding grounds. While its population has declined due to habitat loss, poaching, and ocean pollution, it benefits from numerous conservation efforts and is protected in many countries.
The Keel-billed Toucan is a large, colorful bird found primarily in the tropical forests of Central America, notably in Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, and Mexico. It typically measures about 50 cm in length and weighs between 400 and 500 g. Its plumage is mainly black, with a bright yellow chest and face, and it is easily recognizable by its large, colorful bill, which is primarily orange with shades of red and yellow. The Keel-billed Toucan primarily feeds on fruits, berries, and nuts, but can also consume insects and small reptiles. It generally lives in social groups and is an excellent climber, spending much of its time in trees. While its population remains relatively stable, the Keel-billed Toucan is sometimes threatened by habitat loss due to deforestation.
The Yellow-throated Toucan is a colorful bird found primarily in the tropical forests of Central America, notably in Costa Rica, Panama, Nicaragua, and Honduras. It typically measures about 50 cm in length and weighs between 400 and 600 g. Its plumage is mainly black, with a bright yellow throat and chest, and it has a wide, colorful bill, typically yellow with touches of red and orange. The Yellow-throated Toucan is primarily frugivorous, feeding on fruits, berries, and nuts, but it can also consume insects and small vertebrates. It generally lives in small social groups and is an excellent climber, spending much of its time in trees. While it remains relatively stable in certain areas, it is sometimes threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.
The Emerald Toucanet is a small forest toucan recognizable by its vibrant green plumage, bicolored bill, and compact size. Males and females are very similar, though males may have a slightly longer bill. It inhabits humid mountain forests of Central and South America, from Mexico to northern Bolivia, often seen in small groups in the canopy or foraging for fruit. It is omnivorous, feeding on fruit, insects, small reptiles, and occasionally bird eggs. Though locally threatened by deforestation, it remains widespread overall.
The Ruddy Turnstone is a small migratory bird primarily found on rocky and sandy coastal areas in Europe, Asia, and North America. It typically measures about 22 cm in length and weighs between 60 and 100 g. Its plumage is characterized by earthy colors, with black, brown, and white patches, and a distinctive black band around the neck, which gives it its name. The Ruddy Turnstone primarily feeds on small invertebrates found by probing rocks and beaches, such as crustaceans, mollusks, and worms. It is an excellent migrant, traveling long distances between its breeding sites in Europe and its wintering grounds in Africa and Asia. While its population remains stable in some areas, it is threatened by the loss of its coastal habitat due to urbanization and pollution.
The Turtle Dove is a small, slender dove measuring between 25 and 28 cm in length with a wingspan of 45 to 50 cm. Its plumage is characterized by a rosy chest, a back speckled with black, and a gray-blue head adorned with black and white spots on the neck. It emits a soft, rolling cooing sound, often heard in spring and summer. It frequents clear woods, hedges, and open agricultural areas, where it feeds primarily on seeds fallen to the ground. Breeding occurs from May to July, with one or two clutches of two white eggs. The young leave the nest between 19 and 21 days after hatching. A migratory species, it winters in sub-Saharan Africa. Listed as "Vulnerable" by the IUCN.
The Eurasian Collared Dove is a medium-sized dove, measuring about 32 cm in length with a wingspan of 47 to 55 cm. Its plumage is grayish-beige with pinkish hues on the head and chest. It is characterized by a black half-collar edged with white on the back of its neck. It emits a soft cooing sound, often described as "hoo-hoo-hoo-hoo." Originally from South Asia, it has rapidly expanded into Europe, North Africa, and the Americas. It frequents urban, suburban, and agricultural areas, feeding primarily on seeds, berries, and buds. Breeding can occur year-round, with an average of three to four broods per year. The young leave the nest about 19 days after hatching. The species is listed as Least Concern by the IUCN.
The Black-headed Trogon is a colorful bird found primarily in the tropical and subtropical forests of Central and South America, notably in Mexico, Honduras, Costa Rica, and Panama. It typically measures about 25 to 30 cm in length and weighs between 90 and 120 g. Its plumage is especially vibrant, with a black head contrasting with a brightly colored body, primarily green and red. The Black-headed Trogon primarily feeds on fruits, berries, and small insects. It is often observed in dense forests, where it enjoys perching on tree branches. While its population remains relatively stable, it is sometimes threatened by deforestation and the loss of its natural habitat.
The Massena's Trogon is a colorful bird found primarily in the humid tropical forests and wooded areas of Central America, particularly in Costa Rica, Panama, and Nicaragua. It typically measures about 26 to 30 cm in length and weighs between 90 and 120 g. Its plumage is vibrantly colored, with a green and red body, a yellow chest, and a black head, giving it a distinct appearance. The Massena's Trogon primarily feeds on fruits, berries, and small insects that it finds in the trees. It is often observed perched on branches, where it moves calmly and discreetly. While its population remains stable in some areas, it is sometimes threatened by deforestation and the loss of its natural habitat.
The Northern Lapwing is a medium-sized bird found primarily in grasslands, fields, and wetlands across Europe, Western Asia, and the Middle East. It typically measures about 28 to 32 cm in length and weighs between 150 and 200 g. Its plumage is primarily black and white, with a distinctive crest on its head and a white belly. The Northern Lapwing is a ground-dwelling bird that primarily feeds on insects, worms, and other small invertebrates found in the soil. It is also known for its ground nesting behaviors, often in colonies. While its population remains stable in some areas, the Northern Lapwing is threatened by habitat loss due to intensive agriculture and land degradation.
The Nile Monitor is a large reptile species native to Africa, particularly found in sub-Saharan regions. It is easily recognized by its impressive size, long and powerful body, and smooth scales. This monitor is semi-aquatic and is commonly found near rivers, lakes, and swamps, where it feeds on fish, amphibians, birds, and even small mammals. Highly agile, it is also capable of swimming and climbing with ease. The Nile Monitor is known for its territorial nature and sometimes aggressive behaviors, especially during the breeding season.
The Griffon Vulture is a large bird of prey found primarily in the mountains, hills, and rocky areas of Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It typically measures between 93 and 110 cm in length, with a wingspan of 2.5 to 2.8 meters, and weighs between 6 and 12 kg. Its plumage is mainly light brown, with white feathers around its neck and head, and a large area of bare skin on the neck. The Griffon Vulture is a scavenger, primarily feeding on animal carcasses. It plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by cleaning up carcasses and preventing the spread of diseases. While its population has declined in some regions, the Griffon Vulture benefits from conservation programs, but it remains threatened by habitat loss, illegal hunting, and poisoning.
The Monk Vulture is a large bird of prey found primarily in the mountains of Eastern Europe, Asia Minor, and Central Asia, with populations in Spain, Bulgaria, and Greece. It typically measures between 80 and 100 cm in length, with a wingspan of 2.3 to 2.8 meters, and weighs between 7 and 12 kg. Its plumage is mainly dark brown, with a bare head, distinguishing it from other vultures. The Monk Vulture is a scavenger, primarily feeding on animal carcasses, and plays a crucial ecological role in helping to remove carcasses and prevent the spread of diseases. While it is protected in many regions, it remains threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and poisoning.
The Vicuna is a wild camelid native to the high plateaus of the Andes in South America. This small animal with silky, lightweight fur is closely related to the llama and alpaca, but unlike these, the vicuna is a wild animal. It lives in the mountainous regions of Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, and Peru, at high altitudes, often above 3,000 meters. The vicuna primarily feeds on herbaceous vegetation, especially alpine grasses. Its wool, soft and fine, is highly sought after, but it is protected by strict regulations. It is a timid animal, living in small groups and often moving over great distances in search of food.
The Asp Viper is a venomous snake species found primarily in rocky areas, meadows, and forests of Southern Europe, notably in France, Spain, Italy, and Switzerland. It typically measures between 60 and 80 cm in length, although some individuals can reach up to 1 meter. Its color ranges from gray to brown, with a zigzag pattern on its back and a distinct triangular head. The Asp Viper primarily feeds on small mammals, lizards, and birds. While venomous, its poison is generally harmless to humans, though bites do require medical attention. It is a protected species in many regions but is threatened by habitat loss and human persecution.
The Common European Adder is a medium-sized venomous snake, typically measuring between 60 and 90 cm in length. It exhibits variable coloration, ranging from brown to gray, with a darker zigzag dorsal stripe. Melanistic individuals are entirely black. This species is widely distributed across Europe and Asia, from the United Kingdom to the Pacific coast of Russia, and up to the Arctic Circle. It inhabits various environments, including forests, heathlands, meadows, and wetlands. The adder is diurnal and feeds primarily on small mammals, amphibians, lizards, and birds. It is ovoviviparous, giving birth to 3 to 20 live young in late summer or early autumn. Although its venom can be dangerous, bites are rare and seldom fatal. Listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, it is protected in several European countries.
The European Mink is a small carnivorous mammal primarily found in wetlands, rivers, and marshes of Eastern Europe, notably in Russia, Ukraine, Poland, and Hungary. It typically measures between 45 and 55 cm in length, with a tail of about 15 to 20 cm, and weighs between 700 g and 1 kg. Its fur is generally dark brown on the back and lighter on the belly, with a distinctive black band running across its face. The European Mink is an excellent swimmer and fisher, primarily feeding on fish, crustaceans, and small mammals. Unfortunately, it is critically endangered due to habitat loss, water pollution, and competition with the American Mink, an invasive species. Its population has significantly declined, and it is now classified as an endangered species.
The Elk is a large cervid primarily found in North America, in forests, grasslands, and mountains, notably in Canada and the United States. It typically measures between 1.5 and 2 meters in height at the shoulder and can weigh between 300 and 500 kg. The Elk is easily recognizable by its large antlers, which can reach up to 1.2 meters in width. Its coat varies from light brown to dark brown, with a lighter area around the neck. It primarily feeds on grasses, leaves, and bark, and is especially active during the fall, during the rutting season. While the Elk population is relatively stable, some subpopulations are threatened by habitat loss and disease.
The Common Wombat is a terrestrial marsupial found primarily in Australia, notably in temperate forests and grasslands. It typically measures between 1 and 1.2 meters in length and weighs between 20 and 35 kg. Its fur is generally thick, ranging from brown to gray, and it has a broad head and a short tail. The Common Wombat is herbivorous, feeding primarily on roots, bark, and herbaceous plants. It is nocturnal and spends most of the day in burrows that it digs itself. While its population remains relatively stable, it is sometimes threatened by habitat loss due to urbanization and changes in agriculture.
The Wild Yak is a large species of cattle native to the mountains of the Himalayas, Tibet, and the high plateaus of Central Asia. It typically measures about 2 to 3 meters in length and weighs between 400 and 1,000 kg. Its coat is long, thick, and woolly, ranging from black to brown, which helps it survive in extreme cold conditions. The Wild Yak is primarily herbivorous, feeding on grasses, lichens, and woody plants. It lives in herds in mountainous environments at high altitudes, often above 3,000 meters. While it is a protected species in some areas, the Wild Yak is threatened by illegal hunting and habitat loss due to urbanization and excessive grazing.
The Grevy's Zebra is a species of zebra found primarily in the savannas and grasslands of East Africa, notably in Ethiopia and Kenya. It typically measures about 2.5 meters in length, with a shoulder height of 1.5 to 1.6 meters, and weighs between 350 and 450 kg. Its coat is characterized by narrow and tightly spaced stripes, which are generally finer than those of other zebras. It has a longer and narrower head compared to other zebra species, with long, pointed ears. The Grevy's Zebra primarily feeds on grasses and vegetation, and lives in complex social groups, often led by a dominant mare. Although its population is declining due to habitat loss and poaching, it is protected by conservation programs in some areas.
The Plains Zebra is one of the most common zebra species, primarily found in the grasslands and savannas of East and Southern Africa, notably in Kenya, Tanzania, South Africa, and Botswana. It typically measures between 2.3 and 2.5 meters in length and weighs between 300 and 400 kg. Its coat consists of black and white stripes that cover its entire body, with each individual having a unique stripe pattern. The Plains Zebra primarily feeds on grasses and vegetation, and lives in large social groups often led by a dominant male. While its population remains relatively stable, it is sometimes threatened by habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and diseases transmitted by livestock.